Comprehensive Guide to Deep Vein Thrombosis: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention Strategies
This comprehensive article explores deep vein thrombosis (DVT), covering its causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, treatment options, and effective prevention strategies. Emphasizing lifestyle changes and early intervention, it aims to inform readers about reducing risks and managing this serious vascular condition. Stay informed to safeguard your health and prevent complications associated with DVT.
Comprehensive Guide to Deep Vein Thrombosis: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention Strategies
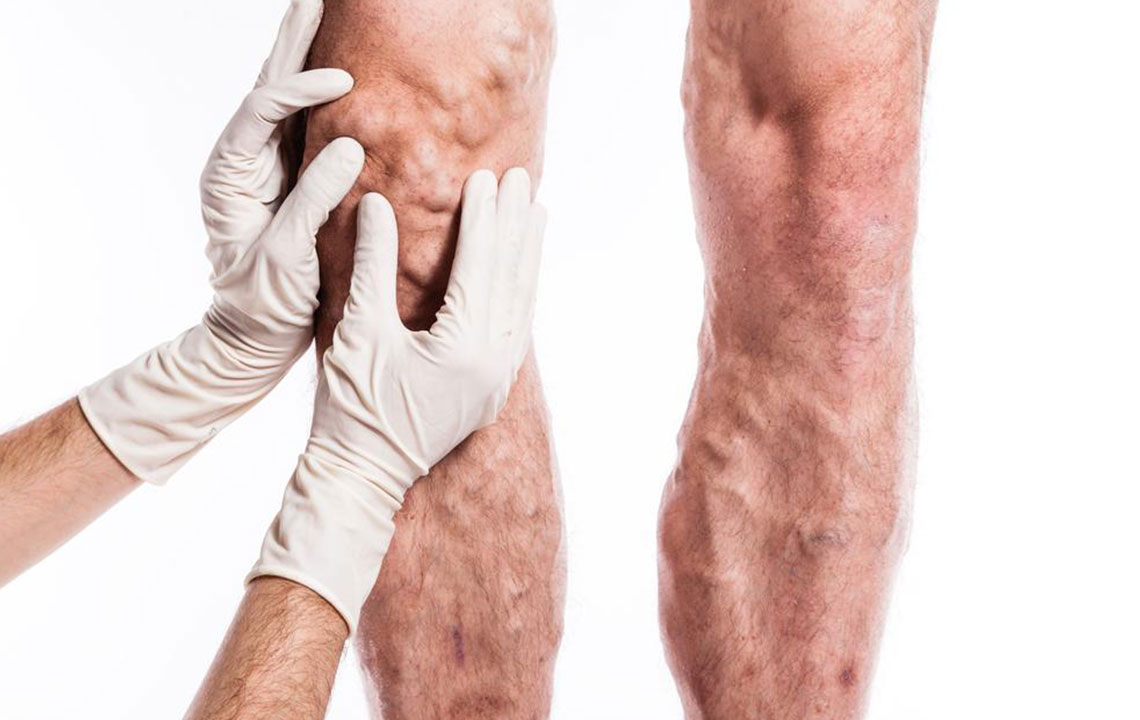
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a significant health condition characterized by the formation of blood clots in the deep veins of the body, most commonly affecting the thighs and lower legs. This condition can pose serious health risks if left untreated, potentially leading to life-threatening complications such as pulmonary embolism, where a dislodged clot travels to the lungs. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and effective prevention strategies of DVT is crucial for maintaining vascular health and minimizing risks.
Deep Vein Thrombosis is also referred to as thromboembolism or post-thrombotic syndrome in medical terminology. It occurs when blood flow in the deep veins slows down or becomes obstructed, resulting in clot formation. Several factors contribute to the development of DVT, including injuries to the veins, prolonged periods of immobility, obesity, genetic predispositions, pregnancy, certain chronic medical conditions such as cancer and heart disease, and lifestyle factors.
Causes and Risk Factors
Vein Injury or Damage: Physical injury to veins, often from surgery or trauma, can trigger clot formation.
Prolonged Immobility: Extended bed rest, long-haul flights, or sedentary lifestyles contribute to sluggish blood flow, increasing clotting risk.
Obesity: Excess body weight puts additional pressure on veins, impairing blood circulation.
Genetic Factors: Hereditary blood clotting disorders, such as Factor V Leiden mutation, heighten the risk of DVT.
Pregnancy: Hormonal changes and pressure from the growing uterus can affect blood flow, making pregnant women more susceptible.
Medical Conditions: Conditions like cancer, heart failure, and certain autoimmune diseases can increase DVT risk.
