Comprehensive Guide to Causes and Management of Joint Discomfort
This comprehensive article explores the various causes of joint discomfort, including arthritis, injuries, and autoimmune diseases. It provides insights into symptoms and effective management strategies such as medication, therapy, and lifestyle adjustments. Understanding these factors can help individuals seek timely medical care and improve overall joint health.

Comprehensive Guide to Causes and Management of Joint Discomfort
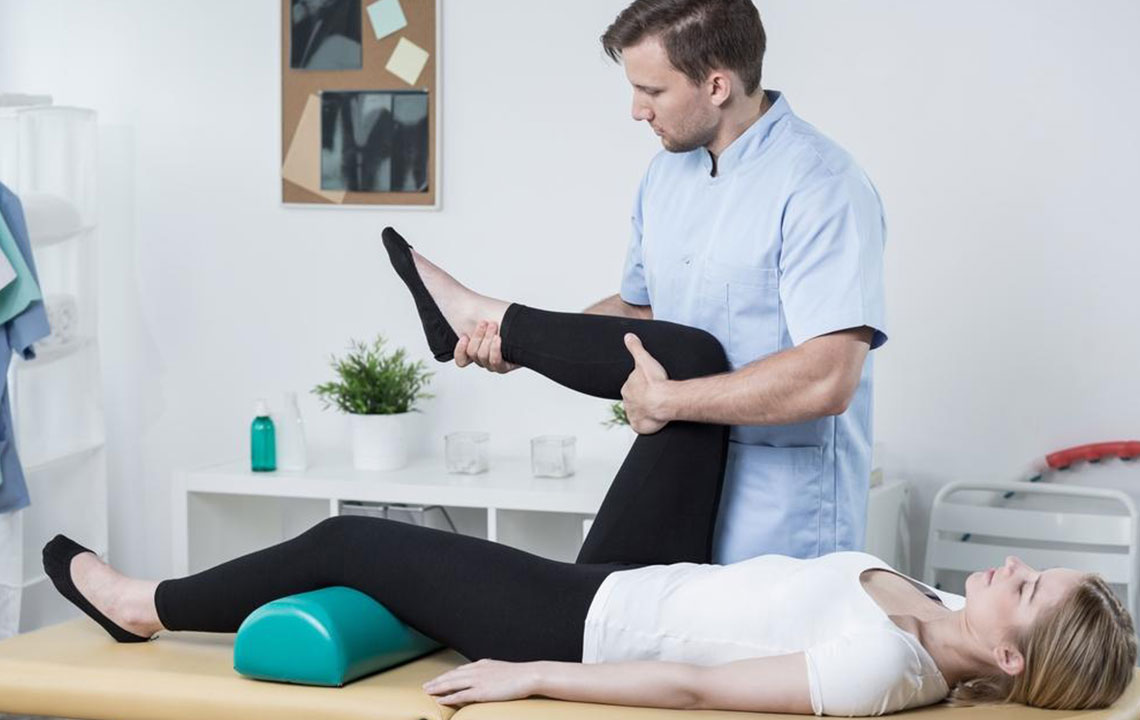
Joints are essential components of the human skeletal system, functioning as pivotal connections between bones that facilitate a wide range of movements necessary for daily activities. These joints include major areas such as the shoulders, elbows, hips, knees, and wrists. Persistent joint pain, characterized by soreness, stiffness, or aching, is a common concern faced by millions worldwide. While occasional discomfort may not be alarming, chronic joint issues can considerably diminish quality of life, hinder mobility, and signal underlying health conditions that require attention.
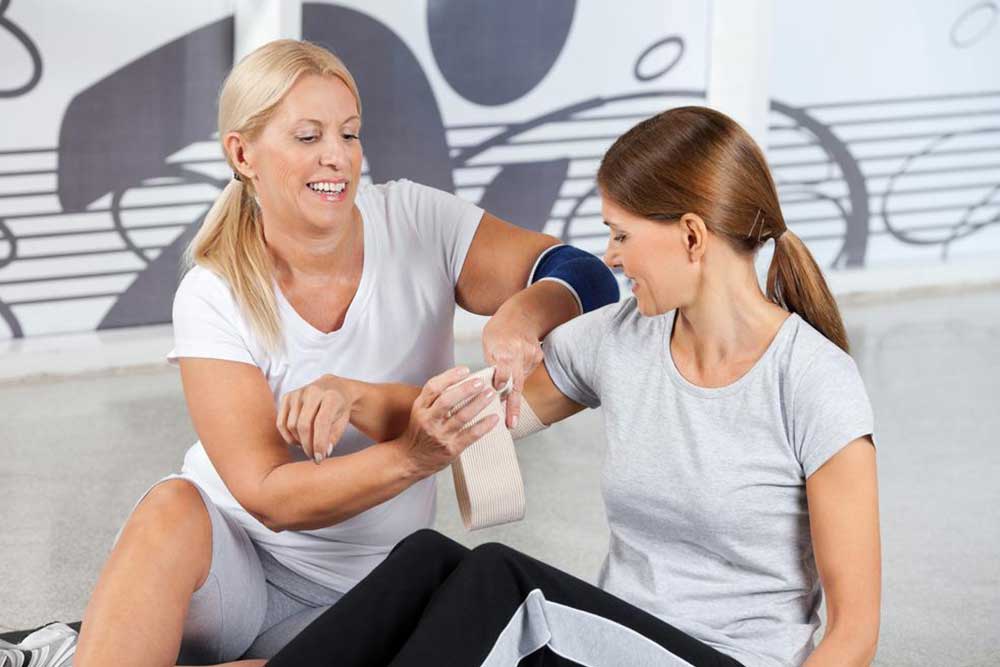
Joint discomfort can vary greatly in intensity—from mild, fleeting aches to severe, debilitating pain. Some episodes are temporary, resolving within a few weeks, whereas others can become chronic, persisting for months or even years. Even short-term swelling and discomfort are significant, potentially affecting daily routines, sleep quality, and overall well-being. Addressing joint pain effectively involves a comprehensive approach that includes physical activity, medication regimes, physical therapy, and sometimes alternative treatments such as acupuncture or dietary modifications.
