Comprehensive Guide to Managing and Treating Psoriasis Effectively
Discover comprehensive strategies for managing and treating psoriasis effectively. Explore topical therapies, systemic medications, light-based treatments, and natural remedies. Learn how personalized treatment plans and lifestyle adjustments can help control symptoms, prevent complications, and improve quality of life for psoriasis patients.

Comprehensive Strategies for Managing and Treating Psoriasis Effectively
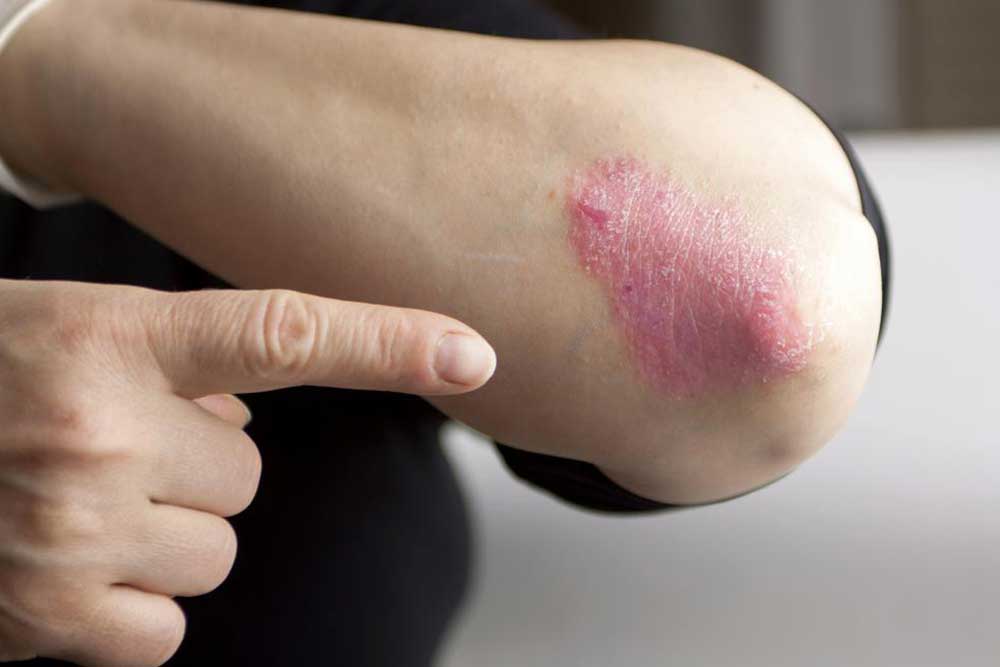
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin condition characterized by rapid skin cell growth, leading to the formation of thick, scaly patches known as plaques. While there is currently no cure for this persistent skin disorder, a variety of treatment approaches can help manage its symptoms effectively and improve the quality of life for those affected. Understanding the available options, including topical therapies, systemic medications, light-based treatments, and natural remedies, is essential for developing a personalized treatment plan that suits individual needs and severity levels.
Psoriasis can sometimes lead to more serious complications, such as psoriatic arthritis, which affects joints and causes inflammation, pain, and stiffness. Proper disease management not only alleviates skin symptoms but also minimizes the risk of associated joint problems. Patients should work closely with healthcare providers to monitor their condition, adjust treatments as needed, and prevent potential complications.
Topical Treatments: Your First Line of Defense
Topical therapies remain the cornerstone of psoriasis treatment, especially for mild to moderate cases. These are applied directly to the skin and aim to reduce inflammation, slow down skin cell proliferation, and remove scales. Salicylic acid is a commonly used keratolytic agent that helps soften and shed psoriatic plaques, making other topical treatments more effective. However, excessive use of salicylic acid can sometimes cause skin irritation or contact dermatitis, so it’s important to follow medical guidance.
Corticosteroid creams are widely prescribed for their potent anti-inflammatory effects. They can rapidly reduce redness, swelling, and itching but must be used judiciously to avoid side effects such as skin thinning, stretch marks, or delayed wound healing. Combining corticosteroids with vitamin D analogs, such as calcipotriene, can enhance therapeutic outcomes and help control symptoms more effectively.
Another topical agent, coal tar ointments, have been used for decades to slow keratinocyte proliferation and reduce scaling. While effective, they can sometimes cause follicular skin pimples and have a strong odor, which might limit their use. Natural topical remedies like moisturizers infused with plant extracts can also help improve skin hydration and barrier function, contributing to symptom relief.
Systemic Medications: For Severe and Persistent Cases
When psoriasis becomes extensive or resistant to topical therapies, systemic medications are often required. These drugs are taken orally or via injections and work throughout the body to modulate immune responses and control disease activity. Retinoids, such as acitretin, influence skin cell turnover and can be particularly helpful for severe psoriasis or pustular forms.
