Comprehensive Strategies to Protect Your Lungs from Pulmonary Embolism
This comprehensive guide explores effective strategies to prevent pulmonary embolism, a dangerous condition caused by blood clots blocking lung arteries. It highlights risk factors, symptoms, and preventive measures including lifestyle changes and medical interventions to protect lung health and ensure early detection.
Effective Ways to Prevent Pulmonary Embolism and Safeguard Lung Health
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a critical medical emergency characterized by a blockage in one of the pulmonary arteries in the lungs. This condition often results from blood clots that originate from deep veins in the legs or other parts of the body and subsequently migrate to the lungs, a process known as venous thromboembolism (VTE). PE can be life-threatening if not promptly diagnosed and treated, making awareness and prevention vital for at-risk populations.
Understanding the underlying causes, early symptoms, and risk factors associated with pulmonary embolism is essential in preventing severe health consequences. This article explores comprehensive strategies to protect your lungs from this potentially fatal condition, including risk reduction, lifestyle modifications, and recognizing warning signs for early intervention.
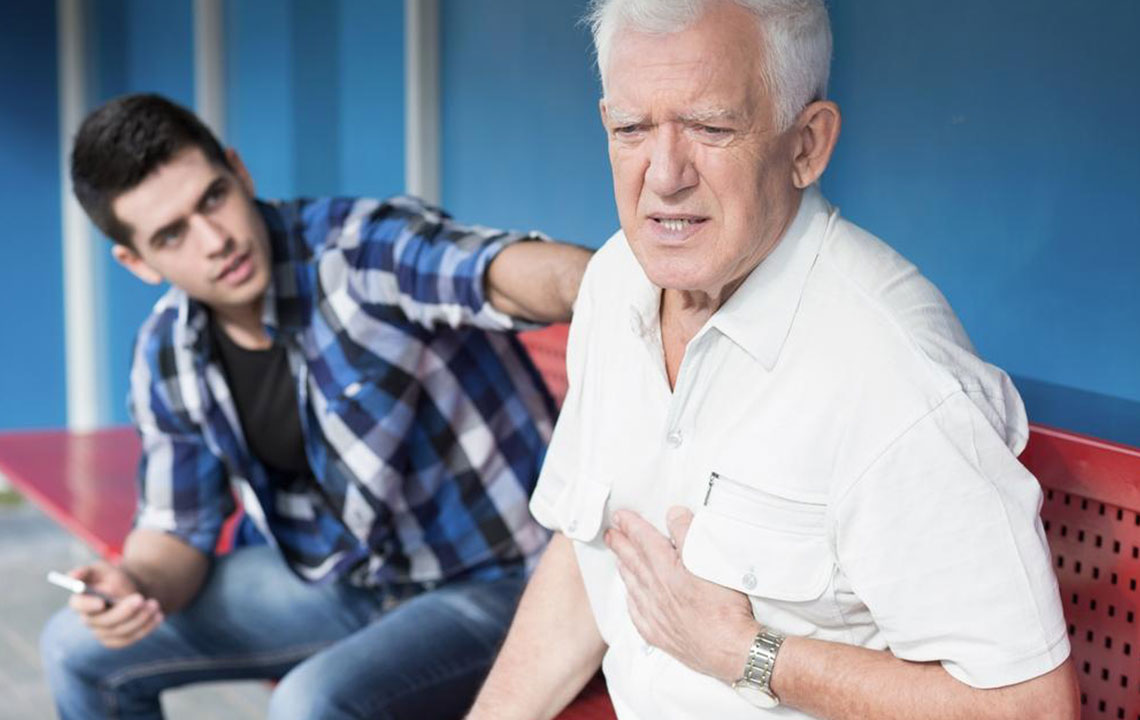
Pulmonary embolism occurs when a blood clot blocks blood flow within the lungs, often causing symptoms such as sudden shortness of breath, chest pain resembling that of a heart attack, and coughing up blood-streaked sputum. These symptoms can vary based on the size of the clot, the extent of lung involvement, and individual health factors.
