Detailed Overview of Pneumonia: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatment Methods
This comprehensive guide provides an in-depth understanding of pneumonia, exploring its causes, symptoms, and the most effective treatment strategies. Learn how early diagnosis and proper care can help prevent complications and promote recovery, emphasizing preventive measures like vaccination and lifestyle changes to reduce risk. Essential for those seeking thorough health information on respiratory infections, this article covers all aspects of pneumonia management for better health outcomes.

Detailed Overview of Pneumonia: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatment Methods
Pneumonia is a common but potentially serious respiratory condition characterized by inflammation in the lungs’ alveoli—the tiny air sacs where oxygen exchange occurs. This inflammation results from infections caused by various microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Among bacterial causes, Streptococcus pneumoniae stands out as one of the most prevalent pathogens responsible for bacterial pneumonia. If untreated, even mild respiratory symptoms such as a persistent cough or cold can escalate into full-blown pneumonia, especially in individuals with weakened immune defenses.
Understanding the Primary Causes of Pneumonia Pneumonia develops due to inflammation and infection of the lungs' air spaces. The infection can stem from different infectious agents, which leads to categorizing pneumonia into several types based on its cause. These classifications include bacterial pneumonia, viral pneumonia, atypical pneumonia such as Mycoplasma pneumoniae, and other less common variants like fungal pneumonia or aspiration pneumonia caused by inhaling foreign substances. The mechanisms vary depending on the causative agent, but all trigger an immune response leading to the symptoms associated with pneumonia.
Distinguishing Symptoms of Pneumonia Recognizing pneumonia early is vital for effective treatment and minimizing complications. While some symptoms are mild initially, the disease can exacerbate quickly without prompt medical attention. Key symptoms include persistent coughing that may produce mucus or phlegm, fatigue, and general weakness. Fever typically presents as high and is often accompanied by chills lasting several days. In children, respiratory distress presents as shortness of breath, while adults might experience chest pain, especially during breathing or coughing. Other common signs include a loss of appetite, bluish discoloration of fingertips—a sign of oxygen deficiency—sleep disturbances, recurrent headaches, and occasionally blood in cough due to severe coughing or tissue damage.
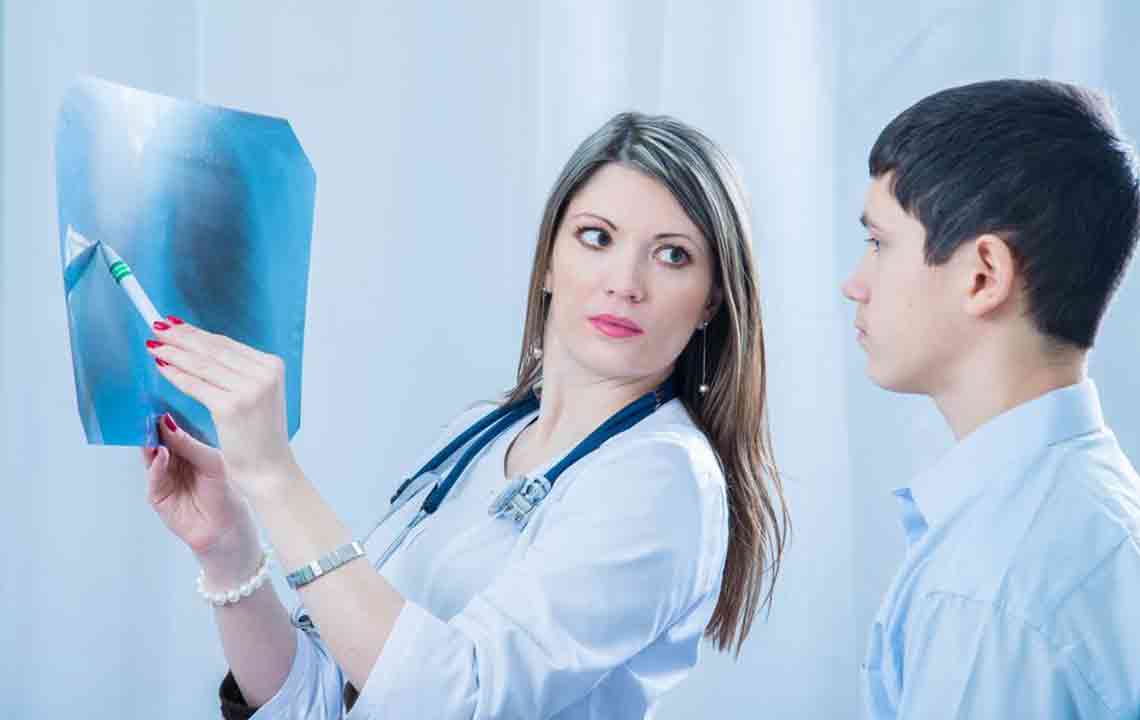
Effective Strategies for Treating Pneumonia Managing pneumonia requires a comprehensive approach combining medication, supportive care, and lifestyle adjustments. Antibiotics are the cornerstone of bacterial pneumonia treatment, and their timely administration can significantly reduce severity and duration. Vaccines, such as pneumococcal and influenza vaccines, are essential preventive tools that can protect at-risk populations from certain types of pneumonia. Early diagnosis relies on medical tests including blood work, chest X-rays, and sputum analysis, which help determine the causative pathogen and guide treatment decisions. Primary goals of therapy include eradicating the infection, alleviating symptoms, and preventing complications. Full recovery can span several weeks, with fatigue sometimes persisting up to a month post-treatment.
Depending on the severity and type of pneumonia, treatment plans typically involve:
Ensuring adequate hydration by drinking plenty of fluids to loosen mucus and prevent dehydration
Completing the entire course of prescribed antibiotics, even if symptoms improve early
Getting sufficient rest to support immune recovery and overall healing
It’s crucial to seek medical attention promptly if you recognize symptoms of pneumonia. Early intervention not only improves recovery outcomes but also reduces the risk of serious complications such as lung abscesses, pleural effusion, or sepsis. Preventive measures, including vaccination and maintaining good hygiene practices, play a vital role in reducing the incidence of pneumonia. Lifestyle adjustments like quitting smoking and managing chronic conditions further enhance resistance to respiratory infections.