Comprehensive Guide to Joint Disorders: Symptoms, Causes, and Risk Factors
Explore a detailed overview of joint disorders, including common symptoms, underlying causes, and key risk factors. Learn how aging, lifestyle, and environmental influences contribute to joint health issues, and discover strategies for prevention and early intervention to maintain joint function and quality of life.

Comprehensive Guide to Joint Disorders: Symptoms, Causes, and Risk Factors
Joint disorders represent a broad spectrum of health conditions that impair the normal function of joints, which are vital components of the human musculoskeletal system. Among these, arthritis stands out as the most common and widely recognized condition. These disorders can present as temporary issues, such as minor joint strains, or evolve into chronic, persistent ailments that significantly impact daily life. In some cases, joint issues necessitate surgical intervention to restore function or alleviate pain. They can affect a single joint or multiple joints across the body, leading to a variety of clinical presentations and challenges.
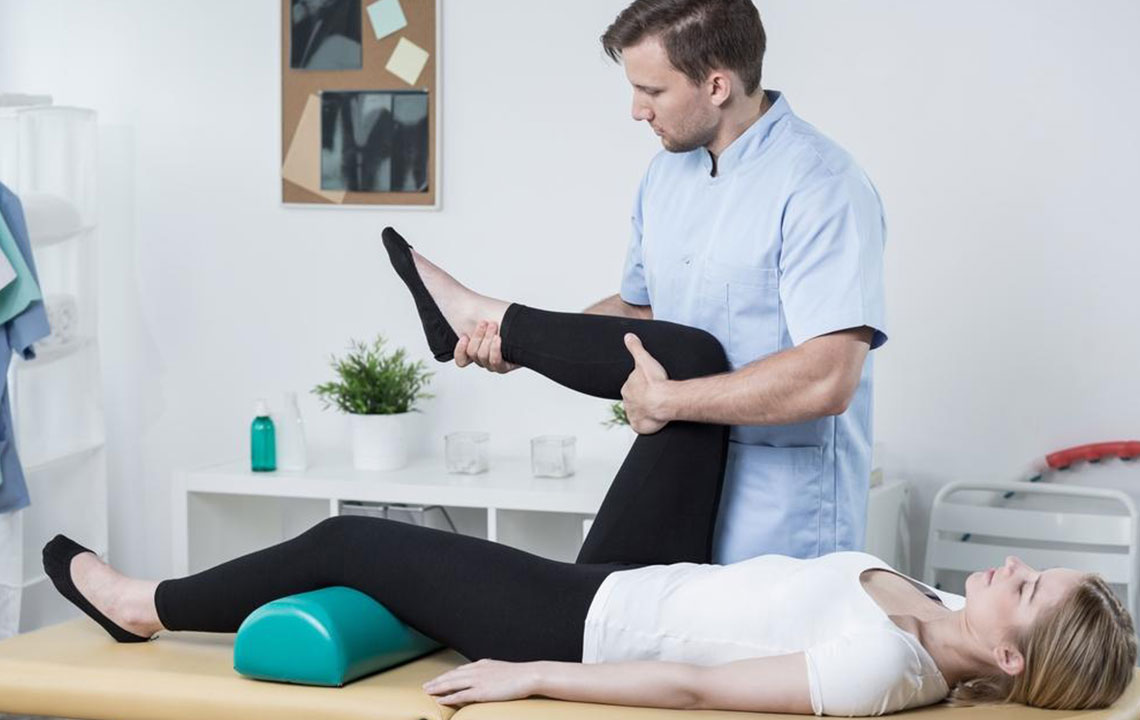
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms of Joint Problems
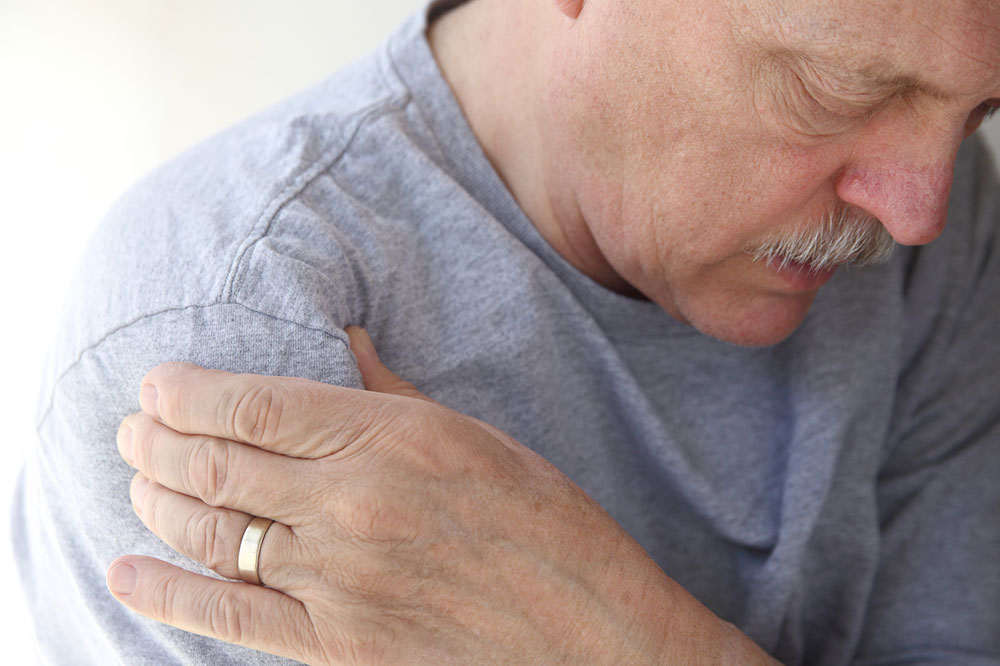
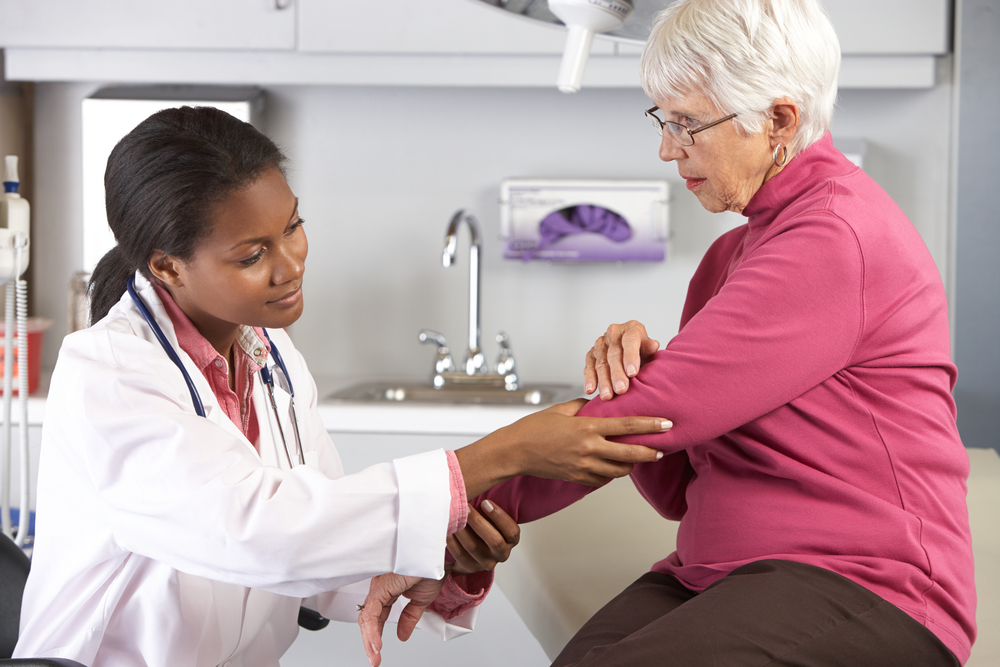
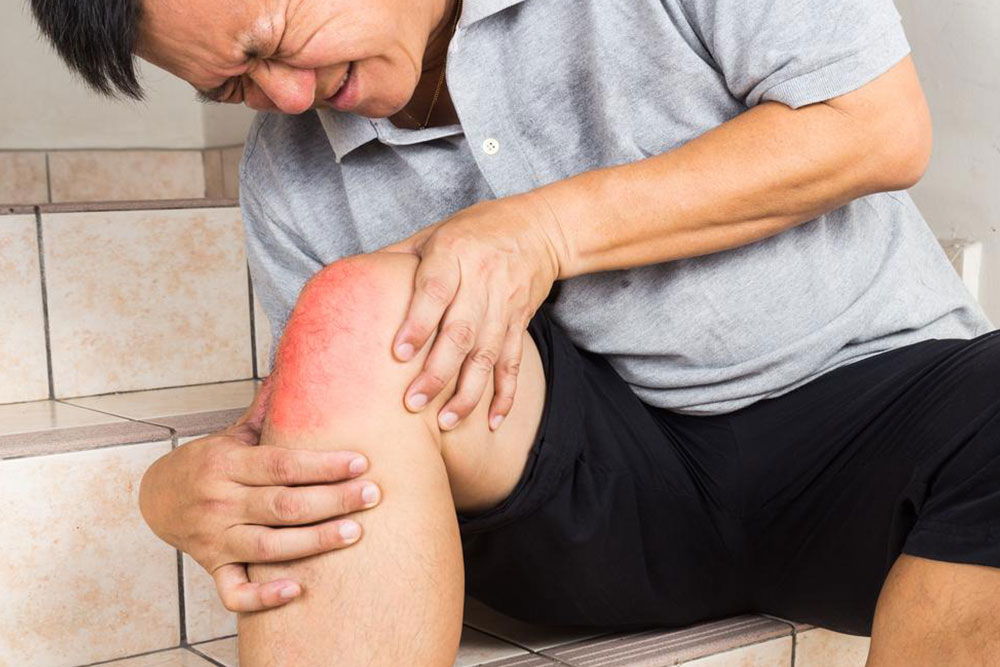
Early detection of joint issues is crucial for effective management and improved outcomes. Common symptoms that indicate potential joint problems include persistent joint pain, swelling, redness, warmth, and tenderness. These signs often signal inflammation or infection within the joint. Visible deformities, such as bulges or irregular shapes, can also be indicative of underlying joint damage. If discomfort or swelling persists beyond a few days, especially following an injury, it is essential to seek medical evaluation. Fever without other symptoms might sometimes accompany joint