Comprehensive Guide to Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis Symptoms Effectively
This comprehensive guide provides effective strategies for managing rheumatoid arthritis symptoms, emphasizing medical treatments, dietary improvements, physical activity, stress reduction, and emotional support. Tailored approaches help patients control pain, inflammation, and joint damage, enhancing quality of life and long-term health outcomes.

Comprehensive Guide to Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis Symptoms Effectively
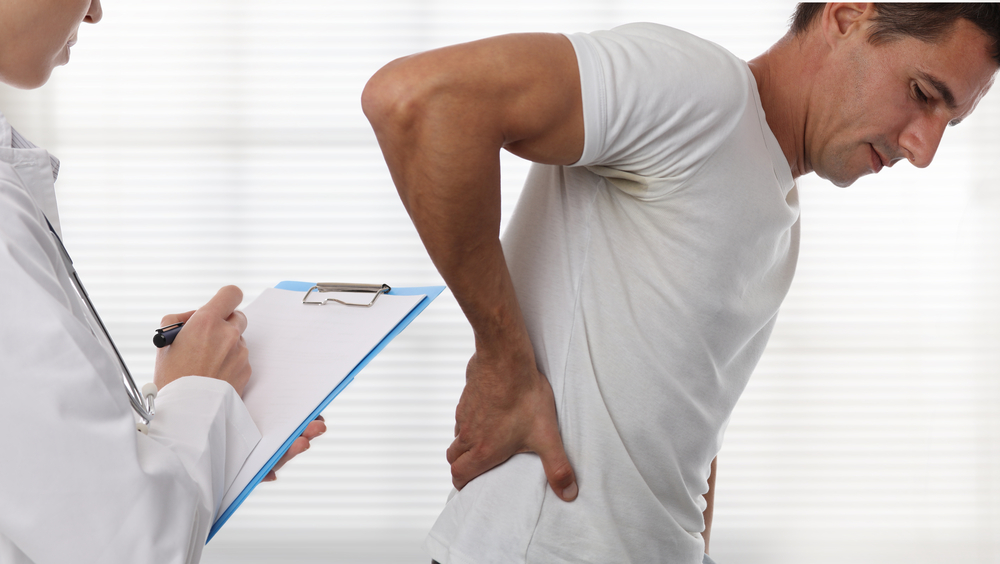
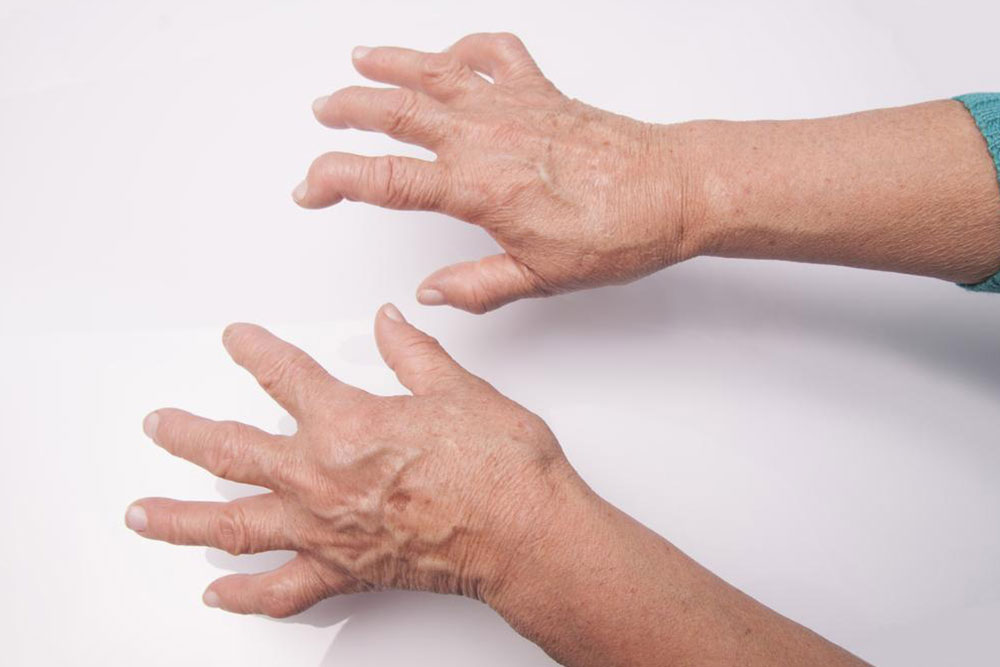
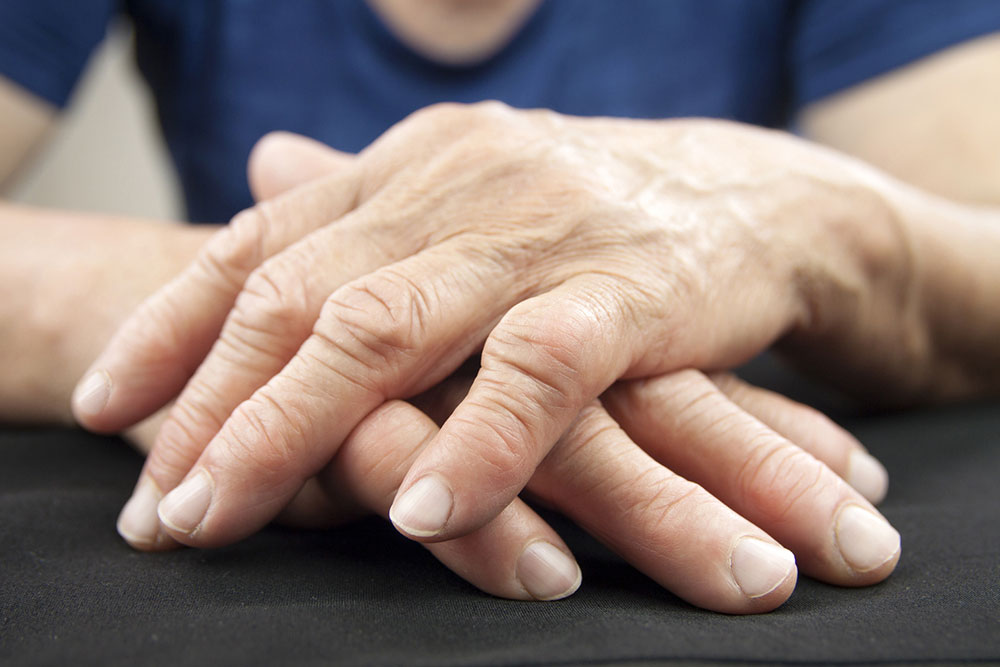
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disorder characterized by the immune system attacking healthy joint tissues, resulting in inflammation, pain, and joint damage. Affecting approximately 1.5 million adults in the United States alone, RA can significantly impact quality of life if not managed properly. Although there is currently no cure for RA, advancements in medical treatments, combined with lifestyle modifications, have made it possible for individuals to control symptoms and maintain an active, fulfilling life. This comprehensive guide explores effective strategies to manage RA symptoms through medical interventions, dietary considerations, physical activity, stress management, and emotional support.
Medical Treatments for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Medications form the cornerstone of RA management. Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) like methotrexate are commonly prescribed to slow disease progression and prevent joint damage. Biologic agents such as Actemra® (tocilizumab) target specific proteins involved in the inflammatory process, drastically reducing symptoms and improving joint function. For patients with psoriatic arthritis, drugs like Tremfya® (guselkumab) inhibit interleukin-23, a key cytokine involved in inflammation, offering relief from pain and swelling. Additionally, drugs like Plaquenil® (hydroxychloroquine) are used adjunctively to reduce joint discomfort and inflammation, especially in early stages or milder cases.
