Comprehensive Guide to Managing Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): Prevention, Treatment, and Care
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a potentially dangerous condition characterized by blood clots forming in deep veins, often in the legs. This comprehensive guide explores risk factors, early signs, diagnosis, and various treatment options including medications, supportive measures, and advanced procedures. Proper management of DVT is crucial to prevent complications such as pulmonary embolism. To ensure safety and efficacy, patients should work closely with healthcare professionals, adopt healthy lifestyles, and remain vigilant about symptoms. Staying informed and proactive can significantly improve outcomes for those affected by DVT.
Understanding Deep Vein Thrombosis and Effective Management Strategies
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a serious medical condition characterized by the formation of blood clots within the deep veins, predominantly in the legs. Recognizing the signs, understanding the risk factors, and exploring effective treatment options are crucial steps in managing this condition to prevent life-threatening complications such as pulmonary embolism.
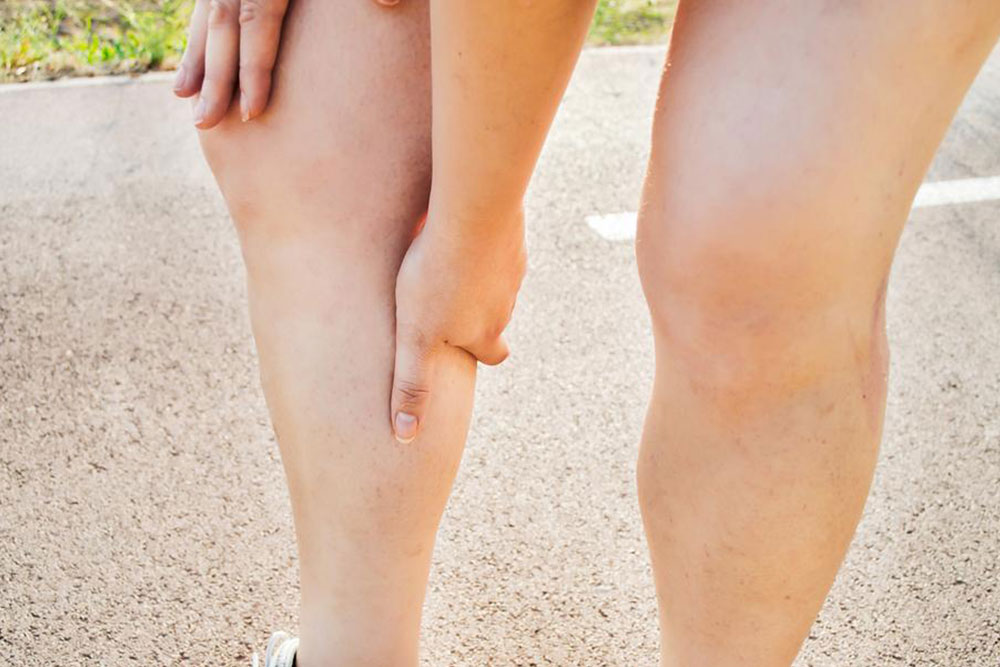
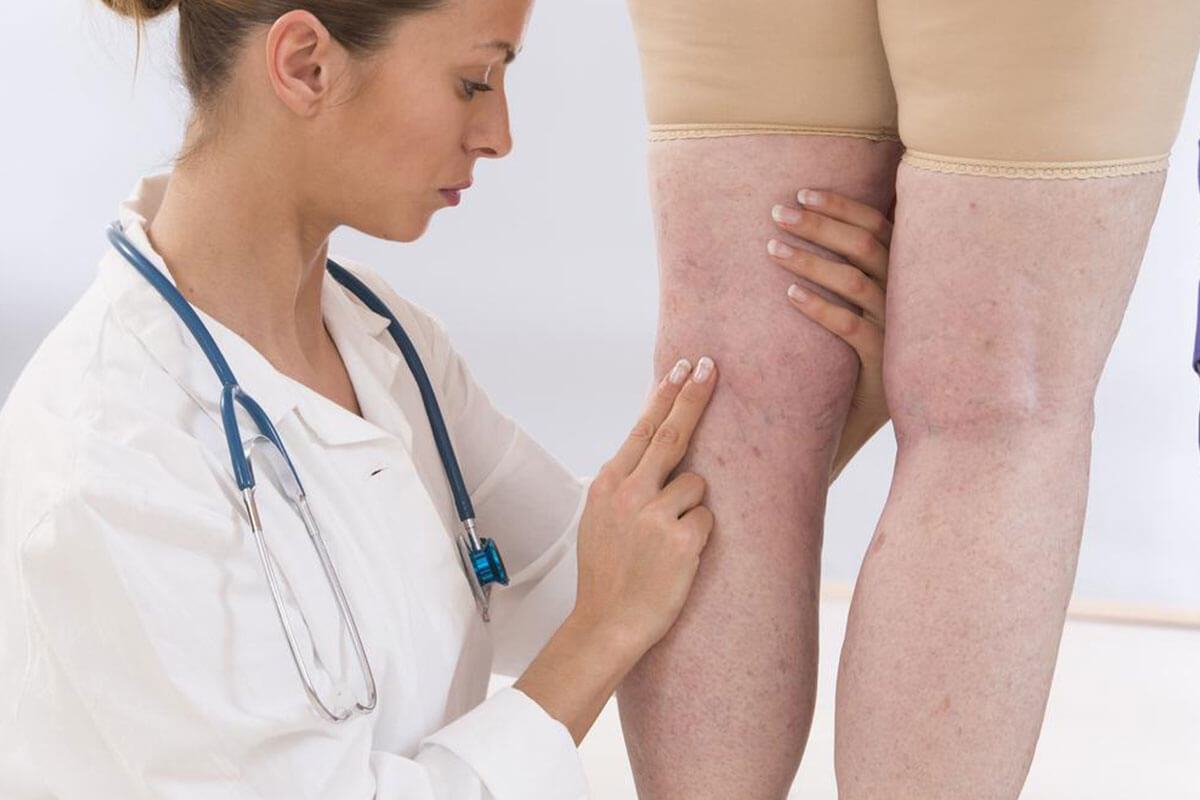
If you notice unexplained swelling, pain, or discomfort in your legs, especially if accompanied by skin redness or warmth, these may be symptoms of DVT. High-risk groups include individuals with sedentary lifestyles, obesity, smoking habits, and those over 60 years of age. Early detection and prompt treatment are key to minimizing the risks associated with DVT.
Early recognition of symptoms such as leg pain, swelling, and tenderness is vital, especially for people in high-risk groups. DVT is a severe condition because blood clots can break loose and travel through the bloodstream, ultimately lodging in the lungs and causing a pulmonary embolism, which requires immediate medical attention. Accurate diagnosis typically involves imaging techniques like Doppler ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or venography to detect blood clots with high precision.
Effective management of DVT focuses on preventing clot enlargement, lowering the risk of pulmonary embolism, alleviating symptoms, and preventing recurrence. Treatment approaches vary depending on individual health profiles and the severity of the thrombosis. The primary treatment options include anticoagulant medications, physical measures, and sometimes surgical interventions.
Pharmacological Treatments for DVT
Anticoagulant drugs play a pivotal role in managing DVT. Common anticoagulants used include heparin, warfarin, and novel oral anticoagulants like rivaroxaban and apixaban. These medications work by thinning the blood, which prevents existing clots from growing and reduces the likelihood of new clots forming. Patients on anticoagulants require regular monitoring to ensure proper dosage and prevent excessive bleeding.