inflammation, suggesting an infectious or systemic cause that requires prompt attention. Emergency signs demanding immediate medical care include sudden, severe swelling, inability to move the joint, intense pain, recent trauma leading to deformity, or any signs of joint dislocation or instability.
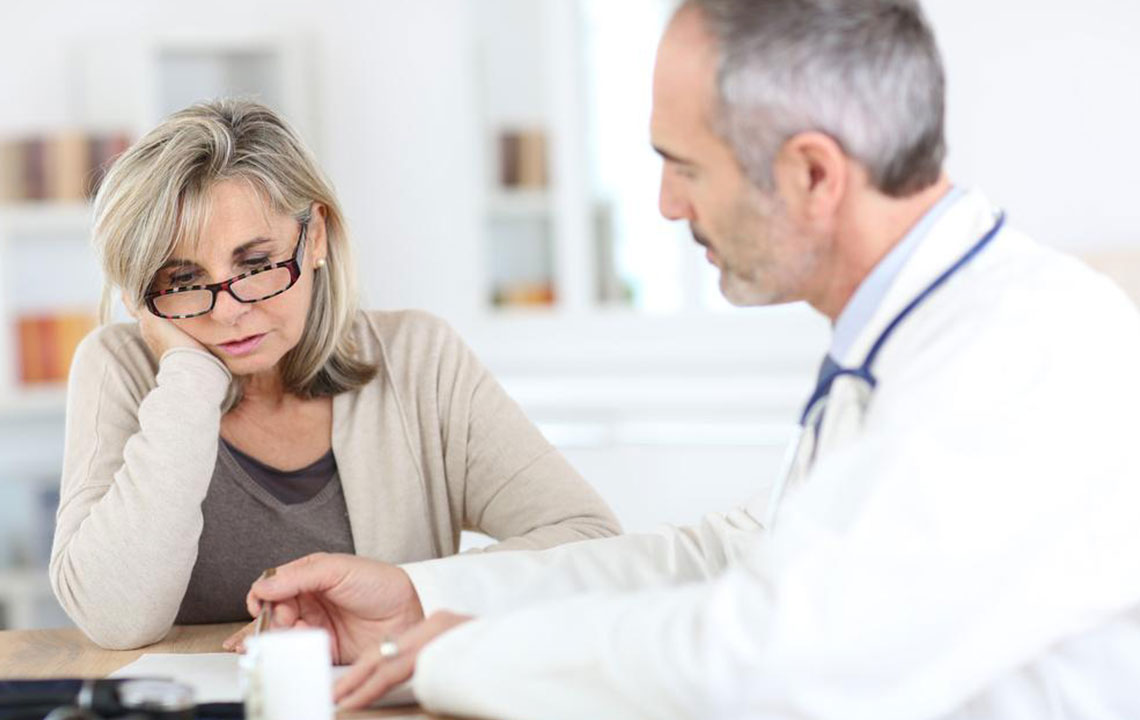
Causes and Contributing Factors Behind Joint Disorders
The development of joint disorders is multifactorial, involving genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Age is arguably the most significant risk factor: as individuals grow older, the wear and tear on cartilage and bones increase, leading to a higher likelihood of joint deterioration. Physical activity, especially high-impact sports or strenuous occupational tasks, can accelerate joint wear if proper precautions are not taken. Certain occupations requiring prolonged standing, heavy lifting, or repetitive motions also elevate the risk of joint strain and injury.
