Comprehensive Home Strategies for Preventing and Managing Venous Thrombosis
Learn comprehensive approaches to prevent and manage deep vein thrombosis (DVT) at home. Explore medication adherence, lifestyle changes, safety tips, and natural remedies to support vascular health and reduce risks effectively. Discover how to stay proactive in your health journey to prevent serious complications like pulmonary embolism.

Comprehensive Home Strategies for Preventing and Managing Venous Thrombosis
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a serious medical condition characterized by the formation of blood clots within the deep veins, predominantly in the calves and thighs. This condition can be life-threatening if not properly managed, as these clots have the potential to dislodge and travel to the lungs, causing pulmonary embolism—a critical and potentially fatal complication. Therefore, understanding effective prevention methods and management strategies that can be implemented at home is vital for individuals at risk or those recovering from DVT.
Understanding and Recognizing DVT
DVT often develops over time due to factors such as prolonged immobility, certain medical conditions, or genetic predispositions. Symptoms may include swelling, pain, tenderness, skin warmth, and discoloration in the affected limb. Early detection and management are crucial to prevent serious complications. Diagnosing DVT typically involves ultrasound imaging and blood tests, but many aspects of prevention and treatment can be managed effectively at home under medical guidance.
Home-Based Prevention and Treatment Options
Adherence to prescribed anticoagulant therapy: Patients prescribed blood thinners such as warfarin, rivaroxaban, or apixaban must take these medications exactly as directed. Consistent medication intake over the course of several months or more is necessary to prevent the clot from enlarging or breaking loose. Adherence to the prescribed dosage, regular blood tests to monitor blood clotting levels, and timely communication with healthcare providers are integral components of safe anticoagulant therapy.
Monitoring and adjusting treatment: Regular blood tests—like INR for those on warfarin or other specific coagulation profiles—are essential to ensure blood remains within a therapeutic range. Healthcare providers may adjust dosages based on test results to optimize efficacy while minimizing bleeding risks.
Safety Precautions When Using Anticoagulants
