Comprehensive Strategies for Preventing Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Protecting Vascular Health
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a serious condition involving blood clots that can lead to dangerous complications like pulmonary embolism. This article offers comprehensive strategies for prevention, including lifestyle modifications, dietary advice, and medical interventions. Emphasizing awareness and proactive health management, the guidance aims to help individuals minimize their risk and protect their vascular health. From managing risk factors to recognizing symptoms early, these preventive measures are vital for maintaining overall well-being and avoiding life-threatening outcomes associated with DVT.

In-Depth Approaches to Preventing Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
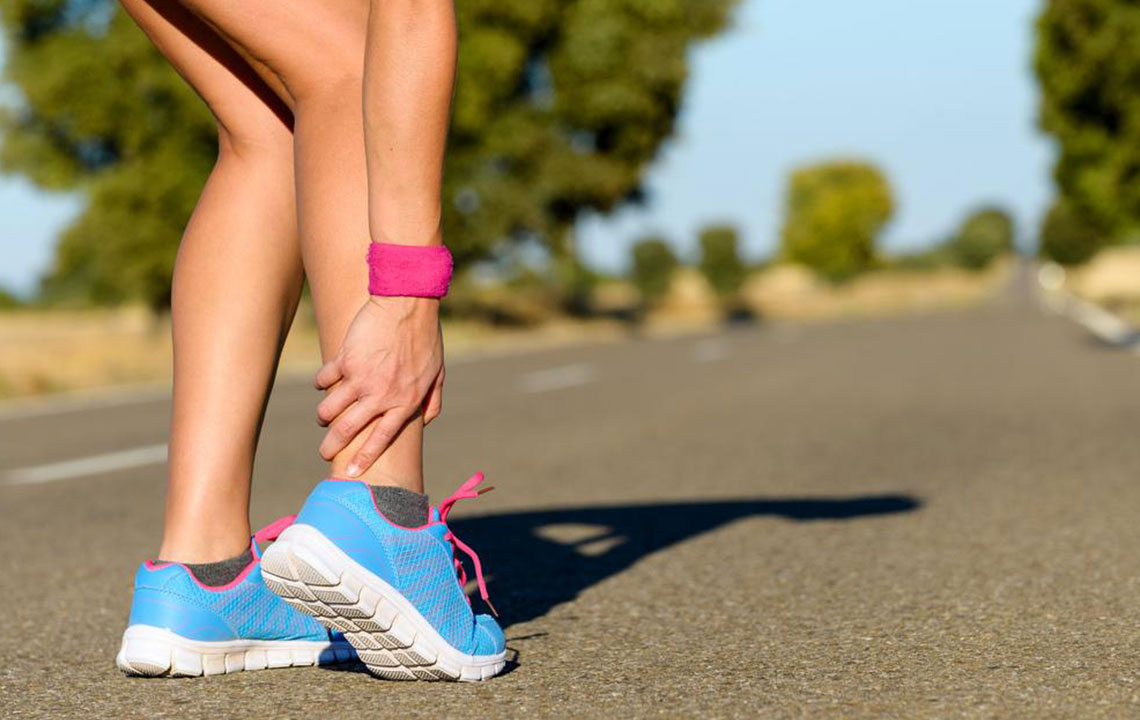
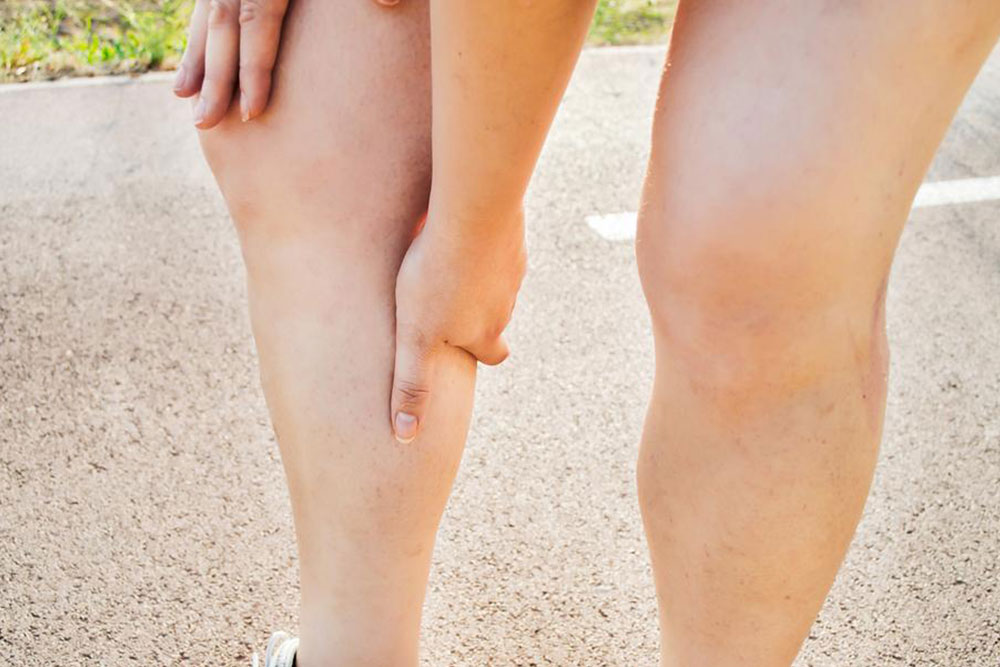
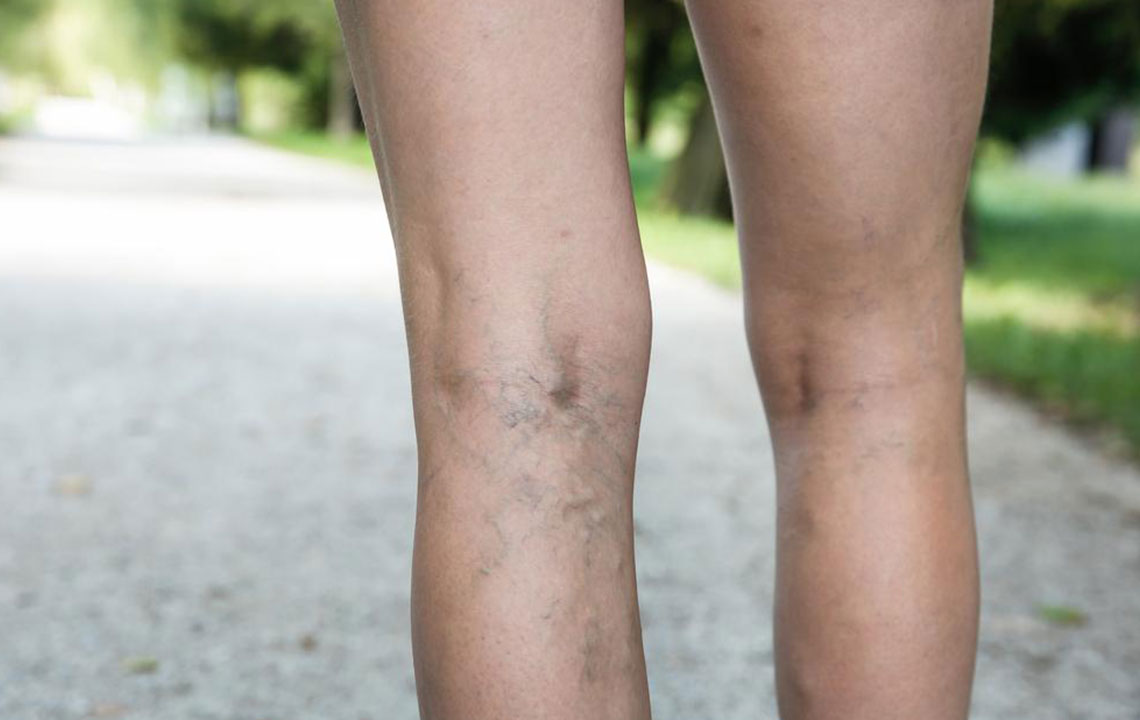
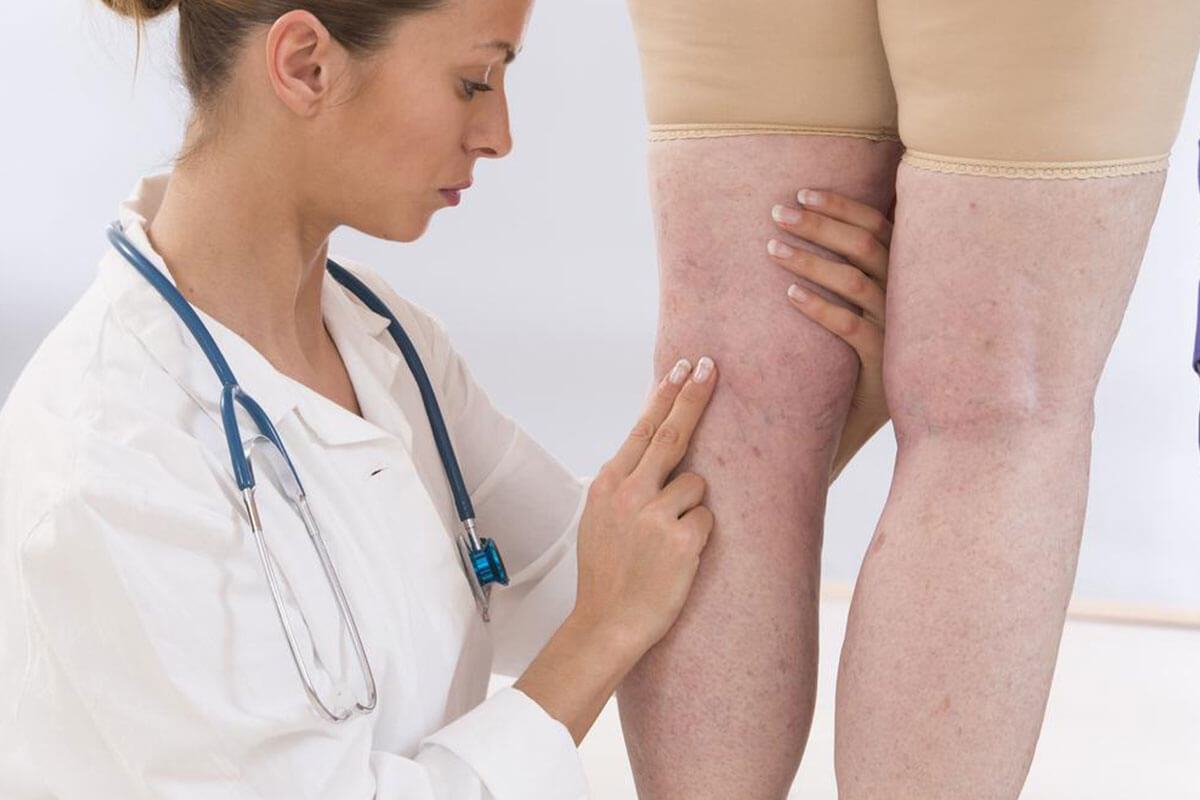
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a serious medical condition characterized by the formation of blood clots within the deep veins, predominantly in the legs. This condition can lead to swelling, pain, and redness, significantly impacting an individual’s quality of life. More alarmingly, if left untreated, DVT may result in a pulmonary embolism—a potentially fatal complication where a clot breaks loose and blocks blood flow to the lungs. Therefore, understanding the risk factors and implementing effective preventive measures are essential for maintaining vascular health and overall well-being.
Age is a notable factor in DVT risk, with incidence increasing among older adults due to changes in blood vessels and decreased mobility. Medical conditions such as previous venous thrombosis, cancer, heart failure, and certain inherited blood clotting disorders further heighten susceptibility. Additionally, lifestyle choices—including prolonged immobility, obesity, smoking, and a sedentary lifestyle—contribute heavily to the development of DVT. Even genetics can play a role, as a family history of clotting disorders may predispose individuals to this condition.