Vitamin D deficiency and inadequate sunlight exposure have been linked to poor bone health, increasing vulnerability to joint problems. Environmental factors such as pollution and exposure to toxins might also influence joint health. Genetic predisposition plays a crucial role, with some individuals inheriting tendencies towards specific joint conditions, like rheumatoid arthritis or osteoarthritis.
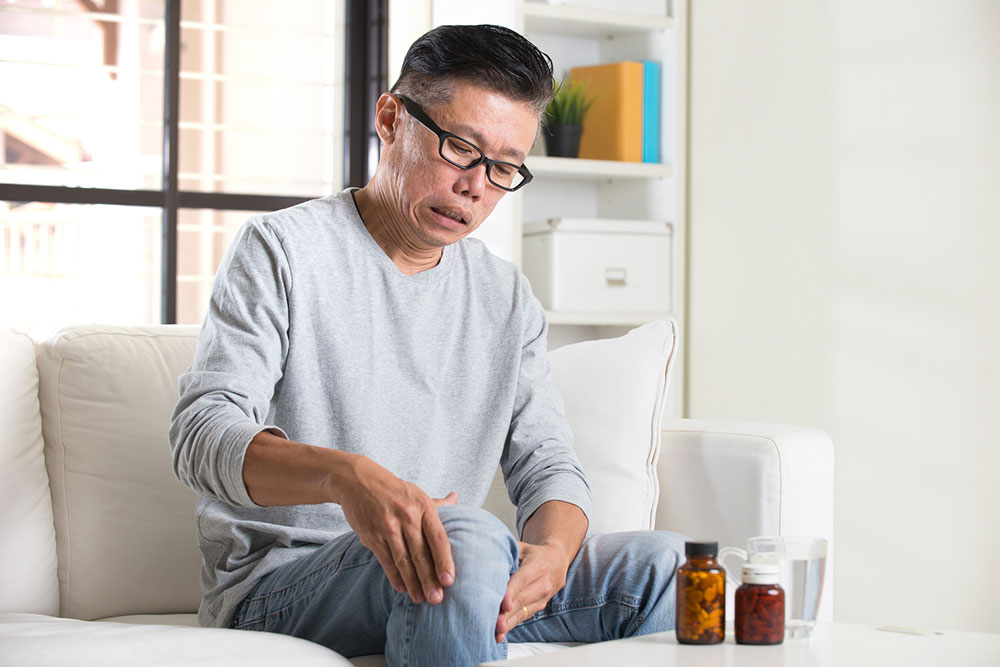
Key Risk Factors Influencing the Development of Joint Conditions
Several factors heighten the risk of developing joint disorders, including advanced age, obesity, gender, and previous injuries. As joints age, their ability to withstand stress diminishes, making age a strong predictor of joint problems. Obesity is a significant modifiable risk factor; excess weight imposes extra pressure on weight-bearing joints such as the knees and hips, accelerating cartilage breakdown and joint degeneration. Women appear more susceptible to osteoarthritis, possibly due to hormonal differences and structural variations. Prior joint injuries—whether resulting from accidents, sports, or occupational hazards—also substantially increase the likelihood of future joint issues. Adopting a healthy lifestyle, maintaining an ideal weight, engaging in joint-friendly physical activity, and seeking early medical advice can effectively help reduce these risks and manage ongoing joint health.