Recognizing Symptoms
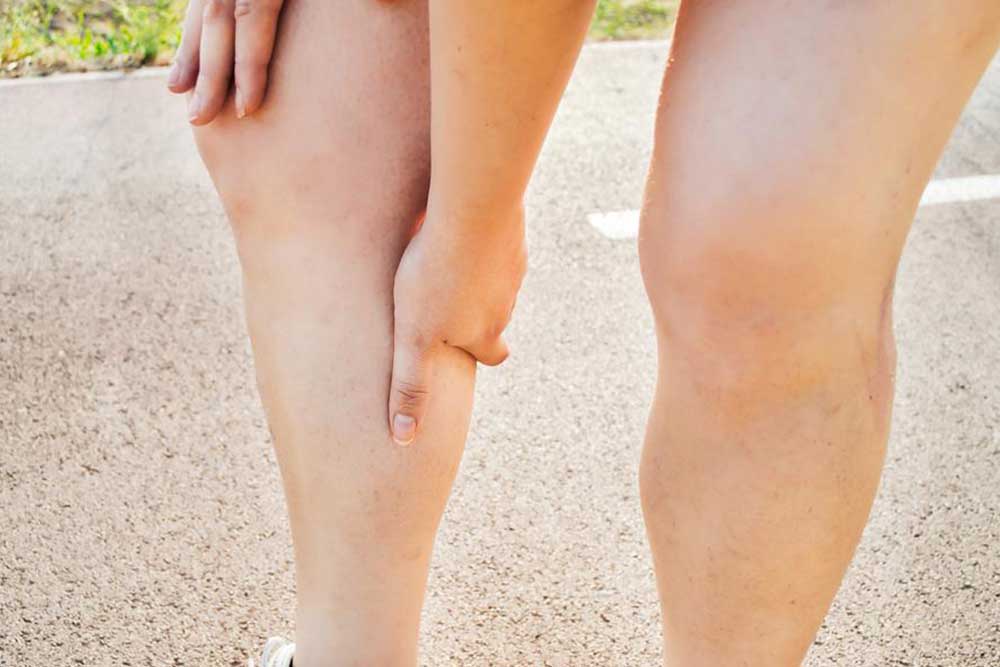
Early recognition of DVT symptoms is vital for prompt treatment. Common signs include:
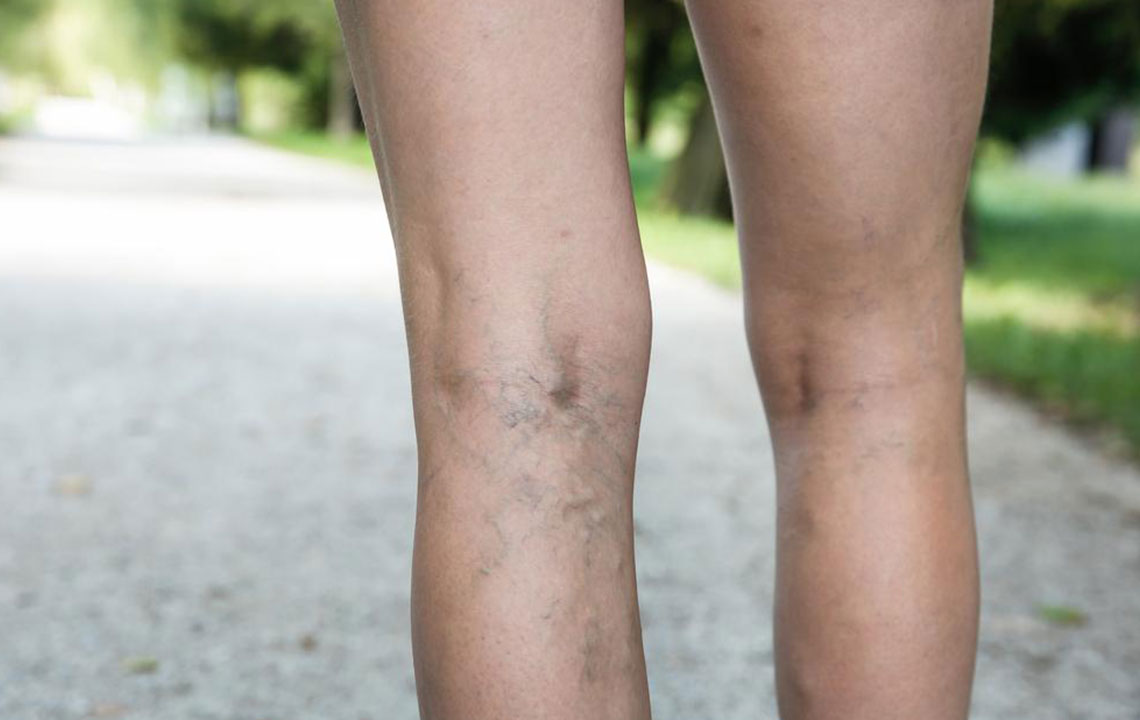
Swelling in the affected leg or calf
Warmth and redness over the impacted area
Sudden or persistent pain, especially when standing or walking
Changes in skin color, such as blanching or bluish tint
It's important to note that some individuals may have DVT without noticeable symptoms, making regular health check-ups critical, especially for those at high risk.