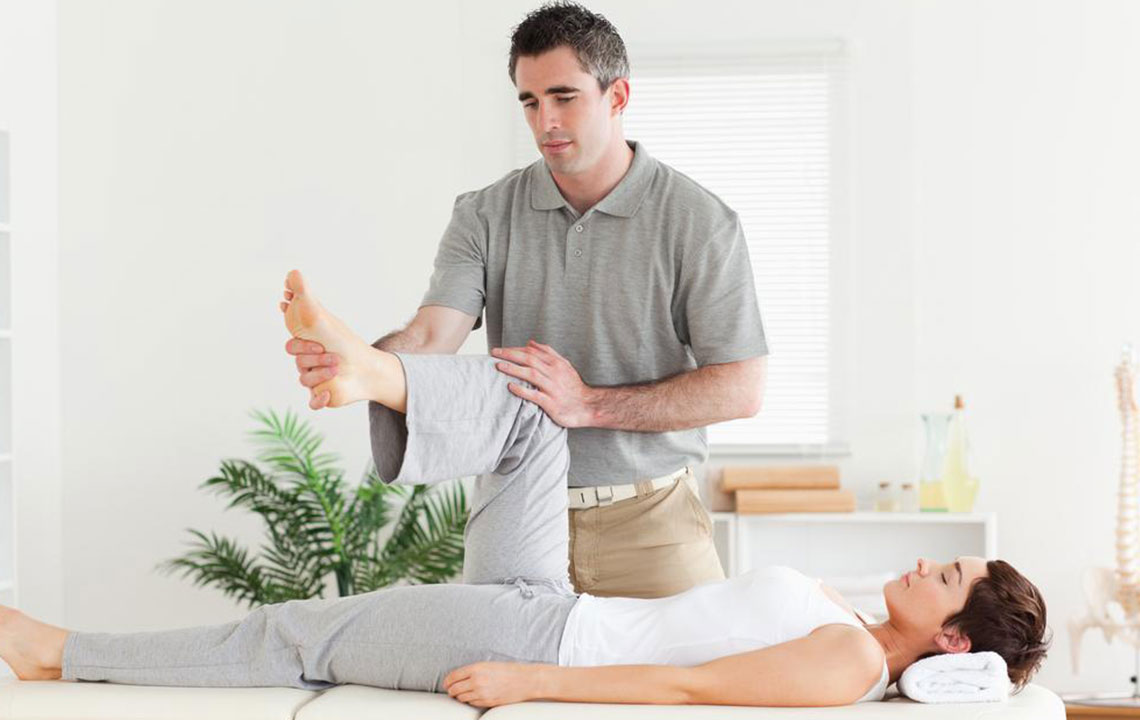
Prevention begins with awareness. Managing medications that elevate the risk of clot formation, such as hormone replacement therapies and certain birth control pills, under medical supervision is vital. Regular monitoring of family health history can help identify genetic predispositions early on. Maintaining a healthy weight through balanced nutrition and exercise reduces pressure on the veins and decreases the likelihood of clot development. Staying physically active—particularly through activities like walking, swimming, or cycling—improves blood circulation, which is key in preventing clot formation.
Diet also plays a crucial role. Incorporating omega-3 fatty acids, commonly found in fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines, can promote healthier blood flow and reduce inflammation. Additionally, staying well-hydrated helps prevent blood from becoming too viscous, further minimizing DVT risk. For long periods of immobility, such as during long flights or bed rest, compression stockings can enhance blood flow in the legs and decrease clot risk. Medical professionals may also recommend blood thinners or anticoagulants for high-risk individuals, particularly after surgeries or during prolonged immobilization.
Other preventive strategies include avoiding smoking, managing chronic illnesses effectively, and ensuring regular health check-ups to detect early signs of vascular issues. Educating oneself about symptoms—such as persistent leg pain, swelling, warmth, and redness—is critical for early intervention. Although DVT can be a silent threat, proactive health management can significantly reduce its occurrence and implications. By adopting these comprehensive strategies, individuals can protect their vascular health and prevent potentially life-threatening complications associated with DVT.