Comprehensive Guide to Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis Effectively
This comprehensive guide delves into effective strategies for managing rheumatoid arthritis, highlighting symptoms, causes, and an array of treatment options including medications, lifestyle changes, surgeries, and complementary therapies. It emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis, regular medical oversight, and holistic approaches to improve daily living quality for individuals suffering from RA. With detailed advice on diet, exercise, assistive devices, and emotional support, this article provides valuable insights for managing this chronic autoimmune condition effectively and sustaining a good quality of life.
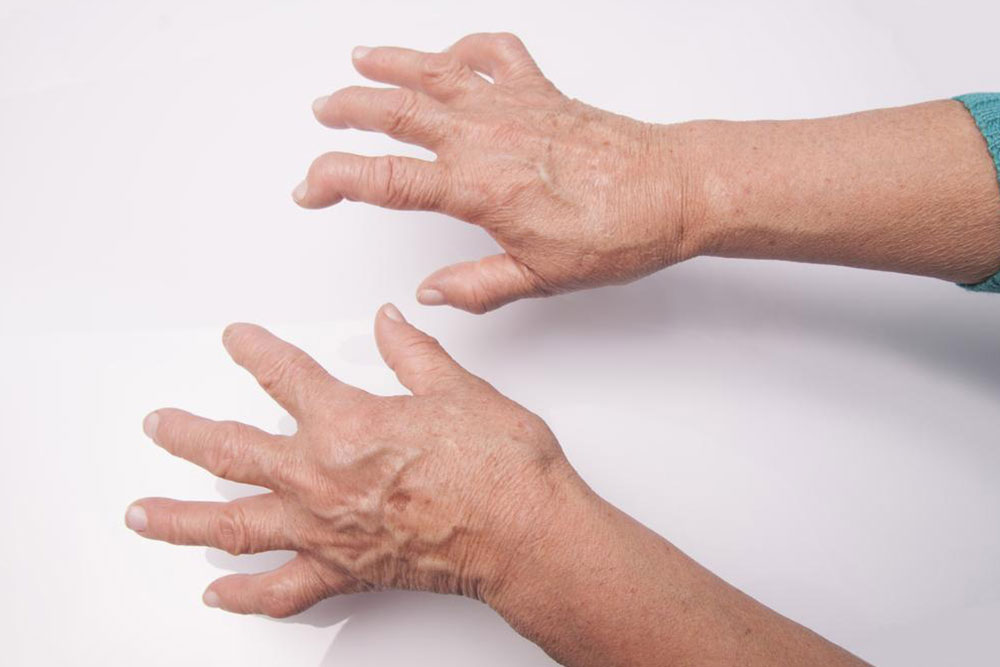
Comprehensive Guide to Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis Effectively
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disorder that primarily targets the joints, leading to pain, swelling, stiffness, and decreased mobility. This condition affects millions worldwide and requires a multifaceted approach for effective management. Understanding the nature of RA, its symptoms, causes, and available treatment options is crucial for those affected, as well as for their caregivers. In this detailed guide, we will explore various strategies to control symptoms, improve joint health, and enhance overall quality of life for RA patients.
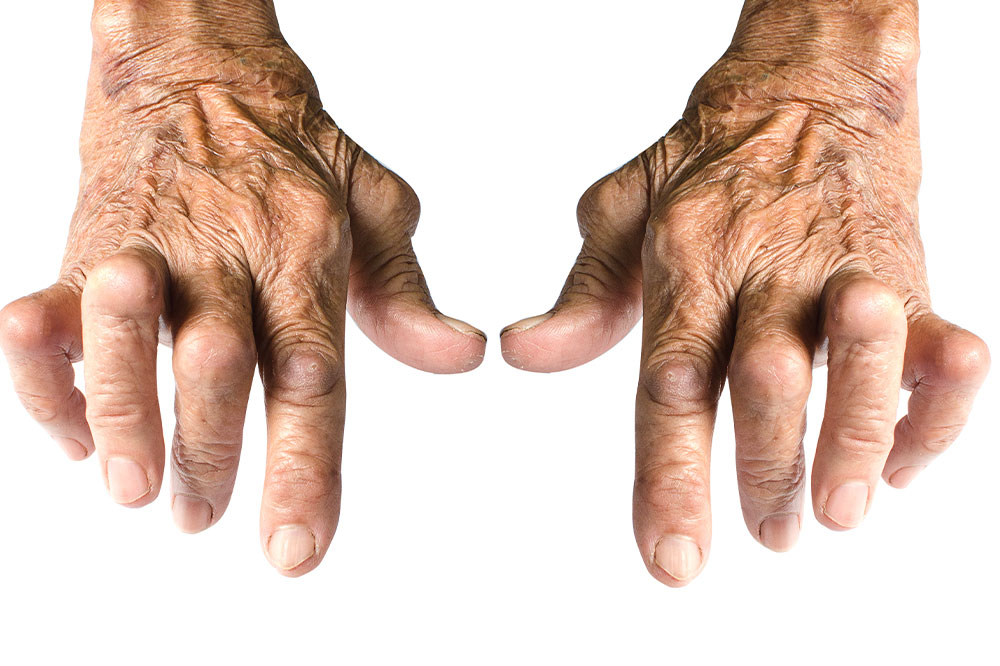
Recognizing Rheumatoid Arthritis Symptoms
Persistent joint stiffness, especially in the mornings
Chronic joint pain that worsens over time
Swelling and tenderness around affected joints
Reduced joint mobility and flexibility
Fatigue and general feelings of malaise
Possible development of subcutaneous nodules
Early diagnosis is vital for managing RA effectively. Diagnosis typically involves comprehensive blood tests to detect inflammatory markers, rheumatoid factor (RF), and anti-CCP antibodies. Imaging techniques like X-rays, MRI, or ultrasound help assess joint damage, while a detailed medical history, including family predisposition, contributes to accurate diagnosis.
