Understanding the Top 8 Causes of Joint Pain and Discomfort
Discover the eight most common causes of joint discomfort and pain, including arthritis, osteoarthritis, injuries, and inflammation. Learn how these conditions develop, their symptoms, and effective management options to improve joint health and mobility. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential for preventing long-term damage and maintaining quality of life.
Understanding the Top 8 Causes of Joint Pain and Discomfort
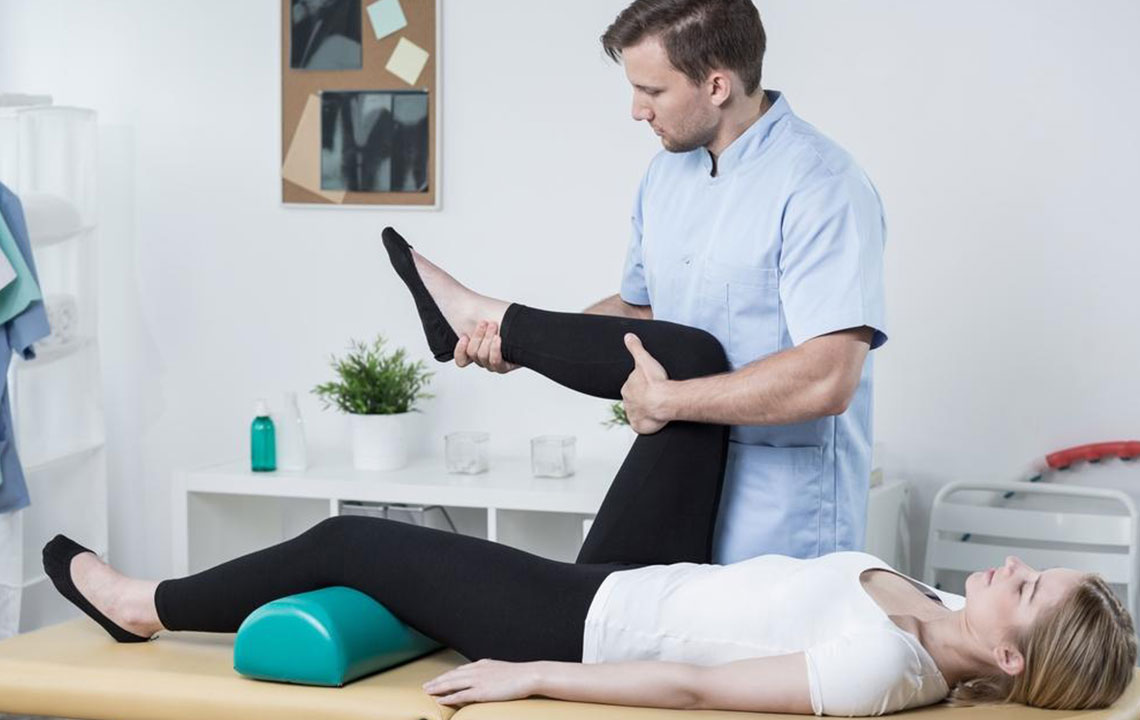
Joints serve as vital connection points between bones, facilitating a wide range of movements essential for daily life. These joints are found in numerous parts of the body, including the shoulders, elbows, hips, wrists, knees, and ankles. While they are designed to withstand regular motion, various factors can cause joint pain, leading to discomfort and restricted mobility. Persistent joint discomfort can significantly impact quality of life, making it crucial to understand the underlying causes for effective treatment and management.
Joint pain may result from injuries, overuse, or underlying medical conditions. Often, early diagnosis can prevent further deterioration and help maintain mobility. Recognizing common causes of joint discomfort can guide individuals toward appropriate medical consultation and treatment options.
Common Causes of Joint Pain
Arthritis:
One of the most prevalent causes of joint pain, arthritis encompasses over 100 different types, with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis being the most common. This condition primarily affects older adults, especially those over the age of 65, but it can also impact younger individuals and even children. Arthritis involves inflammation within the joint, leading to pain, swelling, stiffness, and reduced function. The chronic nature of arthritis means symptoms can worsen over time without proper management. Inflammation damages the joint tissues, causing discomfort that can interfere with daily activities.
