Comprehensive Guide to Recognizing and Detecting Deep Vein Thrombosis Early
Learn about early signs, symptoms, risk factors, and detection methods for Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT). Recognizing these indicators early can significantly improve treatment outcomes and prevent life-threatening complications. This comprehensive guide emphasizes the importance of awareness, early diagnosis, and prevention strategies for maintaining vascular health and avoiding serious health risks associated with DVT.
Understanding the Early Signs and Detection Methods of Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
Early diagnosis of health conditions plays a crucial role in improving treatment outcomes and reducing potential complications. Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a serious medical condition that involves the formation of blood clots within the deep veins of the lower limbs, often leading to life-threatening issues such as pulmonary embolism if left untreated. Despite its severity, DVT's symptoms can be subtle or easily mistaken for minor injuries or other common ailments, making awareness and timely detection essential.
Deep Vein Thrombosis primarily affects the deep veins in the legs, but it can also occur in other parts of the body. Recognizing the early signs of DVT can greatly enhance the chances of prompt medical intervention, potentially preventing serious complications. This comprehensive guide aims to inform readers about the common symptoms, risk factors, and detection strategies associated with DVT, ultimately promoting early diagnosis and effective management.
Symptoms of Deep Vein Thrombosis
One of the challenges in diagnosing DVT is that it often presents with non-specific symptoms or no symptoms at all, especially in the early stages. However, some signs are highly indicative of the condition and should prompt immediate medical attention. The most commonly observed symptoms include:
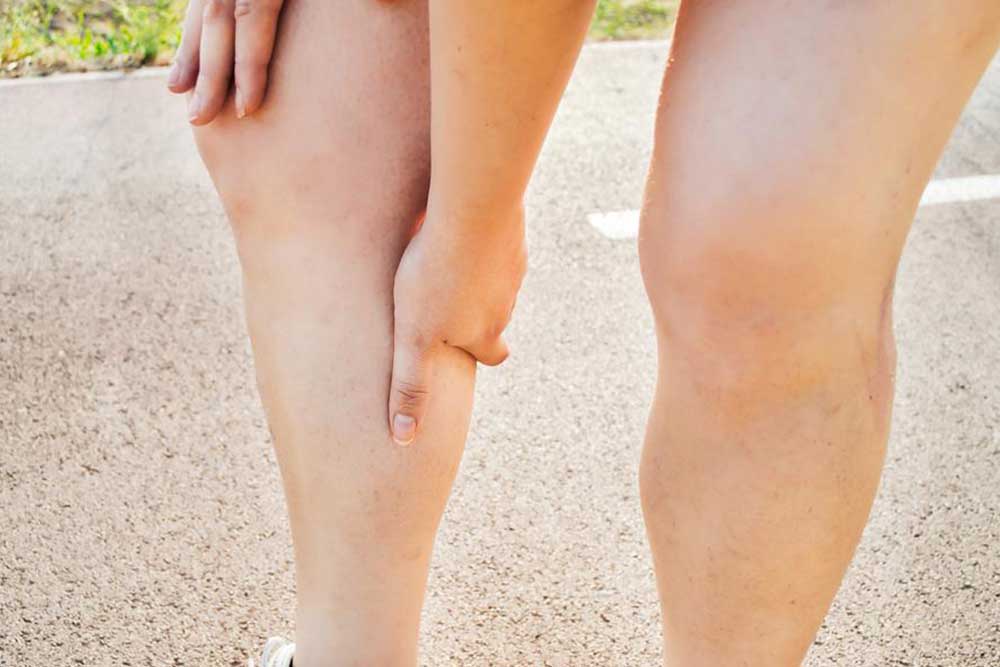
Swelling in one leg or arm: This swelling is usually localized, noticeable, and persistent. It results from the blood clot obstructing normal blood flow, leading to accumulation of fluids in the affected limb.
Localized pain or tenderness: The area around the clot may become tender, especially when touched or pressed, often described as a cramping sensation or soreness.
