Comprehensive Guide to Sjogren’s Syndrome: Causes, Symptoms, and Management Strategies
This comprehensive guide explores Sjogren’s syndrome, an autoimmune disease affecting moisture-producing glands. It covers causes, symptoms, and management options, emphasizing early diagnosis and ongoing care to improve quality of life for patients living with this chronic condition.
Comprehensive Guide to Sjogren’s Syndrome: Causes, Symptoms, and Management Strategies
Medical science continues to make significant strides in understanding complex and chronic diseases, offering new hope to millions affected worldwide. Among these conditions, Sjogren’s syndrome is a particularly challenging autoimmune disorder that impacts various parts of the body, primarily those responsible for producing moisture. While a definitive cure remains unavailable, ongoing research and improved management strategies enable patients to lead more comfortable lives. This detailed guide explores what Sjogren’s syndrome is, its causes, symptoms, and the most effective ways to manage this lifelong condition.
What is Sjogren’s Syndrome?
Sjogren’s syndrome is classified as an autoimmune disease—a condition where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks its own healthy tissues. Specifically, it primarily targets moisture-producing glands, leading to a range of symptoms that significantly affect quality of life. This disorder is chronic, meaning it persists over many years, and it often co-occurs with other autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus, complicating diagnosis and treatment. Although no permanent cure exists yet, advances in medicine have improved symptom management, enabling patients to maintain a functional and comfortable life.
Understanding the Causes of Sjogren’s Syndrome
Despite extensive research, the exact cause of Sjogren’s syndrome remains largely unknown. However, scientists agree that an interplay between genetic, environmental, and possibly hormonal factors contributes to its development. Initial triggers are believed to include exposure to certain infections—bacteria or viruses—that can activate an abnormal immune response in genetically susceptible individuals.
This abnormal immune reaction leads white blood cells—particularly lymphocytes—to target the body's own moisture-producing glands, mainly the salivary and tear glands. This immune attack results in inflammation and damage to these glands, reducing their ability to produce saliva and tears effectively. The underlying mechanisms involve a complex disruption of immune regulation, which causes chronic inflammation and tissue destruction over time.
Environmental factors such as viral infections, smoking, or exposure to certain chemicals may act as triggers, prompting the immune system to misfire. Researchers are still investigating these potential causes, but understanding these interactions is critical in developing preventative strategies and targeted therapies in the future.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Sjogren’s Syndrome
Early diagnosis of Sjogren’s syndrome depends heavily on awareness of its hallmark symptoms. The most common and recognizable symptoms are related to dryness in various tissues and organs. These symptoms can be persistent and troublesome, often requiring ongoing management. Key symptoms include:
Dry Mouth: One of the primary indicators, dry mouth results from decreased saliva production. This condition can cause significant discomfort, making it difficult to chew, swallow, or speak normally. It also raises the risk of developing oral infections such as thrush or dental decay due to an imbalanced oral microbiome.
