Comprehensive Guide to Cellulitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Types You Need to Know
Cellulitis is a widespread bacterial skin infection that can affect any part of the body, leading to redness, swelling, and tenderness. If not treated promptly, it can result in serious health complications. This comprehensive guide covers the causes, symptoms, and different types of cellulitis, emphasizing the importance of early diagnosis and effective treatment. Recognizing signs early, understanding risk factors, and seeking immediate medical care can prevent severe outcomes, especially in vulnerable populations. Stay informed to protect your health from this potentially dangerous condition.
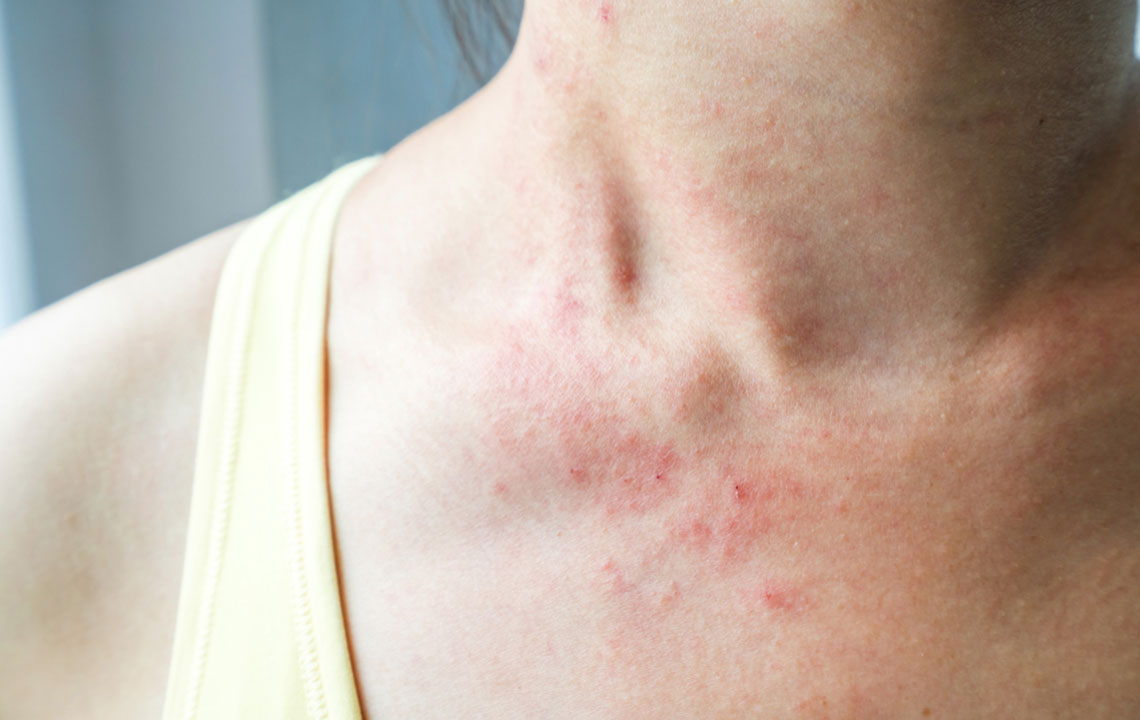
Understanding Cellulitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Types
Cellulitis is a common but serious bacterial skin infection that can affect anyone at any age. It occurs when pathogenic bacteria penetrate the skin through cuts, bites, or other skin injuries, causing infection in the dermis and subcutaneous tissues beneath. If left untreated, cellulitis can lead to severe complications, including the spread of infection to the bloodstream or lymphatic system. Recognizing the early signs of cellulitis and understanding its causes are crucial for timely treatment and preventing complications.
Cellulitis is mainly caused by bacteria such as Streptococcus pyogenes and Staphylococcus aureus, including methicillin-resistant strains (MRSA). Fungi may sometimes cause similar skin infections, but bacterial infections are far more common. The condition develops when the skin’s protective barrier is compromised, allowing bacteria to invade underlying tissues. This can happen through various means, including cuts, surgical wounds, insect bites, or existing skin conditions like eczema and dermatitis, which weaken the skin’s integrity.
Symptoms of cellulitis typically include localized redness, swelling, warmth, and tenderness in the affected area. The skin usually appears inflamed with a sharp border separating infected and healthy tissue. There may be the formation of blisters, skin spots, or streaks extending from the primary infection site. As the infection progresses, systemic symptoms such as fever, chills, fatigue, and malaise can develop, indicating more severe or spreading infection. Immediate medical attention is essential if cellulitis is suspected, especially in vulnerable populations such as the elderly, immunocompromised, or those with pre-existing health conditions.
Types of Cellulitis and Their Characteristics
Cellulitis can manifest in various parts of the body, each with distinct features and considerations for treatment:
Extremity Cellulitis: This is the most common form, affecting the arms, legs, and hands. It often results from cuts, abrasions, or insect bites. Symptoms include swelling, redness, warmth, and tenderness localized to the affected limb. Treatment usually involves oral antibiotics, though severe cases might require hospitalization and intravenous antibiotics.
Facial Cellulitis: Involving the facial area, particularly around the lips and tongue, facial cellulitis can sometimes be associated with dental infections or skin trauma. It often presents with facial swelling, redness, tenderness, and sometimes fever. Due to proximity to the brain and eyes, this form requires prompt medical evaluation to prevent complications such as orbital cellulitis or meningitis.
Periorbital Cellulitis: This infection affects the tissues around the eyes and is particularly common among children and infants. Symptoms include swelling, redness, and tenderness around the eyelids and periorbital area, potentially leading to vision problems if untreated. Emergency care is critical to prevent complications like abscess formation or spread to the brain.
Breast Cellulitis: Usually occurring after breastfeeding or surgical procedures, breast cellulitis causes redness, swelling, warmth, and pain in the breast tissue. It may also spread to adjacent areas and often presents with fever and fatigue. Prompt antibiotic therapy and sometimes drainage are necessary for recovery.
Perianal Cellulitis: This form primarily affects children, especially males, causing pain and swelling around the anal area. Symptoms include difficulty in bowel movements, pain, and sometimes bleeding or blood in the stool. Maintaining good hygiene and timely treatment are vital in managing the condition.
Understanding the various types of cellulitis and their specific symptoms helps in timely diagnosis and effective treatment. If you experience signs of cellulitis, especially in high-risk areas like the face or around the eyes, seek medical care immediately. Untreated cellulitis can lead to severe complications, including abscess formation, tissue necrosis, or far-reaching infections affecting vital organs. Preventative measures such as proper skin care, wound hygiene, and managing underlying health issues play a crucial role in reducing the risk of developing cellulitis.
In the modern medical landscape, advances in diagnostic techniques, antibiotics, and supportive care have significantly improved the outcomes for cellulitis patients. Early intervention remains the key to preventing complications, reducing hospital stays, and ensuring a swift recovery. Moreover, ongoing research continues to explore more effective treatments and preventive strategies, highlighting the importance of awareness and prompt medical consultation for anyone experiencing symptoms of this infection.