Osteoarthritis:
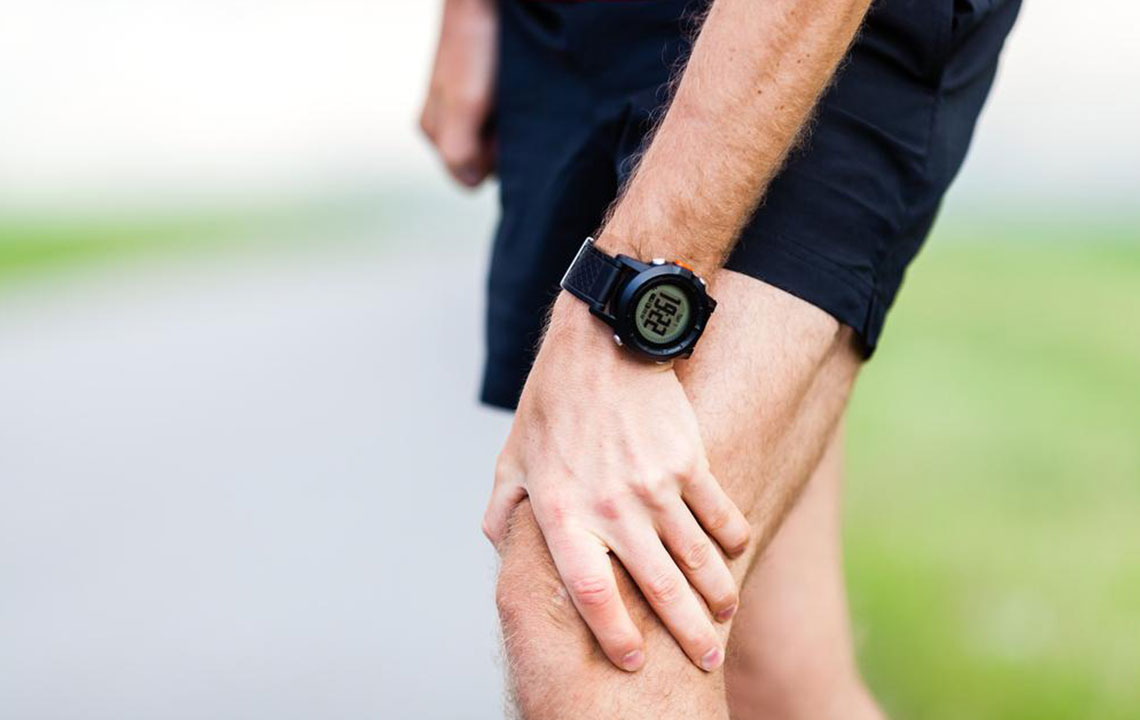
A specific form of arthritis, osteoarthritis results from the gradual wearing down of cartilage—the smooth tissue that cushions the ends of bones within a joint. As cartilage deteriorates, bones may rub against each other, causing friction, inflammation, and pain, especially during movement or weight-bearing activities. Osteoarthritis commonly affects the knees, hips, hands, and spine. While it progresses slowly, the pain can become severe enough to impair mobility and independence if not managed properly.
Sprains and Strains:
These injuries occur due to sudden trauma, overstretching, or overexertion of muscles, tendons, or ligaments around the joints. Sprains involve ligament injuries, while strains refer to muscle or tendon overstretching or tearing. Both can cause localized pain, swelling, bruising, and limited joint movement. In many cases, minor sprains or strains heal with rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE). However, severe injuries may require medical intervention, including physical therapy or surgery.
Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS):
Often underestimated, CFS is a complex disorder characterized by persistent exhaustion and a range of other symptoms, including joint pain. While the exact cause remains unknown, environmental factors, immune dysfunction, and stress are believed to contribute. The joint pain associated with CFS tends to be prolonged, affecting women particularly in their 40s and 50s. Its diagnosis is challenging, as symptoms overlap with other medical conditions, but understanding CFS is crucial for appropriate management.
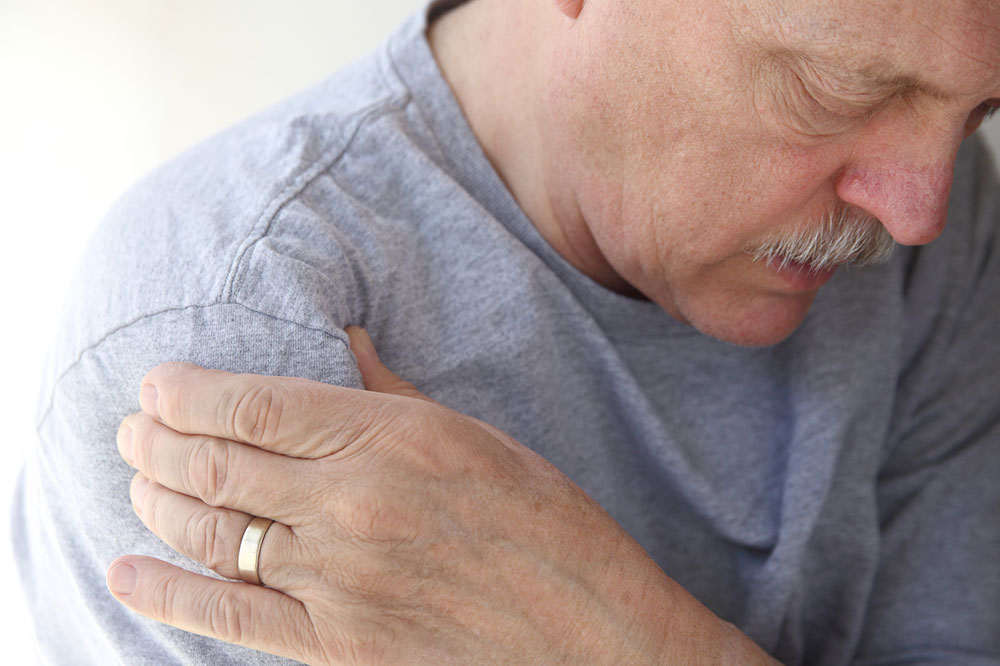
Bursitis:
Bursae are tiny fluid-filled sacs that reduce friction between bones and soft tissues near joints. Inflammation of these bursae, known as bursitis, causes pain, swelling, and increased friction, especially during joint movement. Commonly affected areas include the shoulders, elbows, hips, and knees. Bursitis often results from repetitive motions, friction, trauma, or infections. Proper treatment aims to reduce inflammation and restore joint function through rest, anti-inflammatory medications, or physical therapy.
