Comprehensive Guide to Cellulitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention Strategies
Cellulitis is a bacterial skin infection that can become severe if not treated promptly. This comprehensive guide covers its causes, symptoms, risk factors, and prevention strategies. Recognizing early signs like redness, swelling, and pain can help prevent serious complications. Learn how bacteria invade through skin breaks and the best practices for timely treatment, especially for at-risk groups. Understanding this condition helps in effective management and skin health maintenance to avoid long-term issues or systemic infections.
Comprehensive Guide to Cellulitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention Strategies
Cellulitis is a common bacterial skin infection that can escalate to serious health complications if not diagnosed and treated promptly. Understanding this condition, including its causes, clinical signs, risk factors, and preventative measures, is essential for maintaining skin health and preventing further medical issues. In this detailed guide, we explore what cellulitis is, the bacteria responsible, how it develops, how to recognize its symptoms early, and steps you can take to minimize risk and seek timely treatment.
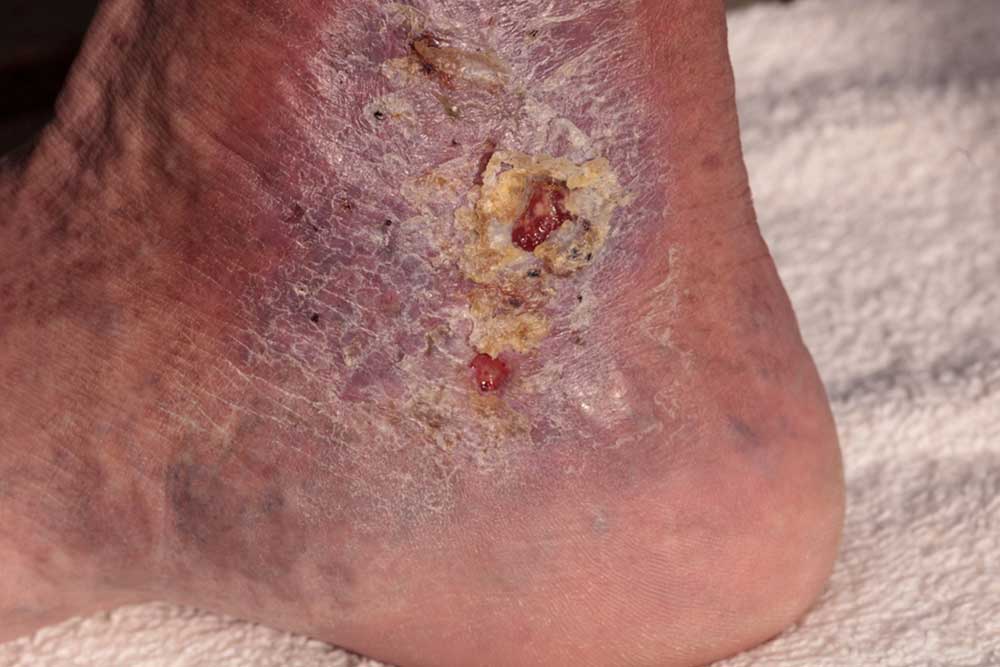
Cellulitis is an infection involving the deeper layers of the skin and the subcutaneous tissues. The skin, serving as the body’s first defense barrier, can become compromised through cuts, wounds, or skin breaking conditions, paving the way for bacteria to enter. Once bacteria breach the skin barrier, they can multiply rapidly, leading to inflammation, redness, and swelling. While the infection commonly appears on the lower extremities, especially the legs, it can also affect the face and arms, making it a concern for a wide demographic.
At the core of cellulitis are bacteria, with Streptococcus and Staphylococcus species, particularly methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), being the primary culprits. These bacteria are normally present on the skin or in the environment but do not cause problems until they enter through a break in the skin. Risk factors significantly increasing the likelihood of developing cellulitis include recent injuries such as cuts, puncture wounds, or surgical incisions. Chronic skin conditions like athlete's foot, dermatitis, or ulcers can also serve as entry points for bacteria. Additionally, immune suppression, diabetes, and poor hygiene can compound the risk.
