Comprehensive Guide to Cellulitis: Causes, Symptoms, Prevention, and Treatment Strategies
This comprehensive guide explores cellulitis, a bacterial skin infection affecting the deeper skin layers. It covers causes, common symptoms, risk factors, prevention tips, and treatment options to help individuals recognize and manage this condition effectively. Early intervention and good hygiene are key to avoiding serious complications, especially for vulnerable groups like the elderly and immunocompromised individuals.
Comprehensive Guide to Cellulitis: Causes, Symptoms, Prevention, and Treatment Strategies
Cellulitis is a common, often serious bacterial skin infection that penetrates beneath the surface of the skin, affecting the deeper layers such as the dermis and subcutaneous tissue. If left untreated, cellulitis can lead to severe health complications, including systemic infections that may jeopardize life. Recognizing the symptoms early and understanding the causes are crucial steps towards effective management and prevention of this condition. In this detailed guide, we explore what cellulitis is, its typical signs and symptoms, risk factors, preventive measures, and treatment options to help individuals protect their health.
Cellulitis can manifest anywhere on the body but is most commonly observed on the face, legs, and neck. It typically begins with a break in the skin—such as a cut, crack, or bite—that allows bacteria to invade. The infection can spread rapidly, making quick and appropriate intervention important. As the population ages, and with the increased prevalence of weakened immune systems, the incidence of cellulitis continues to rise globally, affecting millions each year. Recognizing the vulnerable groups, understanding the symptoms, and adopting effective prevention strategies are essential for controlling this infection.
What are the Common Symptoms of Cellulitis?
Understanding the signs of cellulitis is vital for early detection and treatment. Typical symptoms include:
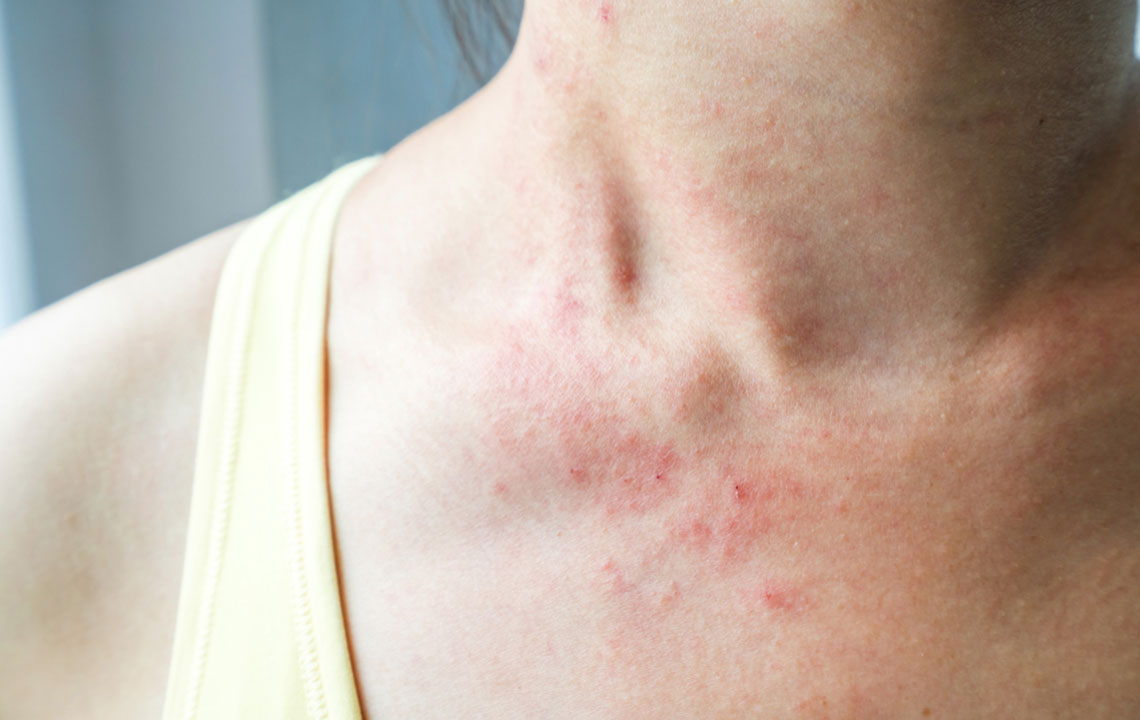
Intense redness that gradually spreads across the skin surface
Swelling and tenderness localized to the affected area
Persistent or sharp pain when touched
The affected skin area feels warm or hot to the touch, indicating inflammation
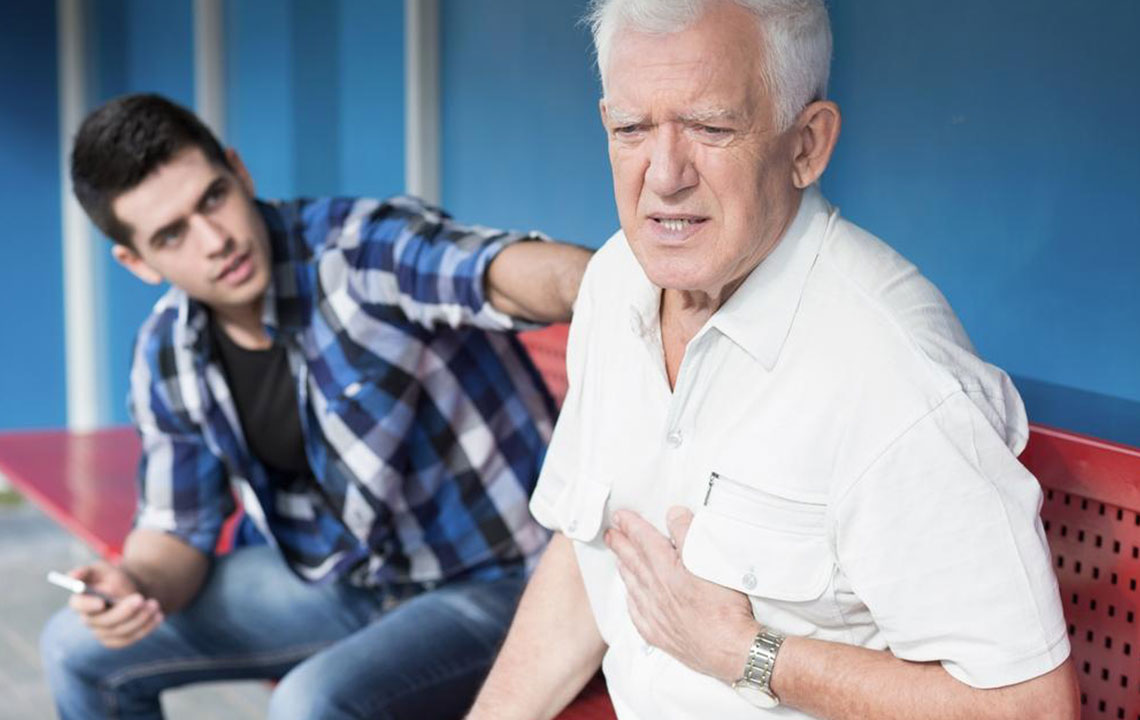
Fever or chills may accompany the infection in some cases, signaling systemic involvement
In certain cases, red spots, blister formation, or skin dimpling may occur, further indicating the severity of the infection
When Should You Seek Medical Attention?
Prompt medical consultation is necessary when experiencing symptoms such as:
The presence of a fever alongside localized redness and swelling
The redness or swelling is spreading rapidly
The affected area becomes increasingly painful or tender
Signs of systemic illness, including chills, fatigue, or malaise
Ulceration or blisters develop on the skin
Early intervention can significantly reduce complications and improve recovery prospects.
