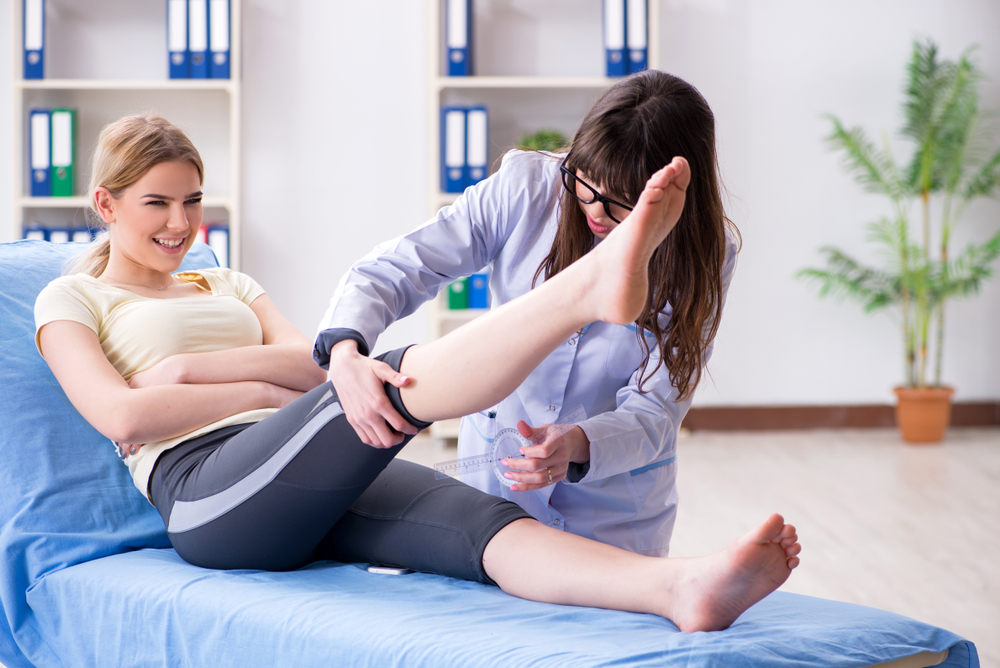
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): Causes, Risks, and Effective Prevention Methods
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a dangerous condition where blood clots form in deep veins, primarily in the legs. Key factors include prolonged immobility, hormonal changes, obesity, and vascular injury. Prevention strategies focus on maintaining mobility, healthy weight, hydration, and medical guidance, especially for high-risk groups. Early detection and treatment are essential to prevent life-threatening complications like pulmonary embolism. This comprehensive guide explains causes, risk factors, and effective preventive measures to help individuals protect their vascular health efficiently.
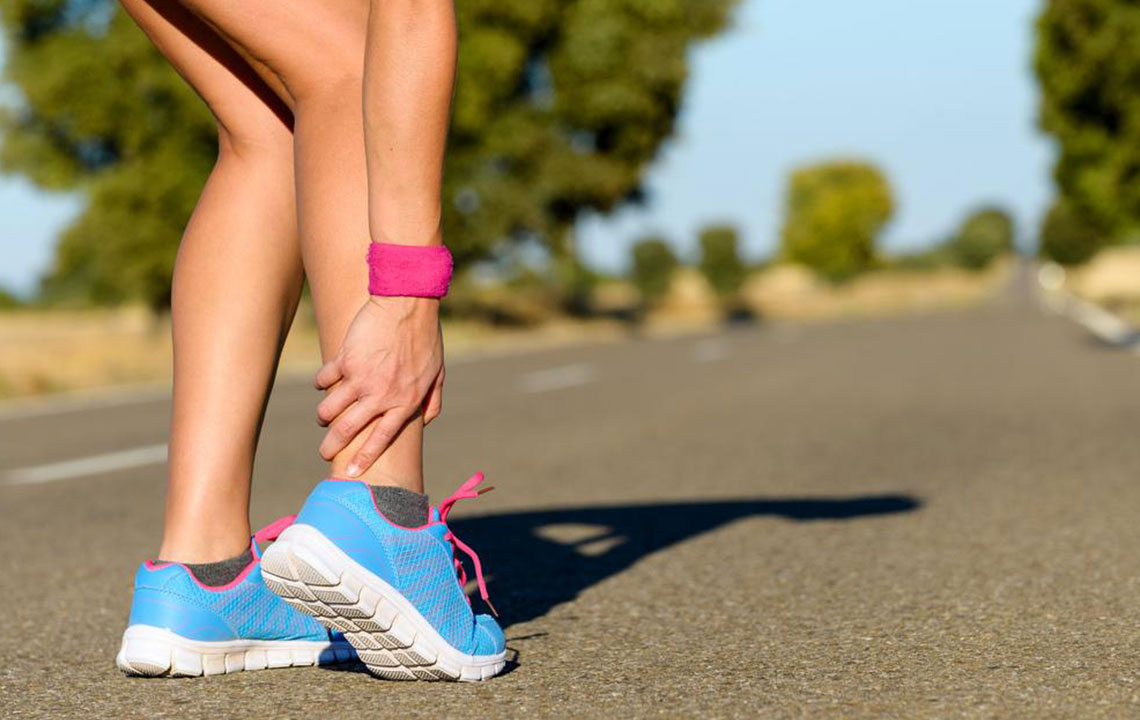

Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): Causes, Risks, and Effective Prevention Methods
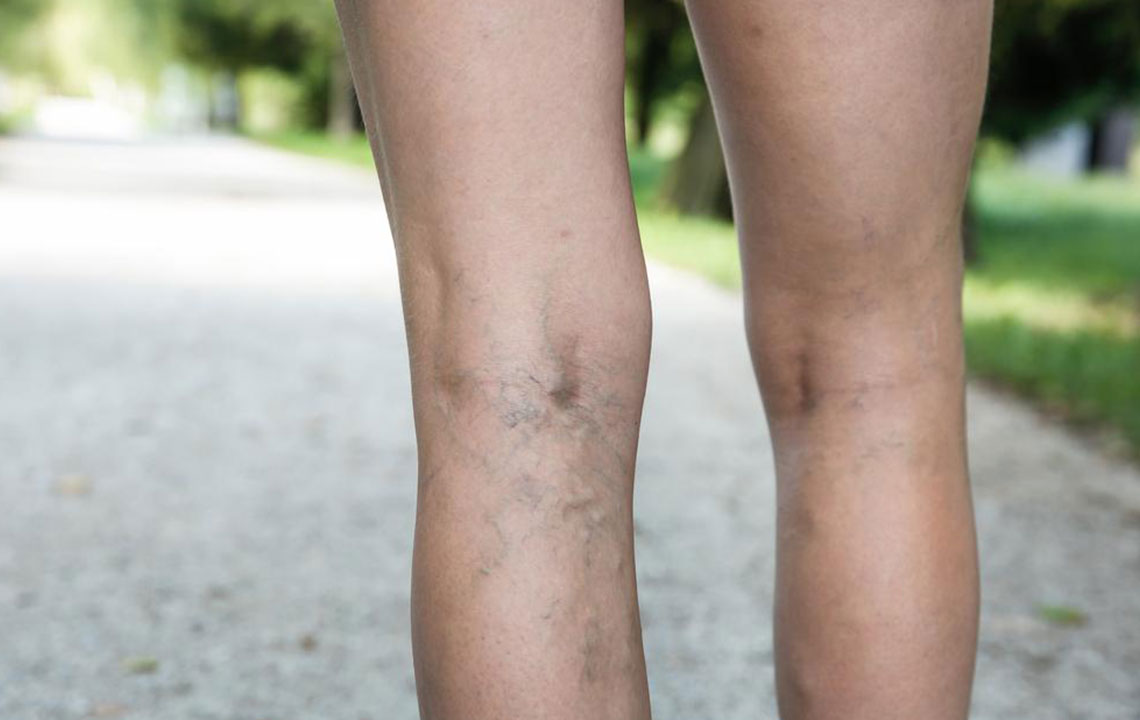
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a serious medical condition characterized by the formation of blood clots in the deep veins, primarily in the legs. This condition can develop without warning, often presenting subtle symptoms such as swelling, tenderness, or redness in the affected limb. If not diagnosed and treated promptly, DVT can lead to life-threatening complications like pulmonary embolism, where a clot travels to the lungs. Understanding what causes DVT, recognizing the risk factors, and implementing preventive measures are essential for maintaining vascular health and avoiding potentially fatal outcomes.
