Identifying Critical Symptoms of Pulmonary Embolism: A Comprehensive Guide
This comprehensive guide details the causes, risk factors, and key symptoms of pulmonary embolism, emphasizing the importance of early detection and prompt medical treatment. Learn how to recognize warning signs and prevent severe complications associated with this life-threatening condition. Regular health checks, awareness of personal risk factors, and swift action can save lives.
Understanding and Recognizing Symptoms of Pulmonary Embolism
What Is Pulmonary Embolism?
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a potentially life-threatening condition that occurs when a blood clot, usually originating from the deep veins of the legs or pelvis, travels through the bloodstream and lodges in the arteries of the lungs. This blockage impairs normal blood flow, leading to reduced oxygen intake and potential damage to lung tissue. The condition demands urgent medical attention because, if left untreated, it can result in severe complications or death.
The primary cause of PE is deep vein thrombosis (DVT), a condition where blood clots form in deep veins. These clots may dislodge and travel through the circulatory system, ultimately blocking pulmonary arteries. While DVT is often asymptomatic, the resulting embolism can produce acute symptoms that require prompt recognition and intervention.
Understanding the mechanisms, risk factors, and symptoms associated with pulmonary embolism is essential for early diagnosis and effective treatment. The quicker PE is identified, the better the chances of preventing permanent lung damage and other serious health consequences.
Risk Factors for Pulmonary Embolism
Numerous factors increase the likelihood of developing a pulmonary embolism. Recognizing these risk factors helps individuals and healthcare providers take preemptive measures to reduce danger:
Recent major surgery, especially involving the hips, knees, or abdomen
Prolonged immobility due to hospitalization, bed rest, or long flights
Active cancer or undergoing chemotherapy
Obesity and overweight conditions
History of blood clots or previous episodes of DVT or PE
Genetic predispositions and inherited clotting disorders
Hormone replacement therapy or use of contraceptives containing estrogen
Pregnancy and postpartum period
Tobacco smoking and unhealthy lifestyle habits
Chronic inflammatory diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease
Common Symptoms and How to Spot Them
Early recognition of pulmonary embolism symptoms can significantly increase survival rates. The symptoms can sometimes mimic those of other respiratory or cardiac conditions, which makes awareness particularly important. Key signs to look for include:
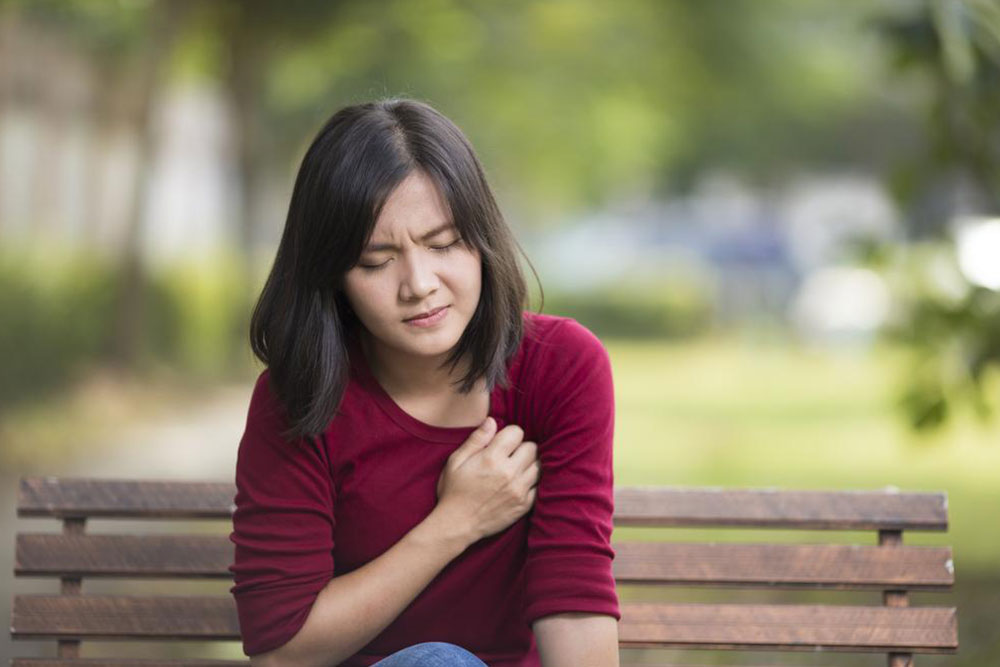
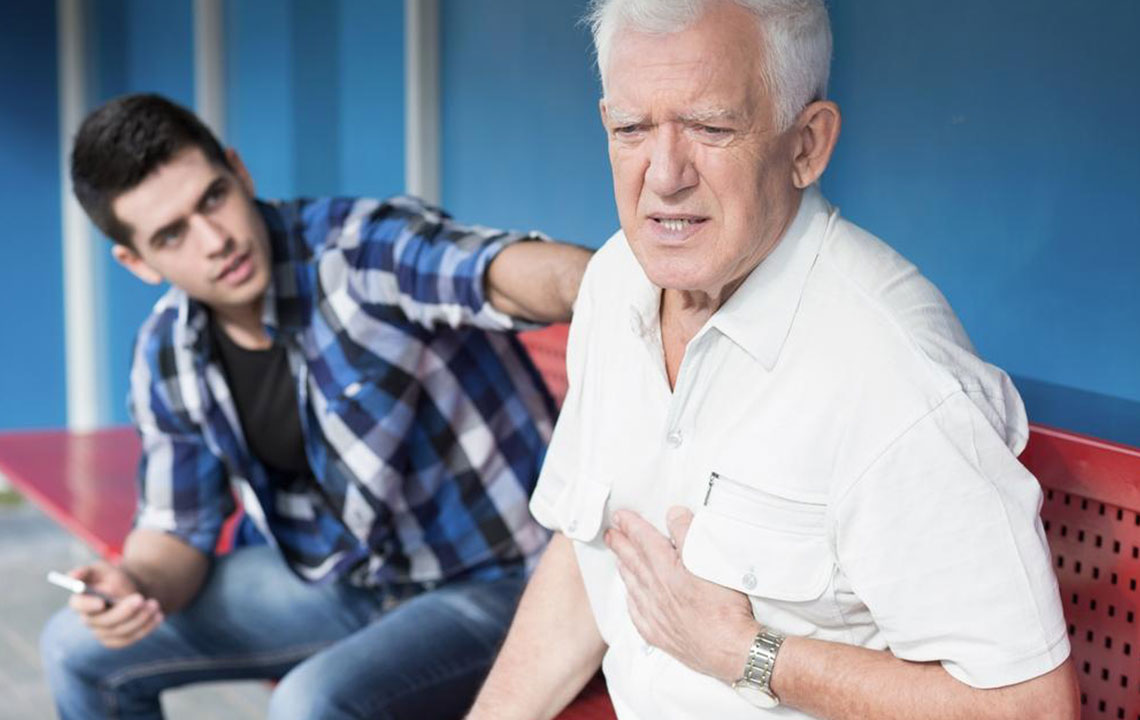
Sudden Shortness of Breath: A hallmark symptom, often unexpected, that worsens with exertion or at rest.
