Comprehensive Dietary Strategies for Managing Psoriatic Arthritis Effectively
Discover evidence-based dietary strategies to effectively manage psoriatic arthritis. This comprehensive guide highlights anti-inflammatory foods, nutrition tips, and lifestyle modifications to reduce symptoms, support joint health, and improve overall well-being. Incorporate these expert recommendations into your daily routine for better symptom control and a healthier life.

Effective Nutritional Approaches for Individuals Living with Psoriatic Arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis is a complex, chronic autoimmune disorder characterized by inflammation that targets joints and skin. It manifests through symptoms such as joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and skin lesions typical of psoriasis. While conventional treatments like anti-inflammatory medications and biologics are essential in managing the disease, increasing attention is being paid to the role of diet and nutrition in controlling symptoms and improving quality of life. Proper nutrition not only supports general health but also plays a pivotal role in reducing systemic inflammation, alleviating discomfort, and potentially minimizing flare-ups associated with psoriatic arthritis.
Key Dietary Strategies for Managing Psoriatic Arthritis
Given the autoimmune nature of psoriatic arthritis, the immune system becomes hyperactive, attacking healthy tissues, which leads to inflammation and joint damage. While medications form the cornerstone of treatment, implementing specific dietary modifications can significantly complement medical therapy, offering relief from symptoms and supporting long-term health.
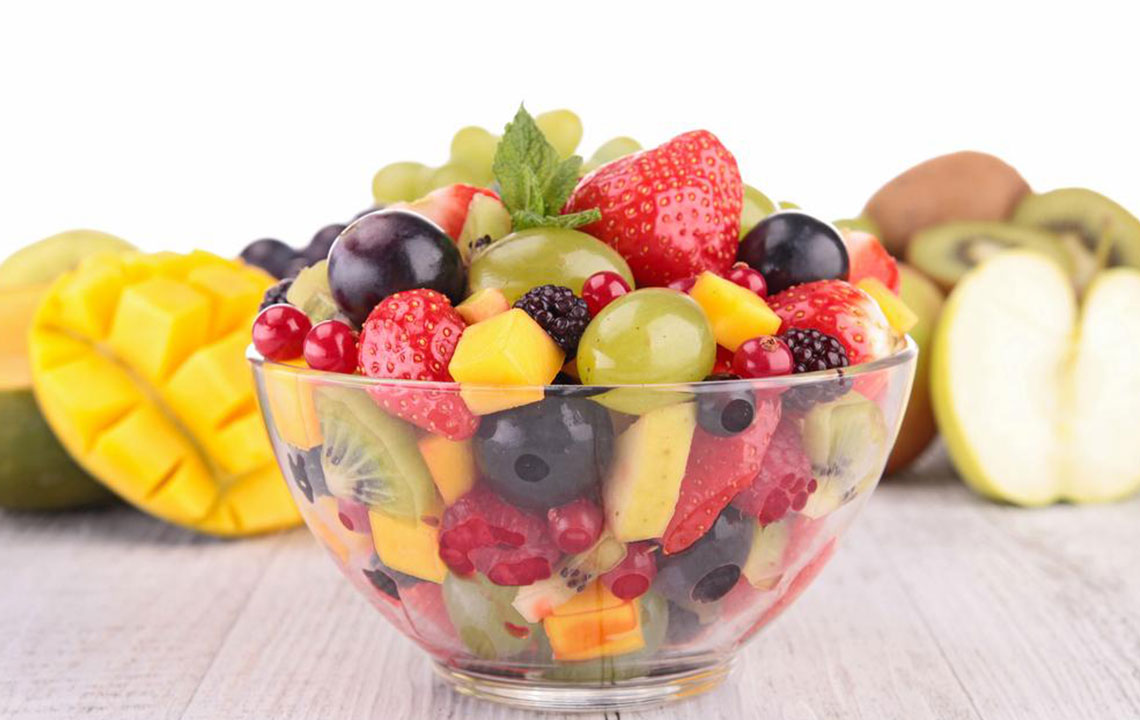
Emphasize the consumption of fresh, whole, and minimally processed foods such as a variety of fruits and vegetables. These foods contain antioxidants and phytochemicals that help reduce inflammation. Regular intake of leafy greens, berries, and colorful produce can strengthen immune function and decrease disease activity.
Incorporate anti-inflammatory fats into your diet, especially omega-3 fatty acids. Sources include wild-caught fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines, as well as plant-based options like flaxseed, chia seeds, and walnuts. These healthy fats have been shown to help lower inflammation markers and improve joint health.
Limit or avoid foods that can exacerbate inflammation. Dairy products and wheat-based foods, particularly those that are highly processed, are common triggers. People with psoriatic arthritis often find that reducing intake of cheese, milk, bread, and baked goods can lead to noticeable symptom improvements.
Choose high-quality sources of lean protein such as grass-fed chicken, wild-caught fish, and grass-finished beef. These options tend to contain higher levels of Omega-3 fatty acids and lower levels of inflammatory additives, supporting joint health and overall wellness.
Stay hydrated and consider incorporating herbal teas with anti-inflammatory properties, such as turmeric latte or ginger tea, into your daily routine. Adequate hydration aids in joint lubrication and toxin elimination.
Adopting this tailored nutritional approach offers a promising way to modulate immune responses, decrease systemic inflammation, and enhance overall quality of life for those affected by psoriatic arthritis. Though a complete cure remains elusive, mindful eating habits and nutritional vigilance can lead to meaningful symptom relief and foster a healthier lifestyle.
In conclusion, integrating dietary strategies alongside medical treatment can not only improve symptom management but also empower individuals to take proactive control of their condition. As research continues, personalized nutrition plans based on individual response and nutritional deficiencies are likely to become integral in comprehensive psoriatic arthritis care.