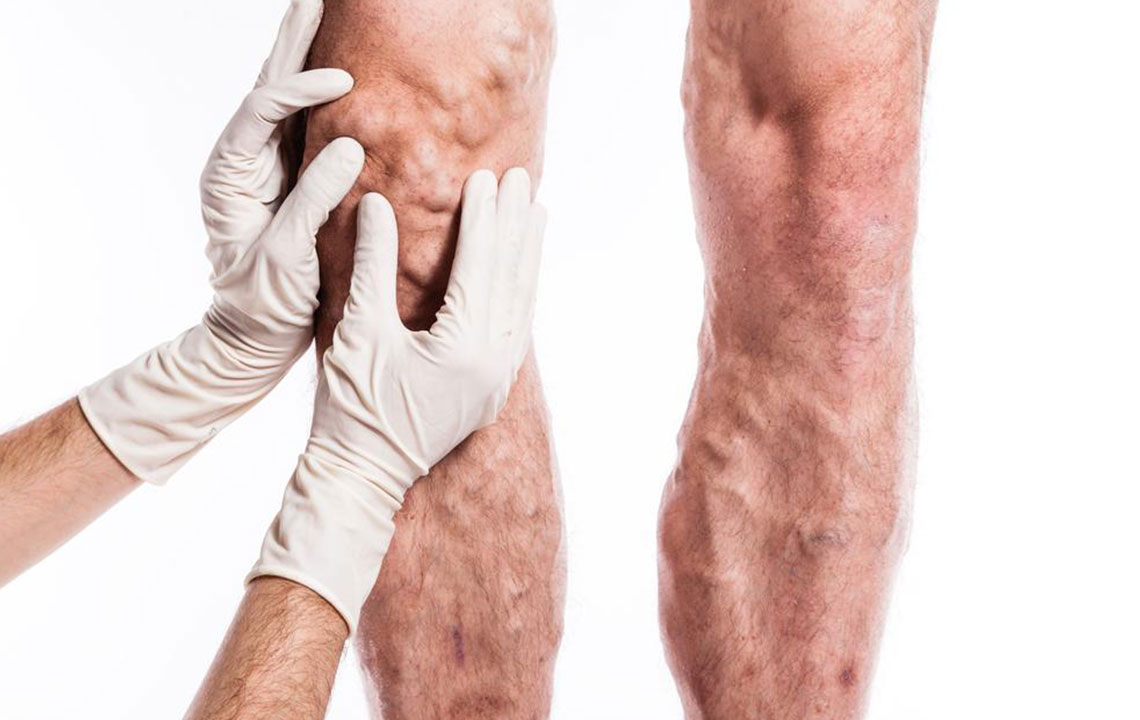
What are the primary causes and risk factors of DVT?
Strategies to effectively prevent deep vein thrombosis
While some risk factors cannot be modified, many preventive measures can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing DVT. Incorporating these strategies into daily routines is especially crucial for individuals at higher risk, such as pregnant women, the obese, or those undergoing surgery.
Maintain active movement and change posture regularly: Avoid prolonged immobility. If your job requires sitting for extended periods, make it a point to stand, stretch, or walk every 30 to 60 minutes. Simple leg exercises such as ankle circles, calf raises, and leg lifts can improve circulation and prevent blood stagnation.
Mobilize soon after surgery: Early early postoperative mobilization, under medical supervision, is vital in preventing blood stasis. Gentle walking and physical therapy help restore normal blood flow, minimizing thrombosis risk.
Adopt healthy lifestyle habits: Maintain a healthy weight through balanced nutrition and regular exercise. Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water helps keep blood viscosity low. Avoid excessive alcohol consumption, which can impair circulation and promote dehydration, leading to thicker blood.
Use compression devices when recommended: Graduated compression stockings or pneumatic compression devices can provide external pressure to leg veins, supporting blood flow during periods of restricted mobility like long flights or hospitalization.
Consult healthcare providers about medications: In high-risk individuals, doctors might prescribe blood-thinning medications such as anticoagulants to prevent clot formation, especially during extended immobilization, pregnancy, or post-surgical periods.