Biologic therapies have revolutionized psoriasis treatment by targeting specific immune pathways involved in disease pathogenesis. Drugs like Enbrel (etanercept), Humira (adalimumab), and Otezla (apremilast) are biologics that inhibit inflammatory cytokines, leading to significant improvement in skin lesions. These treatments are generally reserved for patients who do not respond to or cannot tolerate other therapies and require regular monitoring for potential side effects, including increased risk of infections.
Other systemic options include methotrexate and cyclosporine, which suppress immune function but necessitate careful dose management and monitoring due to their potential toxicity.
Phototherapy: A Safer, Targeted Light Treatment
Phototherapy involves exposing affected skin to controlled doses of ultraviolet (UV) light, primarily UVB, to reduce inflammation and slow skin cell growth. Narrow Band UVB therapy is considered one of the safest and most effective options, especially for moderate to severe psoriasis. It has fewer side effects compared to older UV treatments and can be administered in a dermatologist’s clinic over several sessions.
Light therapy can be combined with topical treatments or used as a standalone approach, offering significant symptom relief and reducing reliance on systemic medications. However, it requires regular visits to a healthcare facility and should be performed under medical supervision to minimize risks such as premature skin aging or potential carcinogenic effects.
Natural Remedies and Lifestyle Adjustments
Many patients seek natural ways to complement their medical treatments and enhance symptom management. Sunlight exposure can help mitigate psoriasis symptoms, as UV rays possess anti-inflammatory properties. Natural sunlight increases vitamin D synthesis, which may help regulate immune responses involved in psoriasis.
Ocean water, rich in minerals like magnesium, has been reported to soothe inflamed skin and improve overall skin health in psoriasis patients. Regular exposure to sea water, such as in seaside environments, can serve as an affordable adjunct therapy.
Proper skin hydration through daily moisturizing, avoiding skin irritants, and managing stress are vital lifestyle measures. Healthy dietary habits, including anti-inflammatory foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, may also contribute to symptom improvement.
It’s essential to have ongoing medical supervision when integrating natural remedies to ensure safety and effectiveness. Combining conventional treatments with lifestyle changes can provide a comprehensive approach to managing psoriasis.
Monitoring and Long-term Management
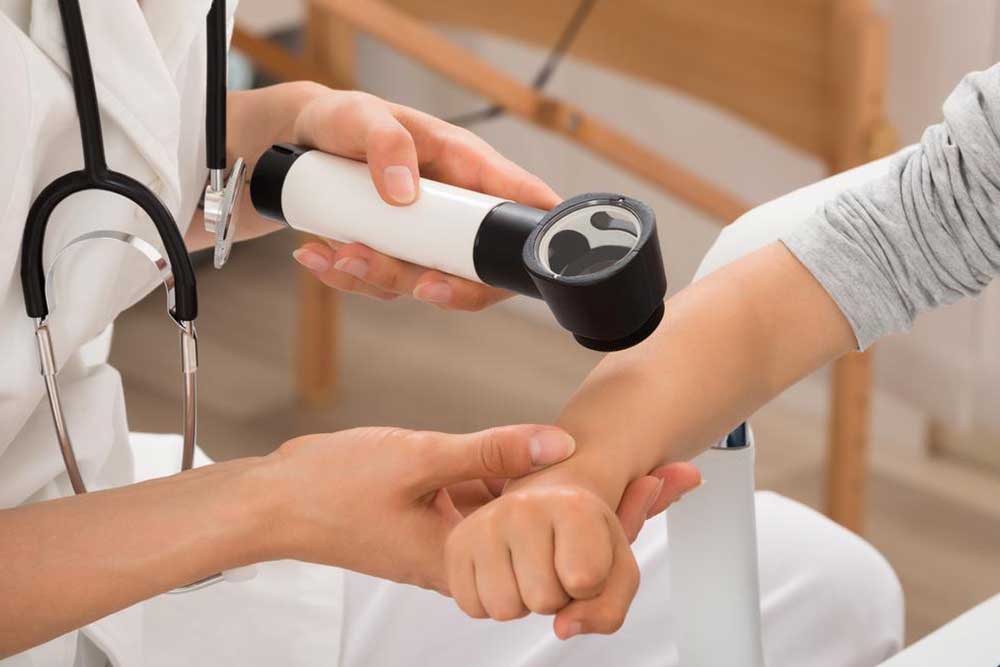
Since psoriasis is a chronic condition, long-term management and regular medical follow-ups are crucial. Patients should be vigilant about monitoring their skin and joint health, reporting any new symptoms or side effects. Blood tests and other assessments might be needed periodically, especially when using systemic medications with potential toxicity.
Emerging therapies and ongoing research continue to expand the options available for psoriasis management. Innovations in biologics, small molecule inhibitors, and personalized medicine aim to improve efficacy while minimizing risks. Patients are encouraged to stay informed and engage actively with their healthcare teams to optimize treatment strategies and enhance their quality of life.