Comprehensive Guide to Rheumatoid Arthritis Management and Expert Care Strategies
This comprehensive guide covers expert management strategies for rheumatoid arthritis, including the roles of various specialists, early symptom recognition, and lifestyle tips for improved quality of life. Learn how a multidisciplinary approach can help manage this challenging autoimmune disease effectively and prevent joint damage through timely intervention and personalized care.
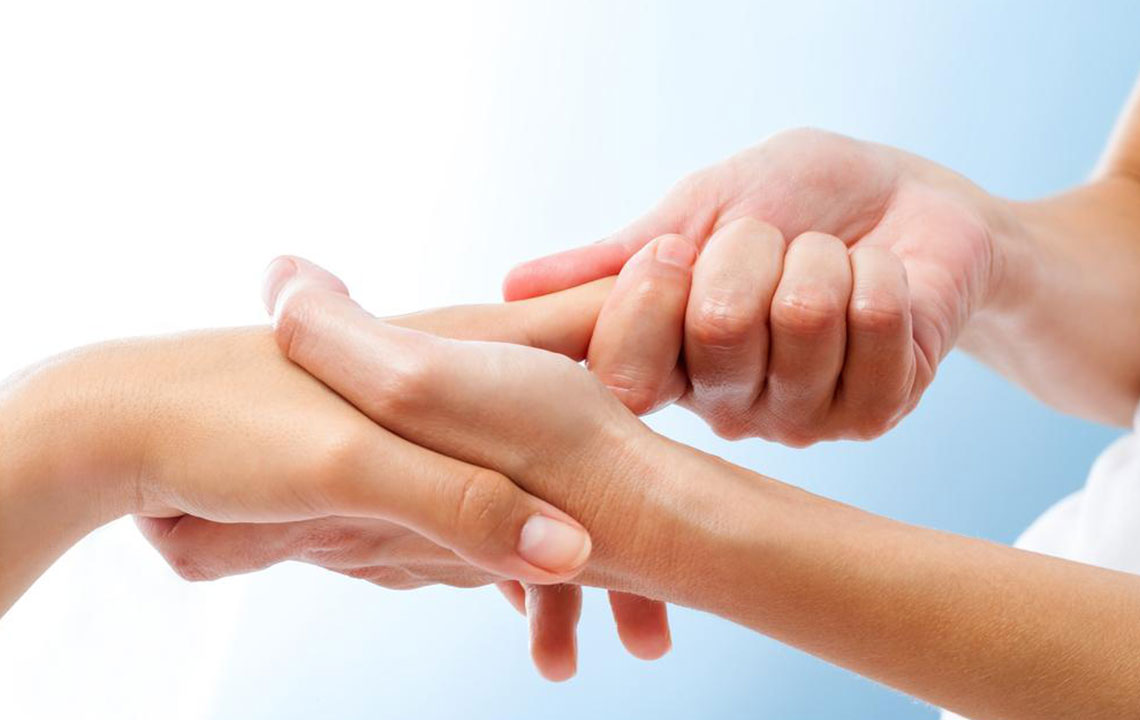

Expert Insights and Effective Strategies for Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis
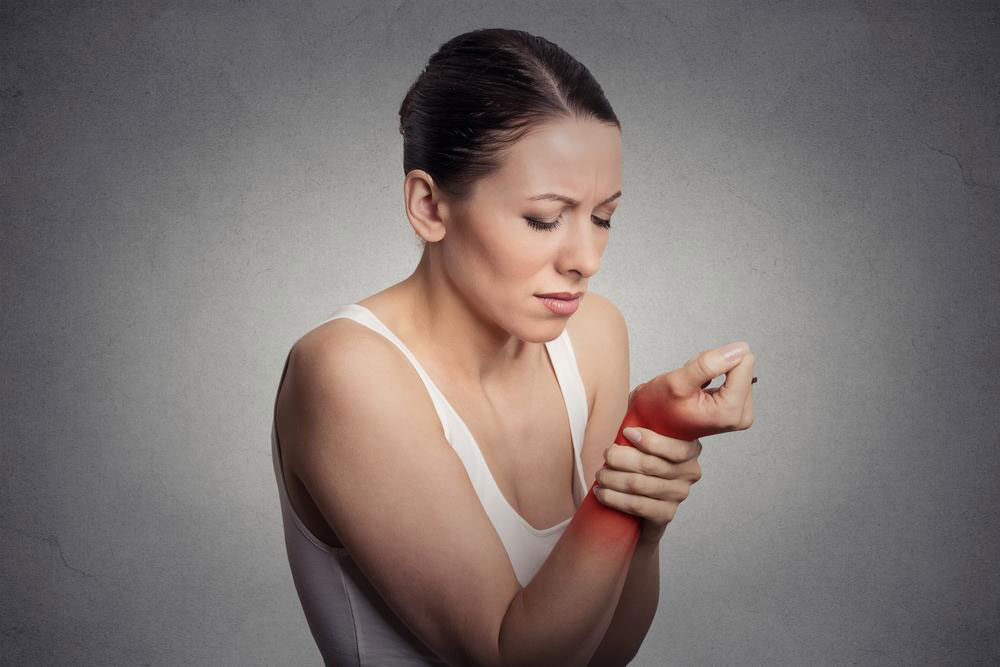
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a complex and chronic autoimmune disorder that affects millions worldwide. Managing this condition requires a coordinated approach involving healthcare professionals, lifestyle adjustments, and personalized treatment plans. Once diagnosed, RA impacts a person’s life long-term, making early detection and ongoing management critical for maintaining quality of life.