For hospitalized patients or those with severe DVT, initial treatment may involve injectable heparin, followed by oral anticoagulants as a long-term therapy. The duration of anticoagulation therapy depends on individual patient risk factors and response to treatment. Compliance with medication and routine blood tests are essential to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Supportive Measures and Lifestyle Adjustments
In addition to medications, supportive measures significantly aid in managing DVT. Compression stockings are highly recommended to help reduce swelling and improve blood flow in the affected limbs. Elevating the legs whenever possible can also alleviate symptoms. Encouraging early mobilization and regular movement are vital, especially for sedentary patients or those recovering from surgery or prolonged bed rest.
Adopting a healthy lifestyle is crucial for preventing DVT recurrence. This includes maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, managing chronic conditions such as hypertension and diabetes, and staying physically active. Educating patients about recognizing early signs and adhering to treatment plans plays a vital role in reducing the risk of complications.
Advanced Therapeutic Procedures
For patients at high risk or those with extensive clot formation, more aggressive treatment options may be necessary. Catheter-directed thrombolysis involves inserting a catheter to deliver clot-dissolving medications directly into the thrombus, resulting in rapid clot dissolution. While effective, this procedure carries increased risks, including bleeding and vascular injury.
In cases where anticoagulation is contraindicated or ineffective, or to prevent recurrent embolism, implantation of a vena cava filter might be recommended. This device prevents dislodged clots from reaching the lungs, serving as a mechanical barrier. The choice of treatment is guided by a thorough evaluation of the patient’s condition, underlying risk factors, and overall health status.
Consultation with a healthcare provider specializing in vascular medicine is vital for developing a personalized treatment plan, which may involve a combination of pharmacological, interventional, and lifestyle strategies.
Understanding and managing DVT is crucial in preventing serious health consequences. Awareness of risk factors, early detection of symptoms, compliance with treatment, and adopting healthy habits form the cornerstone of effective DVT management. With advances in medical technology and a better understanding of blood clotting mechanisms, patient outcomes continue to improve. Remember to seek medical attention promptly if you suspect DVT, and adhere strictly to prescribed treatments to ensure the best possible prognosis.