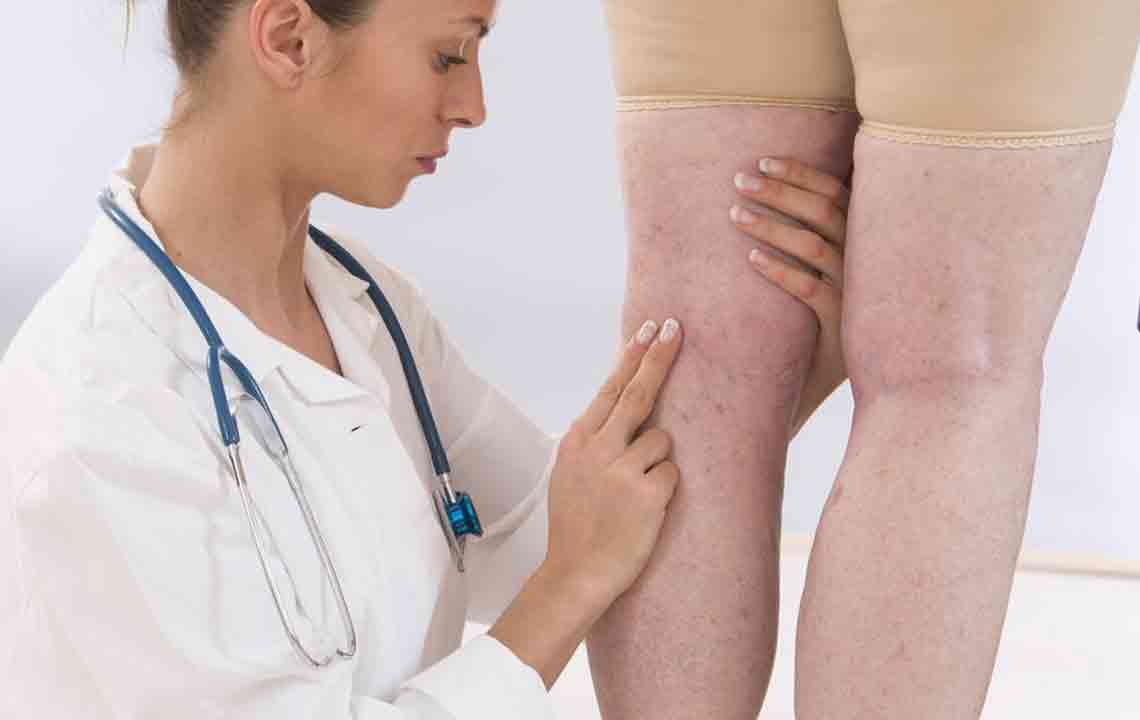
Diagnostic Procedures
Diagnosing DVT involves various imaging tests and clinical assessments, including:
Ultrasound Doppler imaging: The primary tool for visualizing clots in veins
D-dimer blood test: Measures clot-dissolving substance levels, indicating clot presence
Venography: An invasive imaging study used in complex cases
Treatment Options
The main goal of DVT treatment is to prevent clot extension and embolization. Standard therapies include:
Blood Thinners: Anticoagulants like heparin and warfarin help prevent clot growth and new clot formation.
Compression Stockings: Specialized stockings improve venous blood flow and reduce swelling.
Filter Placement: Inferior vena cava filters can be inserted to trap dislodged clots and prevent pulmonary embolism.
Thrombolytic Therapy: In severe cases, clot-dissolving medications may be administered under medical supervision.
Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Changes
Proper prevention strategies are essential for reducing DVT risk, particularly in high-risk populations. Lifestyle modifications include:
Staying physically active: Engage in regular walking, stretching, or aerobic exercises
Avoiding prolonged sitting or immobility: Take breaks during long travels or sedentary work
Maintaining a healthy weight: Achieve and sustain an ideal body mass index (BMI)
Healthy diet: Consume foods rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and fiber to reduce inflammation
Stress management: Practice relaxation techniques to minimize inflammation-inducing stress
Additional Preventive Tips
Hydration: Drink plenty of fluids to keep blood viscosity low
Smoking cessation: Avoid tobacco, which negatively impacts blood vessels
Medication adherence: Follow prescribed medication plans carefully
Regular health screenings: Especially for individuals with familial clotting disorders or chronic illnesses
Importance of Awareness and Early Intervention
Understanding the seriousness of DVT and implementing preventive measures can significantly reduce the incidence of this potentially life-threatening condition. Public health campaigns and medical education play a vital role in promoting awareness, enabling early detection, and encouraging at-risk individuals to seek timely medical care. Early diagnosis coupled with appropriate treatment strategies can prevent complications, improve prognosis, and save lives.
In conclusion, Deep Vein Thrombosis remains a critical health issue worldwide, but with advances in medical technology and increased awareness, its risks can be managed effectively. Maintaining an active lifestyle, making informed health choices, and regular medical checkups are essential steps toward preventing DVT and promoting vascular health.