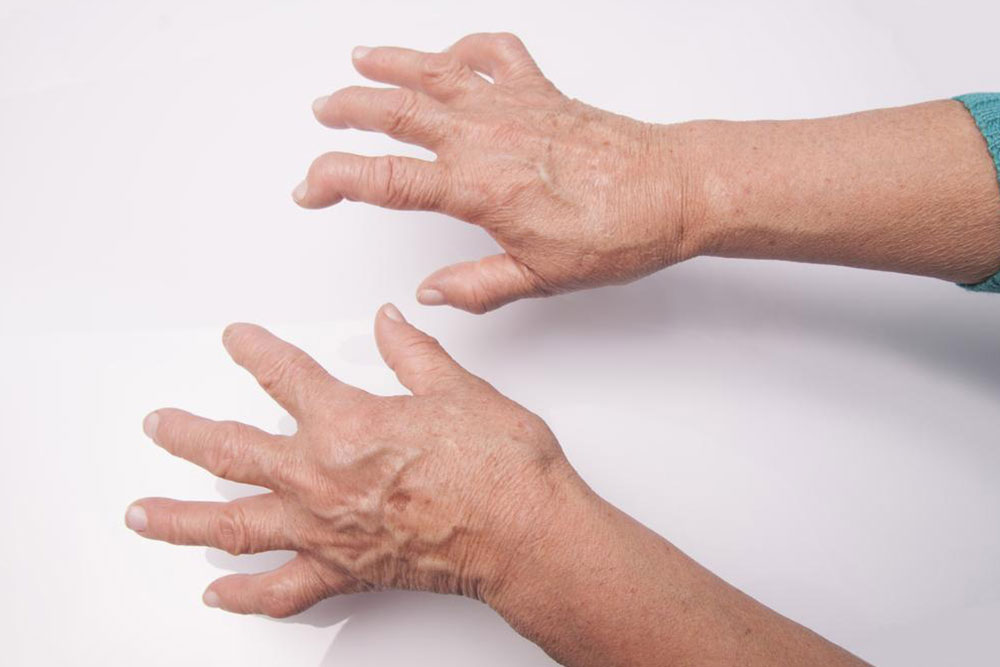
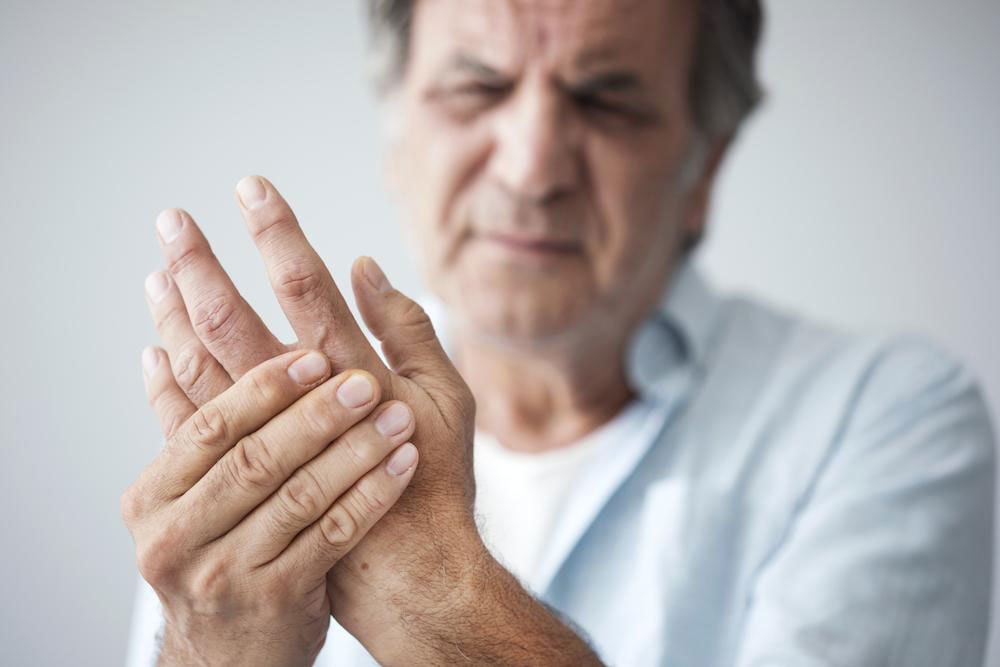
Understanding the signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis is essential for timely medical intervention. While joint swelling, stiffness, and pain are the most common indicators, there are other subtle symptoms that can signal disease progression. These include persistent fatigue, low-grade fever, morning stiffness lasting more than an hour, unintentional weight loss, and nausea. Recognizing these early symptoms can lead to a quicker diagnosis and more effective treatment approach, preventing or minimizing joint damage.