Spondylitis:
Spondylitis refers to an umbrella term for inflammatory conditions affecting the spine and sacroiliac joints. The most common form, ankylosing spondylitis, is a chronic inflammatory disease that primarily affects young men, though women can also be affected. Symptoms include persistent back pain, stiffness, and reduced flexibility, which can lead to deformities and disability if untreated. The exact cause involves a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to manage symptoms and prevent progression.
Bone Infections:
Infections involving bones, known as osteomyelitis, can result from bacterial, fungal, or viral invasion. Typically, these infections originate from bloodstream infections, with Staphylococcus aureus being a common culprit. Bone infections cause severe pain, swelling, redness, and fever. If untreated, they can cause irreversible damage to bones and surrounding tissues, leading to chronic issues and mobility problems. Medical interventions include antibiotics or surgical procedures to remove infected tissue.
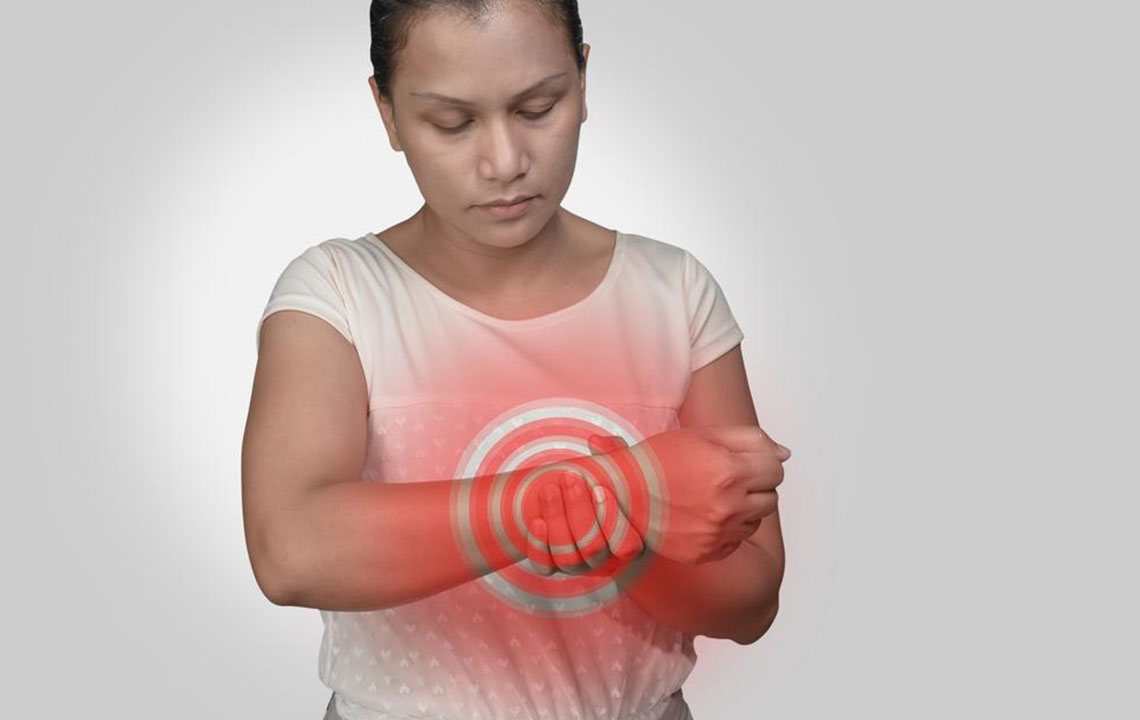
Tendinitis:
Tendinitis is the inflammation of tendons—thick fibers that connect muscles to bones. It often results from repetitive movements, aging, or injury. Tendinitis causes localized joint pain, tenderness, swelling, and difficulty in movement. Common locations include the shoulders, elbows, wrists, heels, and knees. Management involves rest, ice, anti-inflammatory medications, physical therapy, and, in some cases, corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation and promote healing.
Understanding these common causes of joint pain is the first step toward effective treatment. If you experience persistent discomfort, consulting a healthcare professional is crucial for accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment strategies. Maintaining joint health through regular exercise, proper nutrition, and injury prevention can significantly reduce the risk of developing severe joint conditions.