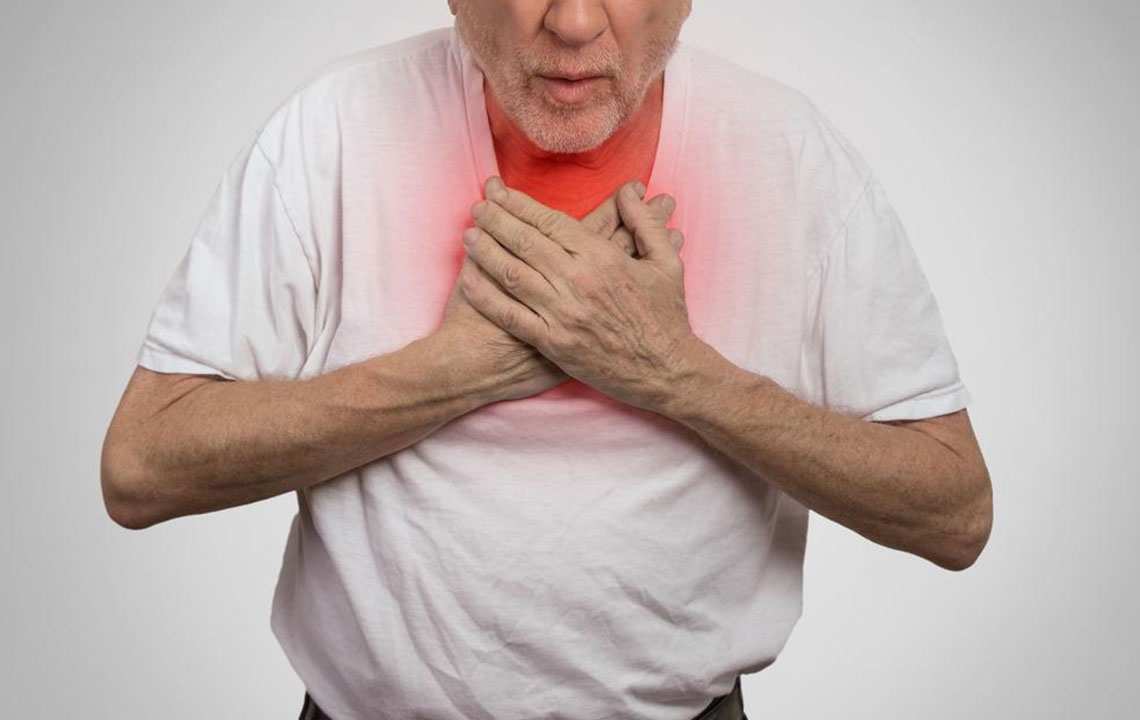
Chest Pain: Typically sharp and localized; may worsen with deep breaths or coughing.
Rapid Heartbeat (Tachycardia): An unusually quick pulse may be evident as the body attempts to compensate for low oxygen levels.
Coughing: Sometimes bloody, indicating lung tissue damage or clot presence.
Leg Swelling or Pain: Signs of deep vein thrombosis, often preceding PE.
Skin Discoloration: A bluish tint around lips and fingertips, indicating insufficient oxygenation.
Fever and Sweating: May accompany other symptoms, especially if an infection is involved.
Restlessness and Anxiety: Feelings of impending doom or severe discomfort may be present.
The Importance of Timely Medical Intervention
Since symptoms of PE are similar to those of heart attack, pneumonia, or other respiratory issues, definitive diagnosis requires professional medical evaluation. If pulmonary embolism is suspected, immediate hospitalization is critical for performing diagnostic tests such as CT pulmonary angiography, D-dimer blood tests, and ultrasound of leg veins.
Early treatment strategies include anticoagulant therapy (blood thinners), thrombolytic therapy to dissolve clots, and sometimes surgical interventions. The goal is to restore blood flow, prevent clot propagation, and reduce the risk of recurrent embolism.
Preventing future episodes involves managing risk factors, lifestyle modifications, and in some cases, long-term anticoagulation therapy. For high-risk individuals, prophylactic measures such as compression stockings and periodic monitoring are recommended.
Conclusion: Stay Vigilant Against Pulmonary Embolism
Pulmonary embolism remains a critical health threat that necessitates awareness and prompt action. Recognizing early signs and understanding risk factors empower individuals to seek immediate medical care, significantly improving outcomes. Routine health checkups, lifestyle adjustments, and adherence to medical advice can help reduce the incidence and severity of PE. If you experience any of the symptoms described, do not delay—seek emergency medical attention to protect your health and life.