Comprehensive Approaches to Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis Effectively
This comprehensive article explores effective strategies for managing rheumatoid arthritis, emphasizing early diagnosis, medication options, physiotherapy, lifestyle changes, and surgical considerations. It provides insights into controlling symptoms, preventing joint damage, and improving overall well-being for those affected by RA, ensuring they can lead active, healthier lives through a multidisciplinary approach.
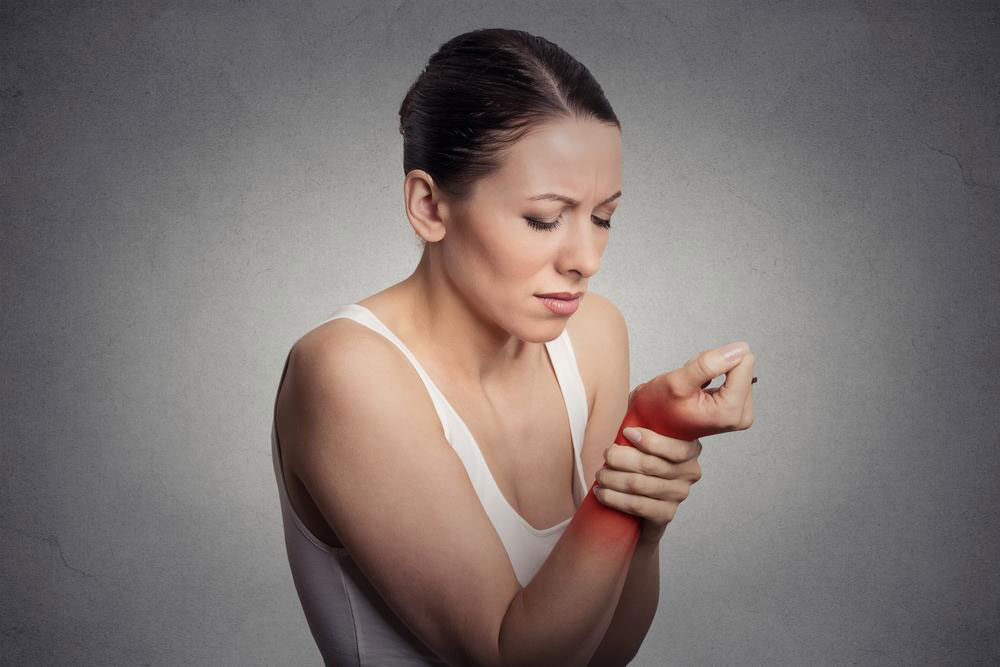

Effective Strategies for Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis
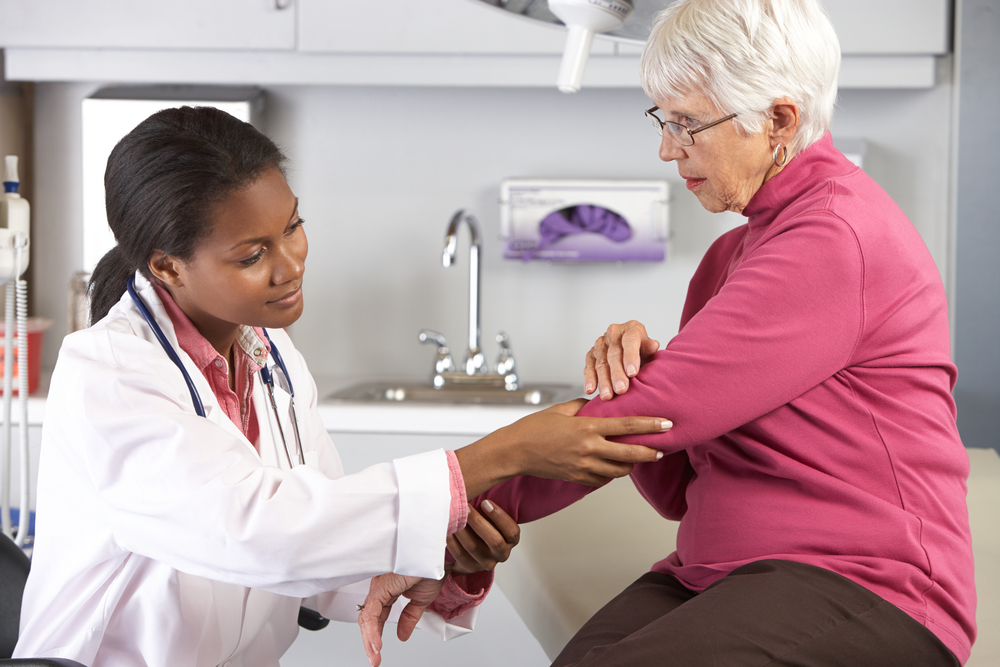
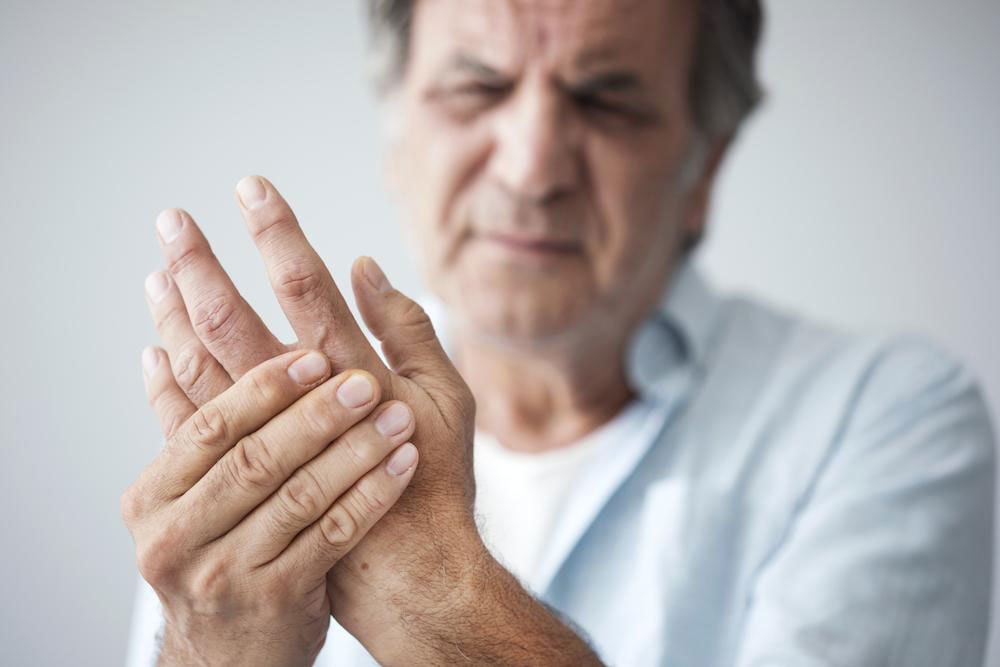
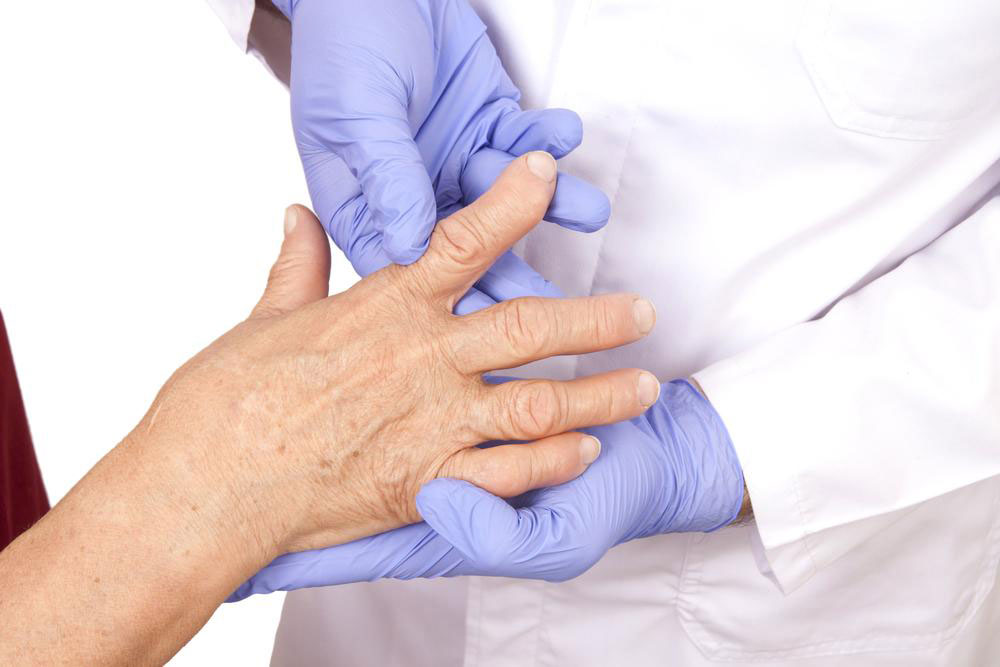
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disorder that primarily targets joints but can also affect various other organ systems. If you're experiencing persistent joint pain, stiffness, swelling, or fatigue, it could be a sign of RA, requiring timely medical intervention. This condition results from the immune system mistakenly attacking the synovial membranes of joints, leading to inflammation, tissue damage, and potential deformities. Recognizing early symptoms and understanding available treatment options are essential to maintaining quality of life and preventing severe complications.
Given that rheumatoid arthritis can have widespread effects on overall health, early diagnosis and comprehensive management are key. While complete eradication of the disease remains challenging, a combination of medical treatments, lifestyle modifications, and supportive therapies can help control symptoms and improve functions. Typical management strategies include the use of medications such as disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), biologics, corticosteroids, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). These medications work by reducing inflammation, slowing disease progression, and alleviating pain.
In addition to pharmacological interventions, physical therapy plays a vital role in preserving joint function and mobility. Physiotherapists often recommend tailored exercise regimens aimed at strengthening muscles around affected joints, improving flexibility, and reducing stiffness. Occupational therapy can assist in adapting daily activities and workplace ergonomics to minimize joint strain. For severe cases or when medication fails to control symptoms effectively, surgical options, including joint repair or replacement, may be considered. Postoperative rehabilitation is critical to ensure optimal recovery and functional improvement.
Complementary treatments like hot and cold compresses, massage, and dietary adjustments also contribute to managing discomfort. Maintaining a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, such as omega-3 fatty acids, fruits, and vegetables, may help alleviate some symptoms. Regular blood work and monitoring are necessary to assess disease activity and medication side effects. Furthermore, lifestyle changes like quitting smoking, managing stress, and maintaining a healthy weight can significantly impact disease severity and overall health outcomes.
Since conditions like psoriatic arthritis share many similarities with RA, treatment approaches often overlap. Both conditions benefit from early intervention and a multidisciplinary management plan. Ultimately, living with rheumatoid arthritis involves ongoing medical care, lifestyle management, and social support to achieve a good quality of life and prevent disease progression.