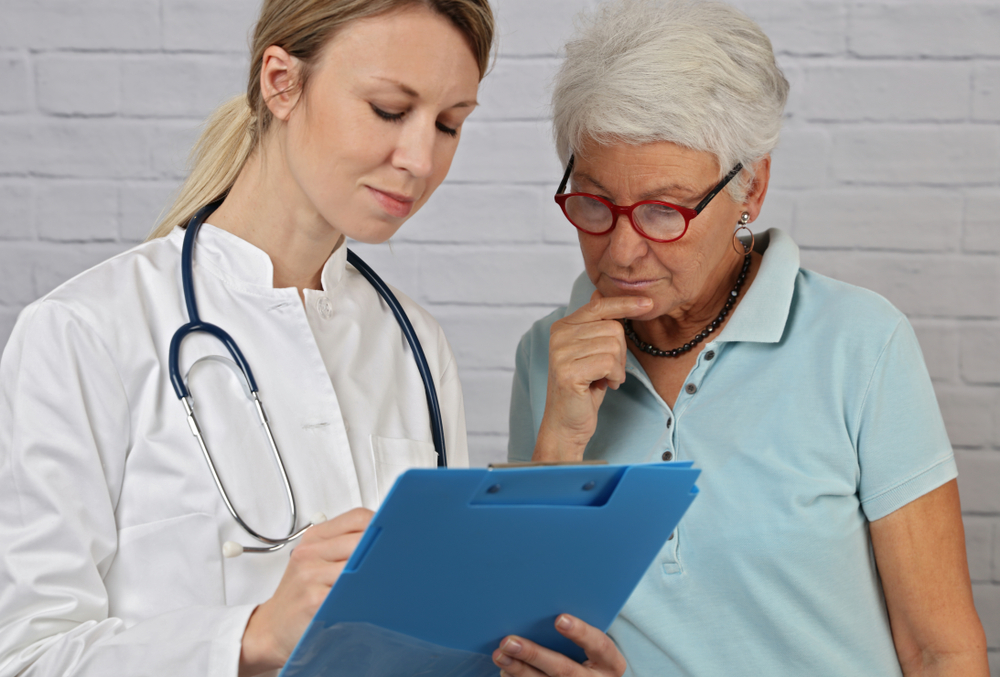
In some cases, visible joint damage or persistent symptoms may require consultation with various specialists. This ensures a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to individual needs. The management of RA involves a multidisciplinary team of healthcare providers, each playing a vital role in improving patient outcomes.
Primary Care Physician serves as the first point of contact, responsible for initial assessment, symptom evaluation, and coordinating referrals to specialists. They also monitor overall health and manage comorbid conditions.
Rheumatologist is the key specialist in RA management. With specialized training in autoimmune and connective tissue diseases, rheumatologists confirm diagnoses through blood tests and imaging, prescribe medications such as DMARDs (disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs), and oversee long-term disease control.
Orthopedic Surgeon may become involved if joint damage is significant, requiring surgical intervention. Procedures such as joint repair, synovectomy, or joint replacement can restore function and alleviate pain in advanced cases.
Physical Therapist plays an essential role in rehabilitation. They develop tailored exercise programs to improve flexibility, strengthen muscles, reduce stiffness, and enhance overall joint function, all of which help maintain mobility and reduce discomfort.
Preparing for Your First Rheumatoid Arthritis Consultation is important for effective treatment planning. Patients should gather comprehensive information including detailed symptom history, progression timelines, affected joints, lifestyle impact, and any family history of autoimmune diseases. It’s also helpful to prepare a list of current medications, supplements, and over-the-counter drugs to facilitate accurate assessment.
Adopting a positive mindset, maintaining regular physical activity, adhering to prescribed treatments, eating a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, and managing stress are crucial elements in managing RA. Support groups and patient education resources can also empower individuals to take an active role in their health.
Consistency in treatment plans and openness in communication with healthcare providers significantly improve the overall quality of life for RA patients. With proper management strategies, individuals with rheumatoid arthritis can lead active, fulfilling lives despite their condition.