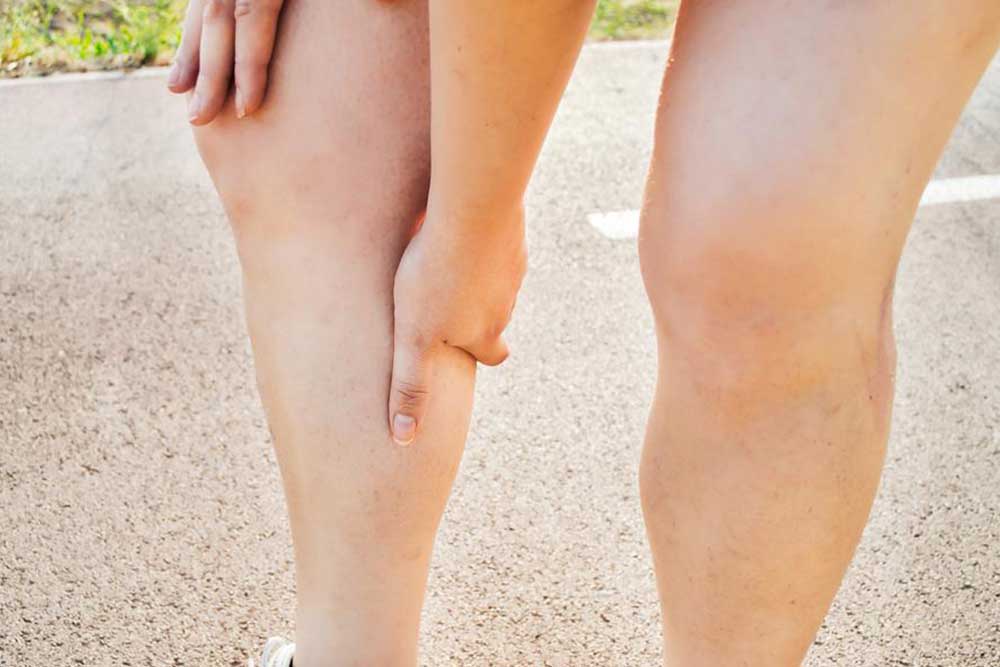
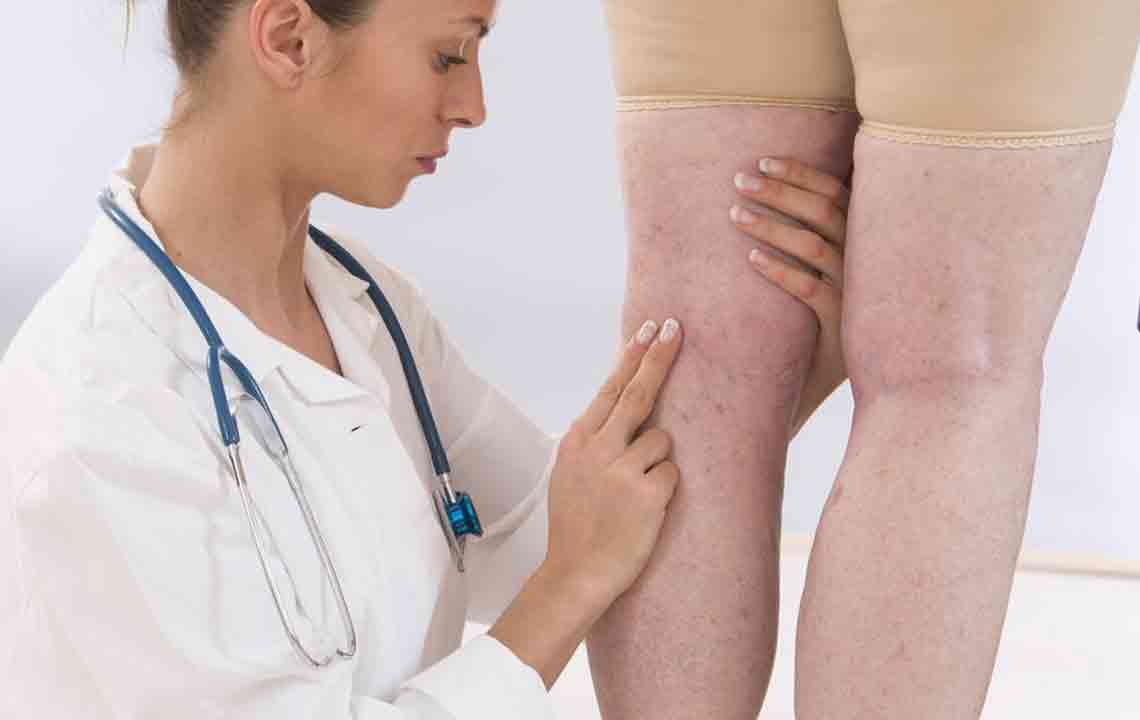
Early detection and treatment of DVT are crucial to prevent severe complications. If you experience symptoms like sudden swelling, intense leg pain, skin warmth, or discolored skin, seek immediate medical attention. Prompt diagnosis with ultrasound examinations and blood tests improves outcomes and reduces mortality risk.
In summary, understanding the causes and risk factors of deep vein thrombosis empowers individuals to take proactive steps for prevention. Adopting active lifestyles, maintaining a healthy weight, and following medical advice can greatly diminish the chances of developing this potentially dangerous condition.