Understanding the Causes of Cellulitis
Cellulitis is most commonly caused by bacterial infections, primarily involving species such as streptococcus and staphylococcus, including resistant strains like MRSA (Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus). The bacteria typically gain entry through breaks in the skin, such as cuts, abrasions, surgical wounds, animal bites, or skin fissures. Several factors predispose individuals to develop cellulitis:
Trauma or skin injuries including cuts, burns, or fractures
Existing skin conditions like eczema, athlete’s foot, or dermatitis that compromise skin integrity
Conditions that weaken the immune system, such as HIV/AIDS, diabetes, leukemia, or the use of immunosuppressive medications
Advanced age, which often correlates with drier, more fragile skin and slower healing
Increased exposure to bacteria due to lifestyle or occupational hazards
Risk Factors That Increase Likelihood of Developing Cellulitis
While anyone can develop cellulitis under the right circumstances, certain groups and conditions increase susceptibility:
Individuals with skin injuries, including cuts, abrasions, or insect bites
People with weakened immune defenses due to chronic diseases or medications
Those suffering from pre-existing skin issues like eczema or psoriasis that compromise skin barrier functions
Patients with a history of cellulitis, as they are at higher risk of recurrence
Obese individuals, as excess body weight can impair circulation and immune responses, making infections more likely
Strategies for Preventing Cellulitis
Prevention plays a critical role in reducing the risk of cellulitis. Maintaining good hygiene and taking proactive measures can significantly decrease exposure to bacteria. Essential prevention tips include:
Carefully cleaning any skin injuries daily with gentle washing; avoid harsh scrubbing that could worsen skin breakage
Applying topical ointments such as Vaseline, Polysporin, or antibiotic creams on minor cuts and abrasions to create a protective barrier against bacteria
Monitoring skin for early signs of redness, swelling, or pain, and seeking medical advice promptly if symptoms arise
Inspecting your feet regularly for signs of injury or infection, especially if you have diabetes or circulatory issues
Keeping the skin moisturized with suitable skincare products to prevent dryness and cracking that can facilitate bacterial entry
Avoiding aggressive or unnecessary cutting of surrounding skin or nails to prevent skin tears and injuries
Wearing protective footwear and gloves in environments where injury risk is high
Treating superficial skin infections aggressively and early to prevent them from worsening into cellulitis
Effective Treatment Options for Cellulitis
When diagnosed early, cellulitis can be effectively treated with antibiotics, either orally or intravenously, depending on the severity of the infection. Treatment strategies involve:
Administering appropriate antibiotics to eliminate the bacterial infection, with choices guided by bacterial culture results when available
Maintaining hydration and rest to support the immune system during recovery
In severe cases, hospitalization may be required for intravenous antibiotics and close monitoring
Manual measures like elevating the affected limb can reduce swelling
Managing associated symptoms such as fever with over-the-counter medications under medical supervision
Complications and When to Seek Urgent Medical Care
If cellulitis is untreated or improperly managed, it can lead to serious complications such as abscess formation, blood infections (sepsis), or spread to lymph nodes and deeper tissues. In critical situations, urgent medical attention is necessary, especially if:
The redness and swelling worsen despite initial treatment
The patient develops a high fever, chills, or severe malaise
Blisters, skin ulceration, or necrosis appears
Signs of systemic infection emerge, such as rapid heartbeat or confusion
Timely medical intervention can prevent these severe outcomes and promote full recovery. Therefore, awareness and prompt care are key to managing cellulitis effectively.
Summary
Cellulitis is a potentially serious bacterial skin infection that can affect anyone but is especially common among those with skin injuries, compromised immune systems, or underlying health conditions. Recognizing early symptoms, seeking prompt medical attention, and adhering to preventive measures are crucial steps in combating this infection. With proper hygiene, timely treatment, and risk management, most cases of cellulitis can be successfully resolved, preventing complications and ensuring skin integrity is maintained.