Anticoagulants increase bleeding risk, so precautionary measures are essential. Individuals should avoid activities that may cause injuries, such as contact sports or hazardous work. Wearing protective gear and using mobility aids can help prevent falls or injuries. It is also important to inform all healthcare providers about current medications, supplements, and underlying health issues to prevent adverse interactions.
Lifestyle Modifications to Support Recovery and Prevention
Elevating the affected limb: Elevate the leg or limb whenever possible to reduce swelling and improve blood flow.
Encouraging mobility: Gentle walking and leg movements stimulate circulation and help prevent clot formation. Avoid prolonged immobility or sitting for extended periods, especially during travel or sedentary work.
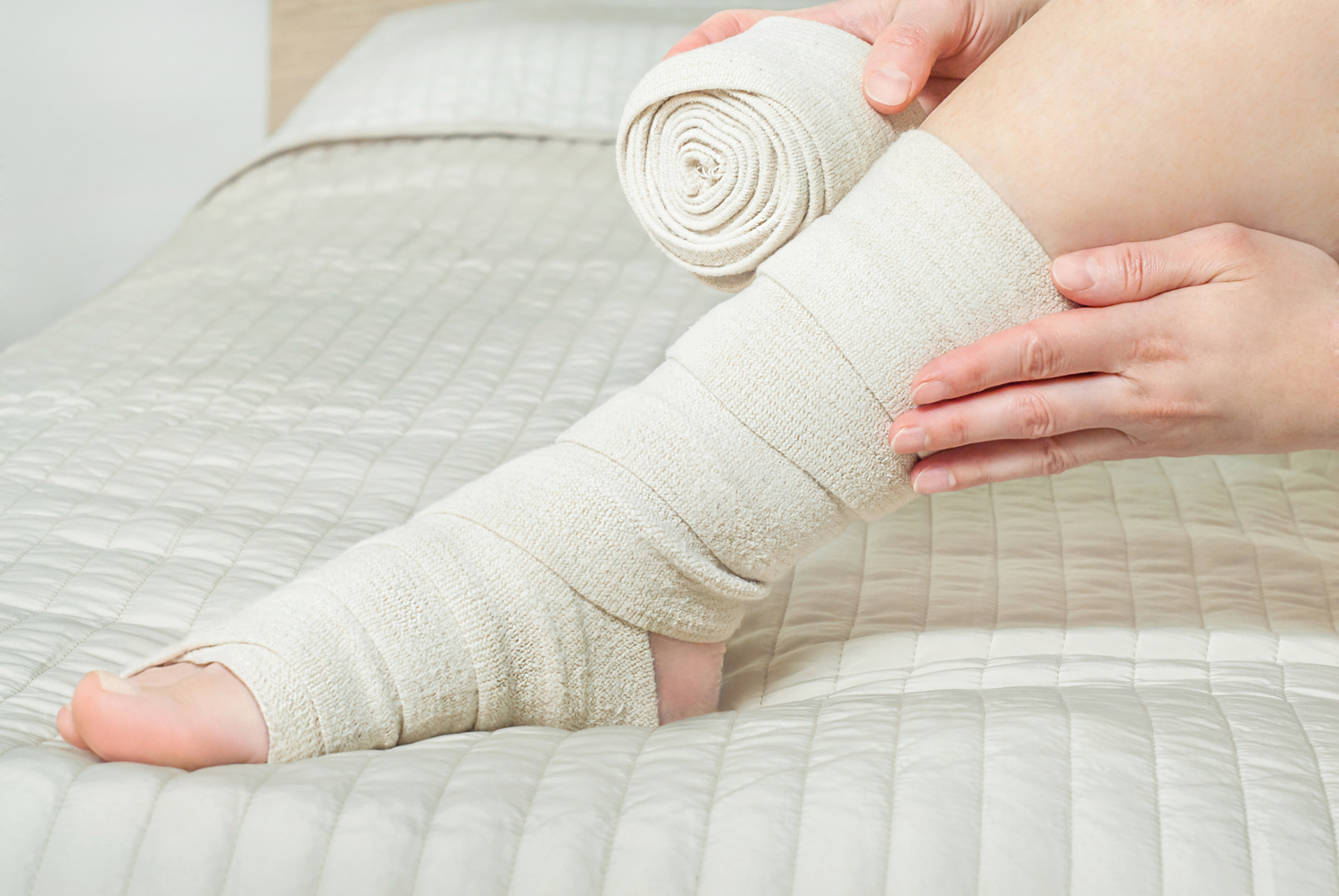
Use of compression stockings: Graduated compression stockings support vein function, reduce swelling, and promote healthy blood flow. Proper fitting and wearing as advised by your healthcare provider are crucial.
Adopting Healthy Lifestyle Changes
Quitting smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels and increases clotting risk. Cessation significantly lowers the chance of recurrent thrombosis.
Weight management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces pressure on veins and minimizes clot risk.
Dietary considerations: Reducing salt intake helps control swelling. Incorporating nutrient-rich foods and staying hydrated support vascular health.
Regular physical activity: Consistent, moderate exercise enhances circulation and overall cardiovascular health, decreasing DVT risk.
Natural Remedies and Supplements
While medical treatments are primary, some natural remedies may support blood circulation and reduce clot formation risk. These include:
Ginger: Known for its anti-inflammatory and blood-thinning properties.
Turmeric: Contains curcumin, which has anticoagulant effects.
Omega-3 fatty acids: Found in fish oil supplements, support vascular health.
Cayenne pepper: Contains capsaicin, which may improve blood flow.
Before incorporating these remedies, consult your healthcare provider, especially if you're on anticoagulants, to avoid potential interactions.
In conclusion, managing and preventing venous clots at home requires a combination of medication adherence, lifestyle modifications, safety precautions, and natural support strategies. Regular consultation with healthcare professionals is essential to tailor treatments to individual needs, monitor progress, and prevent further complications. By remaining vigilant and proactive, individuals at risk can effectively control their condition and maintain a good quality of life.