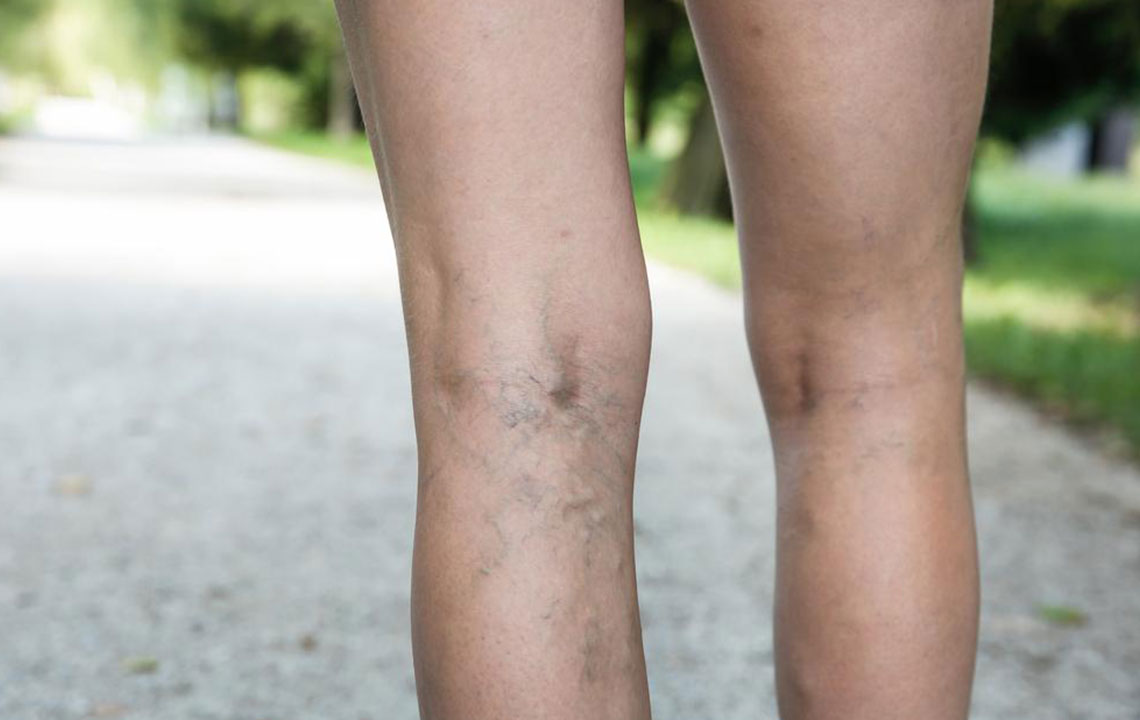
Additional warning signs include swelling or pain in the legs, which might indicate deep vein thrombosis (DVT), skin discoloration or cyanosis, unexplained fever, excessive sweating, irregular heartbeat, dizziness, and fainting. The primary cause is blood clots that form in deep veins, especially in the legs, under conditions favoring blood clot formation such as prolonged immobility, certain medical conditions, or genetic predispositions. Once dislodged, these clots can travel to the lungs and cause blockages, significantly impairing respiratory function and potentially leading to lung tissue damage or infarction.
Preventive measures involve lifestyle changes, medical management, and awareness of risk factors. Maintaining a healthy weight, staying physically active, and avoiding prolonged immobility are key strategies. Medical interventions may include anticoagulant therapy for high-risk individuals, regular health screenings, and managing underlying health conditions such as hypertension or atrial fibrillation. Patients with a history of DVT or PE should follow their healthcare provider’s guidance rigorously. Recognizing early symptoms and seeking immediate medical attention is critical in reducing mortality rates from pulmonary embolism.
In addition, understanding less common causes such as fat embolism, air embolism, or tissue fragments can help in identifying rare but serious instances of PE. Advanced diagnostic tools like CT scans and D-dimer tests support prompt detection, facilitating early treatment and improving outcomes. Public education campaigns and patient awareness programs play a crucial role in reducing the incidence and severity of pulmonary embolism.
Overall, proactive health management, lifestyle modifications, and timely medical intervention are essential in preventing pulmonary embolism. By staying informed about risk factors and early symptoms, individuals can take vital steps toward safeguarding their lung health and saving lives.