What are the causes of joint pain? The most common cause of joint pain is arthritis, with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis being the primary types. According to the American College of Rheumatology, osteoarthritis affects a significant portion of the adult population over the age of 40, making it one of the most prevalent degenerative joint conditions.
Osteoarthritis develops gradually over time, typically impacting weight-bearing joints like the knees, hips, and also the hands and wrists. It is characterized by the breakdown of cartilage, the resilient tissue that cushions bones during movement. This degeneration leads to increased friction, inflammation, and pain. Rheumatoid arthritis, on the other hand, is an autoimmune disorder affecting over 1.5 million Americans, predominantly women. It involves the immune system mistakenly attacking the synovial membranes lining joint capsules, causing swelling, deformation, and chronic pain.
Beyond arthritis, several other factors and conditions can contribute to joint discomfort:
Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursae, small fluid-filled sacs that reduce friction between tissues around joints.
Gout: A form of inflammatory arthritis characterized by sudden, severe pain and swelling, often affecting the big toe, knees, or elbows due to crystal deposits.
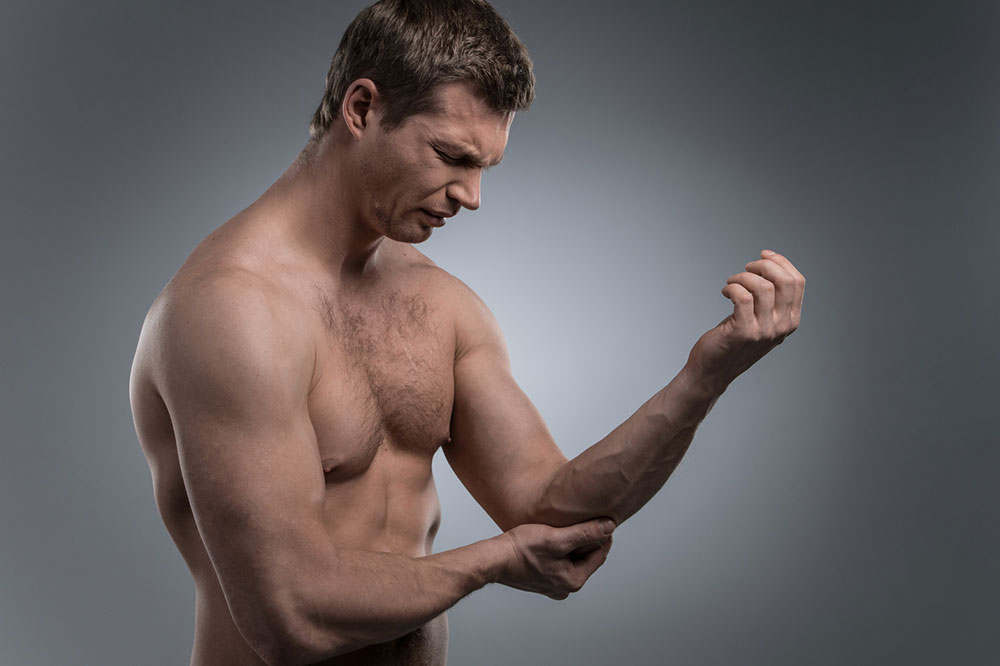
Tendinitis: Inflammation or irritation of tendons that connect muscles to bones, resulting in pain outside the joints, especially in the shoulders, elbows, and knees.
Psoriatic arthritis: An inflammatory condition linked to psoriasis that causes joint stiffness, swelling, and pain.
Cancer: Bone cancers, particularly in long bones, can present with joint pain as a symptom.
Rickets: A deficiency in Vitamin D leading to weakened bones and joint pain, primarily affecting children.
Sarcoidosis: An inflammatory disease characterized by granulomas forming in tissues, including joints, skin, and lymph nodes.
Injury and trauma: Sprains, strains, ligament tears, and fractures resulting from accidents or overuse can cause significant joint pain.
Pseudogout: Crystal-induced joint inflammation similar to gout, leading to sudden pain and swelling.
Blood cancers: Conditions like leukemia can impact bone marrow and joints, causing discomfort.
Avascular necrosis: Disruption of blood supply to bones resulting in tissue death, leading to joint pain.
Infections: Bacterial or viral infections such as influenza or hepatitis can cause joint inflammation as part of systemic illness.
Cartilage disorders: Conditions like chondromalacia, involving cartilage softening or breakdown, contribute to joint discomfort.
Overuse and repetitive strain: Activities that strain joints repeatedly over time can lead to pain and degeneration.
Bone density issues: Osteoporosis and osteomalacia weaken bones, increasing vulnerability to microfractures and joint pain.
Understanding these root causes is crucial for healthcare providers to develop effective treatment plans. Proper diagnosis allows for targeted therapies that can alleviate symptoms, slow disease progression, and restore mobility, ultimately improving patients' quality of life.