While medication remains essential, individual treatment plans should be tailored to each patient's condition and response. Regular monitoring and consultation with healthcare providers ensure optimal outcomes. Moreover, emerging therapies and clinical trials continue to expand options, providing hope for more effective management in the future.
Diet plays a vital supportive role in managing RA. Incorporating omega-3 fatty acids through foods like salmon, mackerel, and sardines can help reduce systemic inflammation. Consuming a diet rich in colorful fruits and vegetables provides antioxidants that combat oxidative stress, which exacerbates joint damage. Whole grains such as oats, brown rice, and quinoa supply essential nutrients and fiber, supporting overall health and gut health, which is increasingly linked to autoimmune conditions. Legumes like beans, lentils, and peas are excellent sources of plant-based proteins, iron, zinc, and other vital nutrients that promote immune regulation and joint repair.
Physical activity is equally crucial. Low-impact exercises such as walking, swimming, and cycling help improve joint flexibility, strengthen muscles around affected joints, and alleviate stiffness. Regular exercise also contributes to weight management, reducing mechanical stress on joints, especially during flare-ups. It’s essential to tailor activity routines to individual capabilities to avoid overexertion. Engaging in gentle stretching and physical therapy can also enhance mobility.
Stress management techniques are often overlooked but play a significant role in controlling RA symptoms. Techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or tai chi can help lower stress hormones that may trigger flare-ups. Mindfulness practices promote mental calmness and resilience, improving overall well-being. Adequate sleep hygiene is also vital, as restful sleep aids recovery and reduces inflammation.
Living with RA requires daily activity management. Planning routines that balance activity and rest prevents fatigue and overexertion. Utilizing ergonomic tools and adaptive devices can ease joint strain during daily tasks. Support from family, friends, and support groups offers emotional comfort and shared experiences that foster resilience. Counseling and mental health support are also beneficial in coping with the psychological impact of chronic illness. Remember, maintaining a positive outlook and staying informed empower patients to take charge of their health.