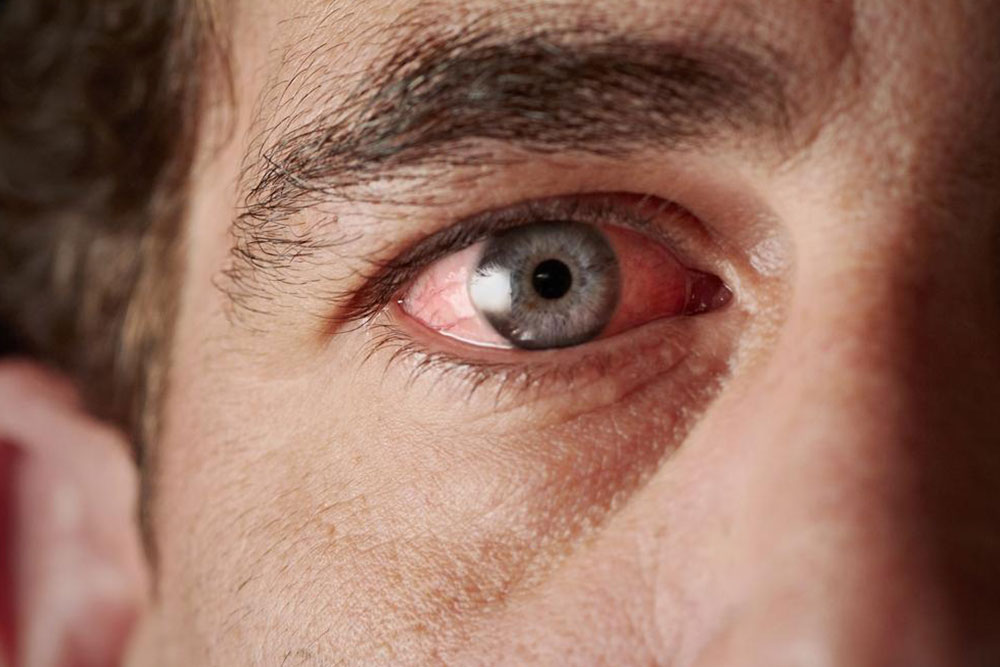
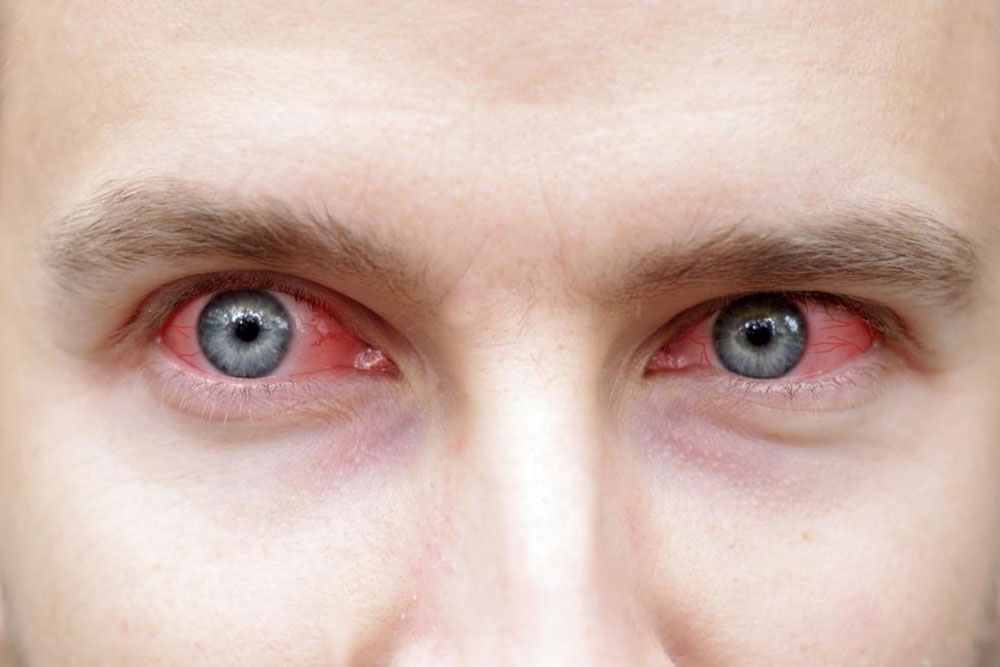
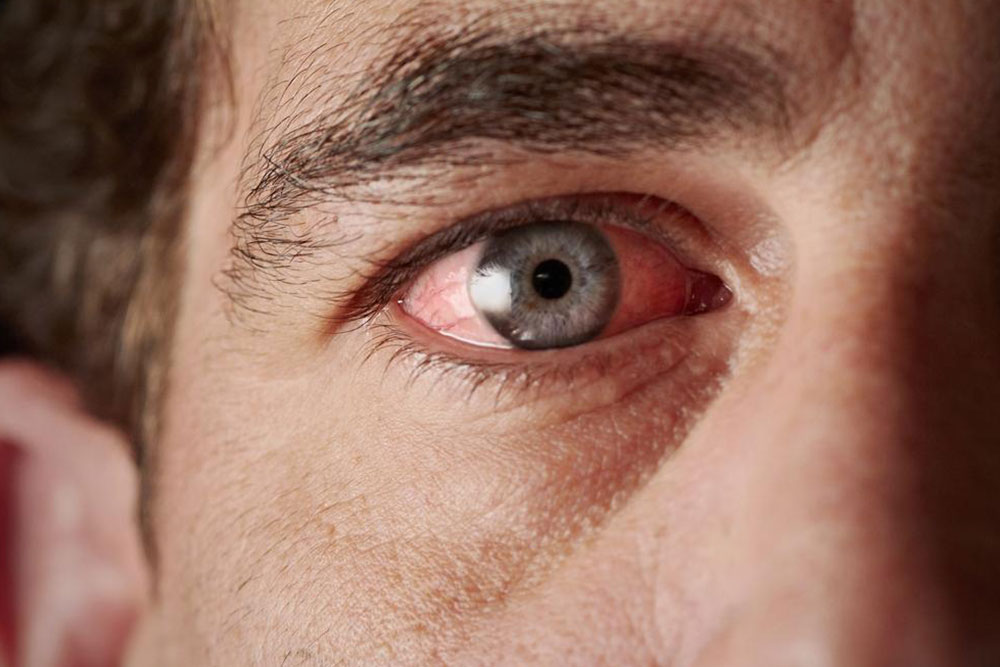
Dry Eyes: Patients often experience burning, itching, redness, and a gritty sensation in the eyes. If untreated, dry eyes can lead to vision problems or corneal damage. Eye drops, artificial tears, and anti-inflammatory medications are commonly used to relieve these symptoms and protect overall eye health.
Facial and Body Discomfort: Sjogren’s can affect other mucous membranes, leading to dry, cracked lips, nasal dryness, and discomfort in the throat. Swelling of salivary or lymph nodes in the face and neck may also occur due to immune activity.
Systemic Symptoms: In some cases, Sjogren’s affects the skin, joints, muscles, and internal organs, causing symptoms such as dryness, pain, and fatigue. This systemic involvement can complicate the clinical picture and requires a comprehensive treatment plan.
Understanding these symptoms and recognizing their pattern is vital for early diagnosis and effective management. Over time, if left untreated, dryness and inflammation can lead to more severe complications, including dental erosion, corneal damage, or systemic organ involvement.
Managing Sjogren’s Syndrome
Although a cure for Sjogren’s syndrome is still under research, numerous treatment options focus on alleviating symptoms and preventing complications. The cornerstone of management involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, medications, and regular monitoring.