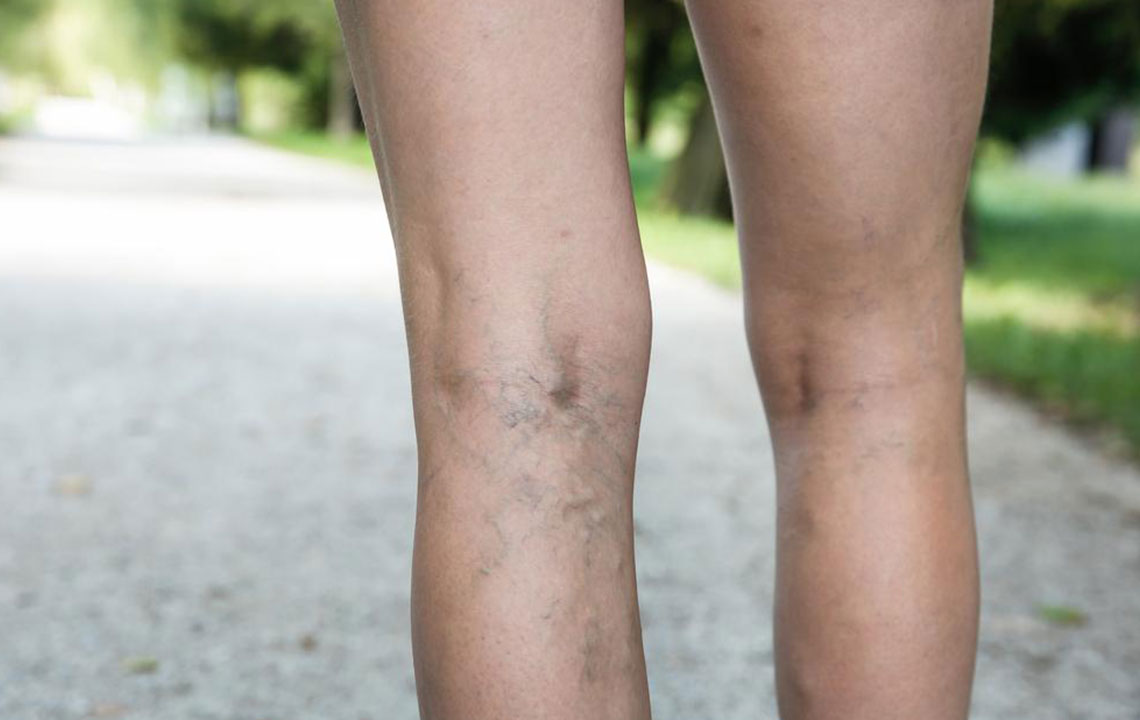
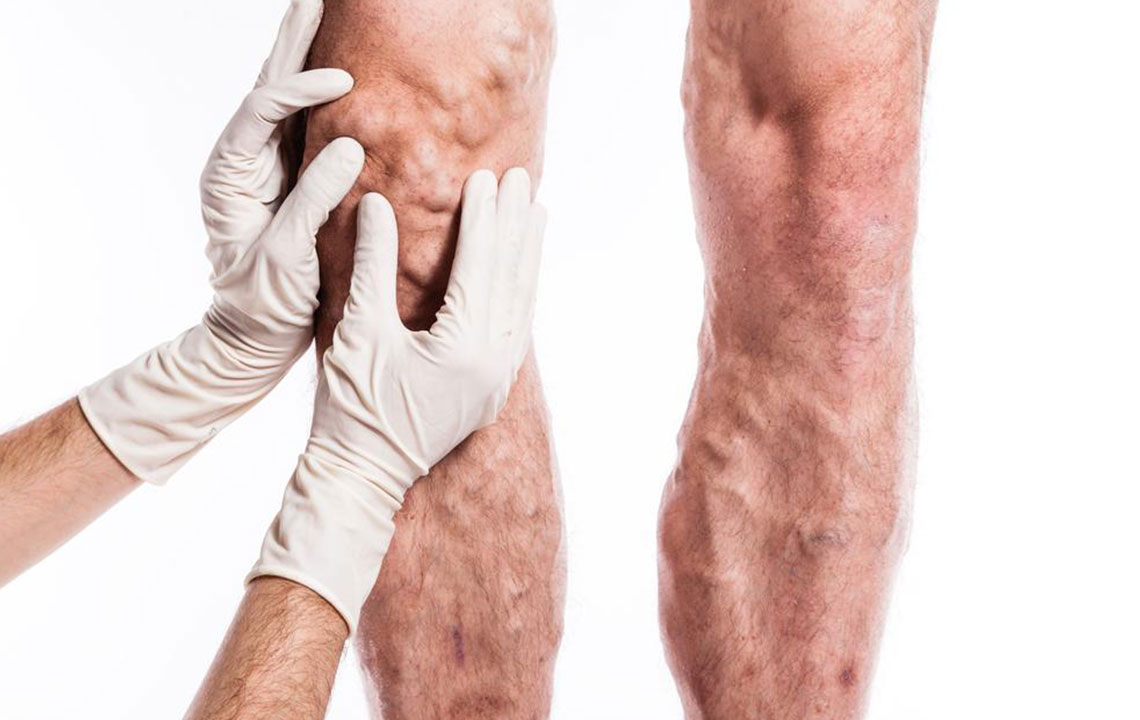
Skin discoloration: The skin over the affected area may turn red, bluish, or a darker shade due to impaired blood flow or inflammation.
Warmth in the affected area: The skin might feel warmer compared to surrounding areas, caused by inflammation and increased blood flow.
Changes in skin texture: The skin may appear tight or shiny, and in some cases, the surface may become abnormal or ulcerated if the clot causes significant damage.
Recognizing Less Obvious Symptoms
In some instances, individuals with DVT might not experience the classical symptoms, especially if the clot is small or in the early stages. Unexplained or persistent leg discomfort, such as heaviness or aching, can sometimes be an early sign of thrombosis. Additionally, some patients report episodes of mild cramping or fatigue in the limb, which may be dismissed as fatigue or muscle strain. Therefore, maintaining awareness of these subtle clues is vital for early detection.
