Essential Strategies for Effective Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Effective management of rheumatoid arthritis involves a combination of regular exercise, strict adherence to medication, dietary adjustments, joint protection, hydration, and stress reduction. These strategies help reduce symptoms, prevent joint damage, and improve quality of life. Consult healthcare professionals to develop a personalized management plan tailored to your needs, ensuring long-term health benefits and comfort.
Essential Strategies for Effective Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a complex, chronic autoimmune disease characterized by the immune system mistakenly attacking the joints, leading to inflammation, persistent pain, swelling, and potential joint damage. If not properly managed, RA can significantly impair mobility, cause joint deformities, and diminish overall quality of life. Understanding how to effectively control the symptoms and slow disease progression is crucial for patients living with RA. This comprehensive guide explores proven strategies and lifestyle adjustments to help individuals better manage their condition and maintain a more active, comfortable life.
Maintain Regular Physical Activity to Support Joint Health
While the discomfort caused by RA may deter some from staying active, engaging in gentle, consistent physical activity plays a vital role in managing symptoms. Activities like walking, swimming, stretching, and light gardening can enhance joint mobility, increase muscle strength, and improve overall flexibility. Regular movement prevents stiffness, reduces fatigue, and maintains muscle tone, which in turn alleviates stress on the joints. It is essential, however, to balance activity levels and avoid overexertion that might exacerbate inflammation.
An active lifestyle supports joint health by strengthening muscles around affected areas. Engaging in low-impact exercises tailored to individual abilities can significantly reduce disability, improve endurance, and promote better mobility over time. Consulting with healthcare providers or physical therapists can help design an exercise regimen suited to specific needs, ensuring safety and effectiveness.
Adhere Strictly to Medical Treatment Plans
Consistency in medication and therapy adherence is paramount in RA management. Many patients tend to discontinue or reduce their medications once symptoms improve, but such decisions without medical consultation can lead to symptom flare-ups and irreversible joint damage. Always follow the prescribed treatment plan and communicate with your healthcare provider regarding any concerns or side effects. If doses need adjustment, do so under professional guidance to maintain optimal disease control.
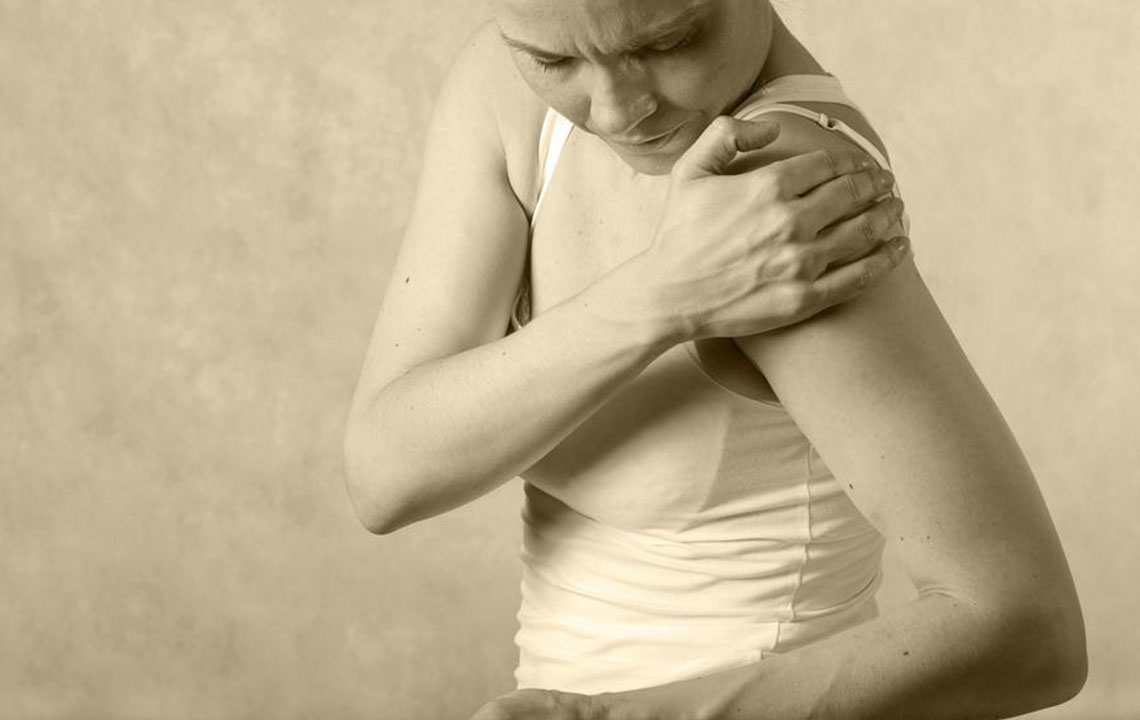
Prevent Overexertion and Protect Joints During Daily Tasks
Activities involving heavy lifting, vigorous physical exertion, or repetitive motions can worsen inflamed joints and accelerate tissue erosion. Use ergonomic tools, supportive braces, and splints to minimize joint stress during daily activities, work, or exercise. Avoid movements that cause pain or discomfort, and prioritize proper body mechanics to prevent injury. Listening to your body and resting when needed can significantly help in maintaining joint integrity and reducing long-term damage.
Optimize Your Diet for Better RA Management
Complement your medical treatment with a nutrition plan focused on anti-inflammatory foods. Reduce intake of processed foods, sugary snacks, and beverages containing preservatives and unhealthy fats, as these can exacerbate inflammation. Instead, focus on consuming whole foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish (salmon, mackerel), flaxseeds, and walnuts, which have been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties. Incorporate plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and nuts to support overall health and immune function.
Protect Your Joints During Everyday Activities
Using supportive devices like wrist braces, knee supports, or orthotic splints can help reduce joint strain during busy or physically demanding tasks. When walking or exercising, proper footwear with cushioning and arch support can lessen impact on joints. Simple modifications such as ergonomic tools and ergonomic furniture can further decrease joint stress. Prioritizing joint protection not only reduces pain and swelling but also prevents further damage and deformities in the long run.
Stay Adequately Hydrated
Dehydration can worsen joint pain and fatigue, and impair metabolic processes essential for healing and immune function. Aim to drink at least 8 to 10 glasses of pure water daily, adjusting for activity level and climate. Proper hydration helps maintain synovial fluid within joints, providing lubrication and cushioning that reduce friction and discomfort. Additionally, drinking sufficient water supports kidney health, prevents kidney stone formation, and promotes detoxification, all of which contribute to better management of RA symptoms.
Manage Stress Effectively to Reduce Flare-Ups
Stress is a well-known trigger for rheumatoid arthritis flare-ups, affecting both perception of pain and immune response. Incorporate stress-reducing activities such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or engaging in hobbies that bring joy and relaxation. Maintaining a strong emotional and mental state can significantly influence disease activity and improve overall well-being. Building a support system through counseling or support groups can also help in managing emotional stress and maintaining a positive outlook during challenging times.
In summary, managing rheumatoid arthritis effectively requires a multifaceted approach combining medical treatment, lifestyle modifications, and emotional self-care. By staying active, adhering to treatment plans, protecting joints, eating anti-inflammatory foods, staying hydrated, and managing stress, patients can improve their quality of life, reduce symptoms, and slow disease progression. Regular consultation with healthcare providers is essential to tailor these strategies to individual needs and evolving health conditions, ensuring optimal disease control and enhanced well-being.