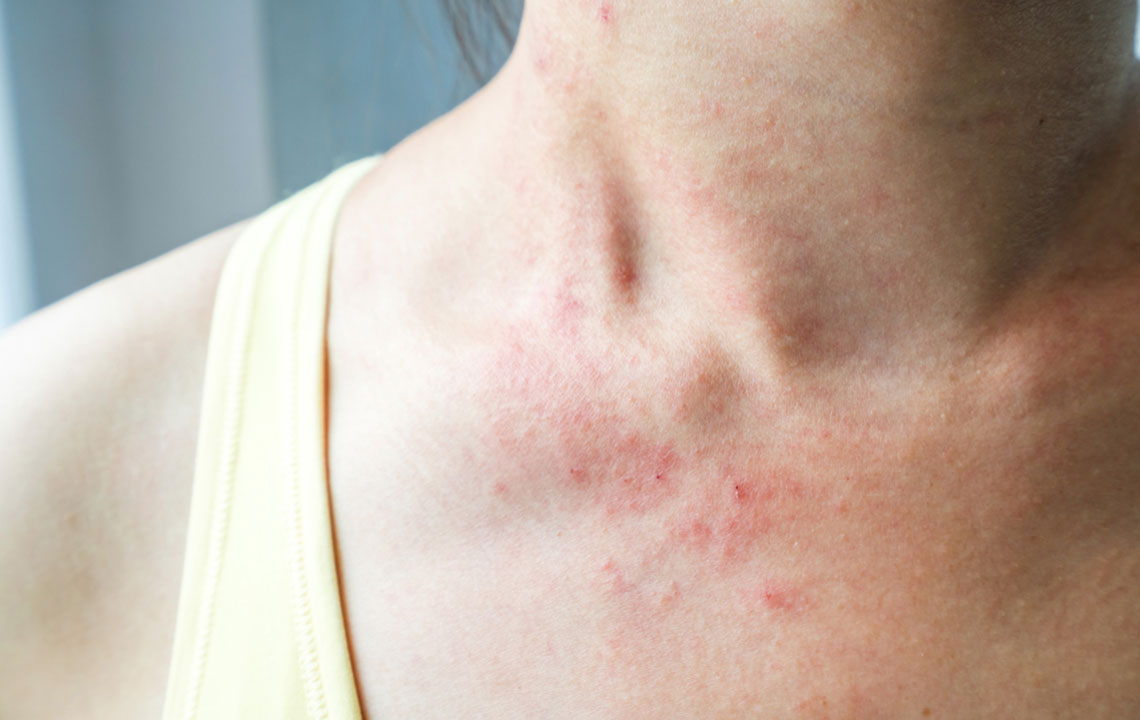
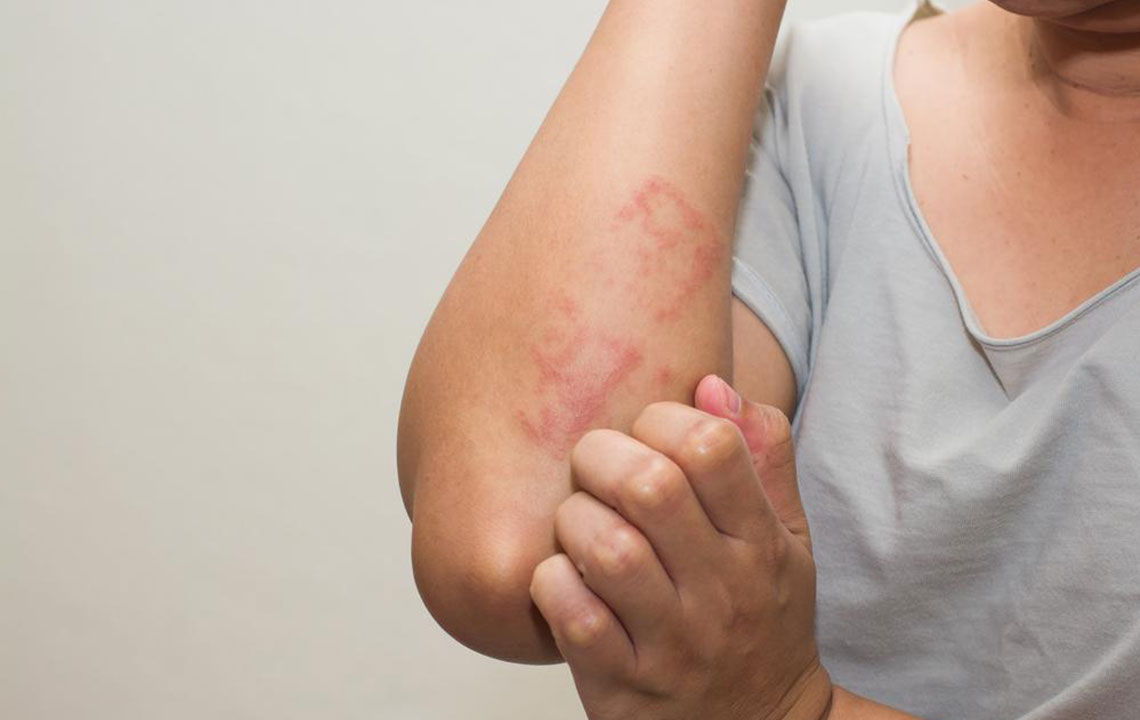
The development of cellulitis begins when bacteria invade areas of the skin that are dry, flaky, or inflamed. The symptoms often start subtly but can rapidly escalate. Typically, the affected area becomes visibly red, warm to touch, swollen, tender, and painful. The redness tends to expand over time, forming irregular borders around the infection site. Accompanying symptoms might include fever, chills, malaise, and general discomfort, indicating systemic involvement. Sometimes, blistering or skin dimpling occurs, signaling more severe skin involvement. If untreated, the infection can spread to deeper tissues or enter the bloodstream, leading to serious complications such as sepsis.
Quick recognition of cellulitis symptoms is essential for effective management. Early intervention with antibiotics can prevent the infection’s progression and reduce the risk of chronic swelling or tissue damage. Medical professionals may prescribe oral or intravenous antibiotics depending on the severity. Supporting treatments include elevating the affected limb, maintaining skin hygiene, and monitoring for signs of spreading infection or worsening symptoms. Preventative measures involve good wound care, skin protection, managing underlying health conditions, and avoiding known risk factors such as animal bites and skin injuries in vulnerable individuals.
In summary, cellulitis is a potentially serious bacterial skin infection that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment. Recognizing early signs like redness, swelling, and pain can lead to faster medical intervention, preventing more complicated and chronic skin issues. Maintaining good skin hygiene, protecting cuts and wounds, and seeking medical care when symptoms develop are crucial steps in managing risk and ensuring skin health. Although common, cellulitis should not be underestimated, especially in high-risk populations such as diabetics, immunosuppressed individuals, and those with skin conditions. With proper care, most cases recover fully without long-term effects.