Risk Factors that Increase the Likelihood of DVT
Understanding the factors that predispose individuals to DVT helps in identifying those at higher risk. Common risk factors include:
Prolonged immobility: Extended bed rest, long flights, or sedentary lifestyles can hinder blood flow and lead to clot formation.
Recent surgery or trauma: Especially surgeries involving the legs, pelvis, or abdomen that can damage blood vessels or induce immobility.
Obesity: Excess weight increases pressure on veins, reducing blood flow and increasing clot risk.
Pregnancy and hormonal therapy: These conditions influence blood coagulability, elevating DVT risk.
Age: The risk of DVT increases with age, particularly after 50 years.
Smoking: Tobacco use damages blood vessels and promotes clotting.
Preventive Measures and When to Seek Medical Help
Prevention is the key to managing DVT risks. Regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding prolonged immobility are crucial. People at higher risk should consider compression stockings or anticoagulant medications as prescribed by healthcare professionals. Importantly, individuals experiencing symptoms such as unilateral leg swelling, pain, or skin discoloration should seek immediate medical evaluation to confirm diagnosis and initiate appropriate treatment.
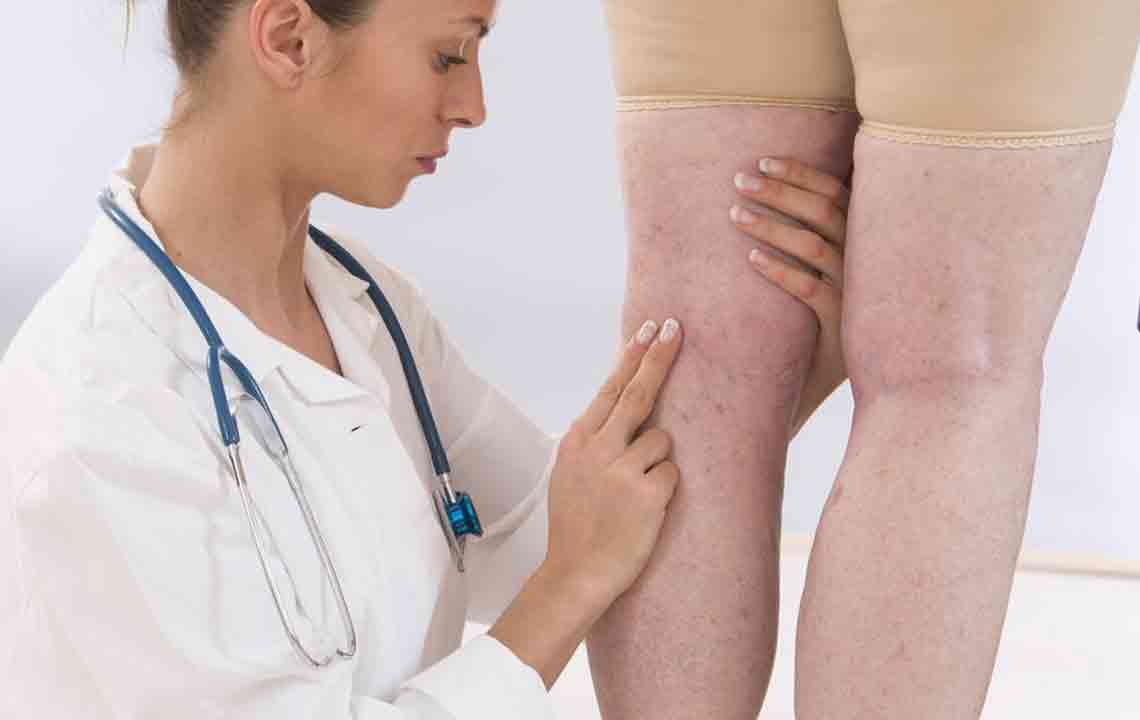
Diagnostic and Detection Techniques
Detecting DVT often involves a combination of clinical assessment and imaging tests. Healthcare providers may employ several diagnostic tools, including:
D-dimer test: A blood test that measures a substance released during clot breakdown; elevated levels suggest a clotting process.
Ultrasound Doppler imaging: The primary non-invasive test used to visualize blood flow and identify clots in deep veins.
Venography: An imaging procedure where contrast dye is injected into veins to highlight blockages, usually reserved for complex cases.
MRI or CT scans: Advanced imaging techniques to detect deep vein abnormalities when ultrasound results are inconclusive.
Conclusion: The Significance of Awareness and Early Detection
Deep Vein Thrombosis remains a potentially life-threatening condition, but early recognition can significantly improve treatment outcomes and reduce the risk of severe complications like pulmonary embolism. Educating oneself about the signs and risk factors, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and seeking prompt medical attention when symptoms arise are critical steps toward effective management. If you experience persistent swelling, pain, or skin discoloration in your limbs, do not hesitate to consult a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and appropriate intervention.
Remember, vigilance and proactive health measures are your best defenses against the dangers of DVT. Regular health check-ups and awareness are vital tools in safeguarding your vascular health and preventing serious medical emergencies.