Saliva and Tear Substitutes: Artificial saliva and lubricating eye drops are essential to combat dryness. These products help maintain moisture, improve comfort, and reduce the risk of infections and damage.
Immunosuppressive and Anti-Inflammatory Medications: Drugs such as corticosteroids, hydroxychloroquine, and other immunomodulators help control immune activity, reduce inflammation, and prevent tissue damage.
Dental Care: Regular dental check-ups, fluoride treatments, and good oral hygiene practices are vital to prevent cavities and oral infections related to dry mouth.
Eye Care: Prescribed eye medications and protective measures help safeguard vision and alleviate eye discomfort.
Lifestyle Adjustments: Adequate hydration, avoiding smoking, minimizing alcohol and caffeine intake, and practicing good skincare can significantly reduce symptom severity.
Monitoring and Support: Regular medical evaluation is crucial to monitor disease progression and adjust treatment as needed. Support groups and counseling can help cope with the emotional and psychological impacts.
Emerging therapies and ongoing research aim to improve quality of life and develop targeted treatments that address the underlying immune dysfunction. Patients are encouraged to work closely with healthcare providers to tailor management plans that best suit their individual needs.
By understanding the causes and symptoms of Sjogren’s syndrome, patients and healthcare providers can improve early diagnosis and optimize treatment strategies, leading to better health outcomes and enhanced quality of life.