Understanding the Underlying Causes of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Genetic predisposition plays a significant role, with family history increasing risk
Environmental factors like smoking significantly contribute to disease development
Obesity and excess weight put additional stress on joints, exacerbating symptoms
Joint injuries or trauma can trigger or worsen RA
Hormonal factors, particularly in women, influence disease onset and progression
Despite ongoing research, the exact cause of RA remains elusive. It involves a complex interaction between genetic, environmental, and immune system factors that lead to the body's immune defenses attacking joint tissues.
Strategies for Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis
The management of RA requires an integrated approach involving medication, lifestyle modifications, and supportive therapies. Here, we delve into the most effective strategies to control and mitigate RA symptoms.
Pharmacological Treatments
The cornerstone of RA management involves medications that reduce inflammation, halt joint destruction, and alleviate pain. Main classes include:
Corticosteroids: Such as prednisone, which provide rapid anti-inflammatory effects but are used cautiously due to potential side effects.
Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Like ibuprofen and naproxen, which help reduce pain and swelling.
Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs): Such as methotrexate and sulfasalazine, which slow disease progression and joint damage.
Biologic Agents: Including TNF inhibitors like etanercept and infliximab, targeting specific immune pathways involved in RA.
Analgesics: Acetaminophen and other pain relievers used for symptom relief.
It’s essential for patients to follow prescribed therapies and have regular monitoring to adjust medications as needed, minimizing side effects and maximizing benefits.
Physical Activity and Exercise
Maintaining active joints is crucial for managing RA. Gentle exercises like swimming, walking, and particular yoga poses can enhance flexibility, strengthen muscles around affected joints, and reduce stiffness. Over time, consistent physical activity helps preserve joint function and reduces disability.
Working with physiotherapists can lead to tailored exercise programs that suit individual needs, ensuring safe and effective movement. Avoiding overexertion is key, and patients should listen to their bodies to prevent exacerbating symptoms.
Assistive Devices for Daily Support
Using braces, splints, crutches, or supportive bars can significantly improve stability, reduce joint strain, and enhance daily mobility. Proper ergonomic setups at home and work reduce unnecessary stress on joints and prevent deformities.
Dietary Modifications to Reduce Inflammation
Adopting an RA-friendly diet can play a supportive role in symptom management. Foods rich in anti-inflammatory properties include berries, dark leafy greens like spinach, fatty fish such as salmon, walnuts, flaxseeds, and olive oil. Including antioxidants, vitamins, and omega-3 fatty acids helps combat inflammation and promotes joint health.
Conversely, patients should limit intake of trans fats, processed foods, high-carb snacks, and sugars, as these may promote inflammation and worsen symptoms.
Surgical Options for Advanced Cases
When medication and lifestyle adjustments are insufficient, surgical interventions might be necessary. Procedures such as joint replacement (arthroplasty), joint fusion, or tendon repair can restore function and relieve pain. The decision to proceed with surgery depends on the severity of joint damage and overall health status.
Lifestyle Changes for Long-term Management
Quitting smoking is a critical step, as smoking not only damages lung health but also significantly increases RA risk and severity. Maintaining a healthy weight reduces stress on weight-bearing joints, decreasing pain and slowing disease progression.
Stress management techniques such as meditation, mindfulness, and adequate rest are vital in preventing flare-ups and maintaining mental well-being. Building a strong support network, including family and support groups, provides emotional resilience during treatment.
Complementary and Alternative Therapies
Aromatherapy, acupuncture, massage therapy, and herbal supplements can complement conventional treatments. These therapies may help reduce pain, improve circulation, and promote relaxation, contributing positively to overall well-being.
Topical and Localized Treatments
Applying NSAID creams or gels directly to affected joints can provide targeted relief. In severe cases, intra-articular injections of corticosteroids may be administered to quickly reduce inflammation and pain.
Professional Support and Rehabilitation
Engaging with occupational therapists and physiotherapists equips patients with techniques and tools to perform daily activities with less pain and strain. Therapeutic practices like thermotherapy (heat application) and electrotherapy can also offer symptom relief.
Hydrotherapy, Massage, and Manual Techniques
Water-based exercises and professional massage therapies help reduce stiffness and improve circulation. Osteopathy, involving gentle manual adjustments, can help alleviate joint discomfort and improve mobility.
While a definitive cure for RA is currently unavailable, these comprehensive management strategies significantly improve patients' quality of life. Long-term disease control involves a combination of medical treatment, lifestyle adjustments, and emotional support. Patients are encouraged to work closely with healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan. Stress reduction, proper nutrition, and maintaining an active lifestyle are crucial components of living well with RA.