Comprehensive Guide to Atopic Dermatitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Management Strategies
This comprehensive guide provides in-depth information on atopic dermatitis, covering its causes, symptoms, and effective management strategies. It highlights the importance of identifying triggers, maintaining skin health through proper moisturizing, and seeking professional medical advice to manage flare-ups. The article emphasizes lifestyle modifications, medication options, and preventive measures that can improve quality of life for affected individuals. Suitable for those seeking a thorough understanding of eczema, this guide offers valuable insights into controlling and managing this chronic skin condition effectively.
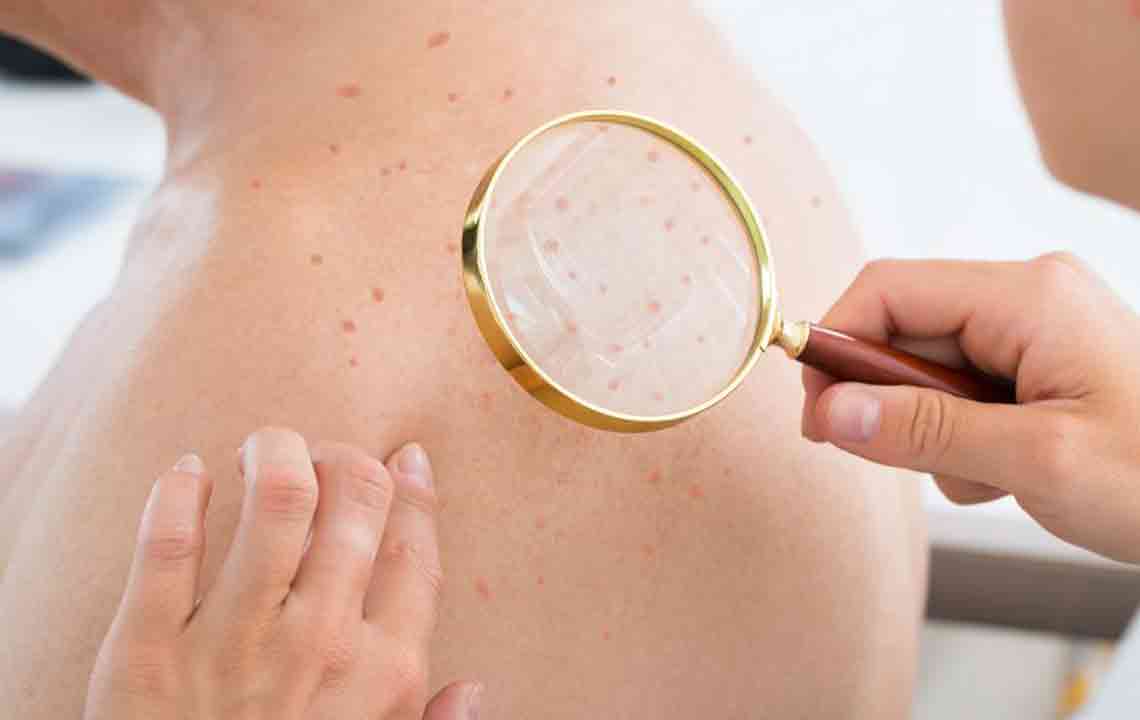
Comprehensive Guide to Atopic Dermatitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Management Strategies
Atopic dermatitis, widely recognized as eczema, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that affects millions worldwide. Characterized by persistent redness, dryness, and severe itching, this skin disorder can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. While it is most commonly observed in children, many adults also experience symptoms during different stages of life. Despite extensive research, the exact underlying cause of atopic dermatitis remains elusive. Nonetheless, scientists agree that it results from a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune system factors.
The disorder is marked by a compromised skin barrier—the natural protective layer that helps retain moisture and shield against external irritants and pathogens. When this barrier is disrupted, the skin becomes dry, sensitive, and highly reactive to various triggers. This causes episodes of flare-ups, characterized by intense itching, inflammation, and lesions that can sometimes lead to secondary infections. Atopic dermatitis is often part of a broader spectrum of allergic conditions, including hay fever (allergic rhinitis), asthma, and food allergies, suggesting a shared genetic predisposition and immune dysregulation.
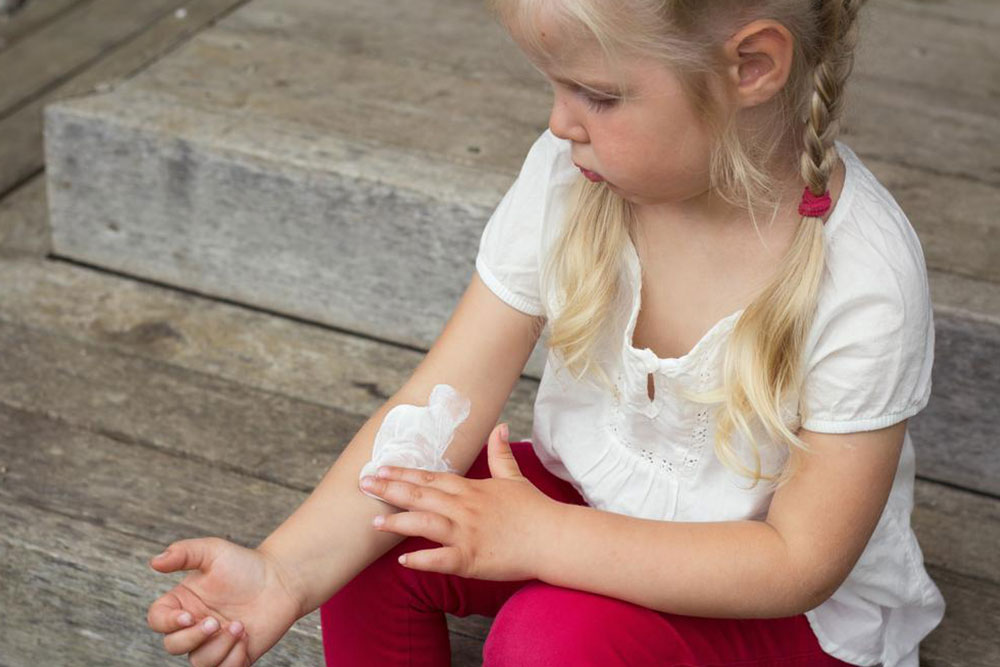
Identifying and managing triggers play a vital role in controlling eczema. Maintaining healthy skin with proper moisture retention helps prevent irritant penetration and infection. In individuals with atopic dermatitis, the skin’s ability to hold moisture diminishes, leading to dryness and increased vulnerability to environmental and internal factors.
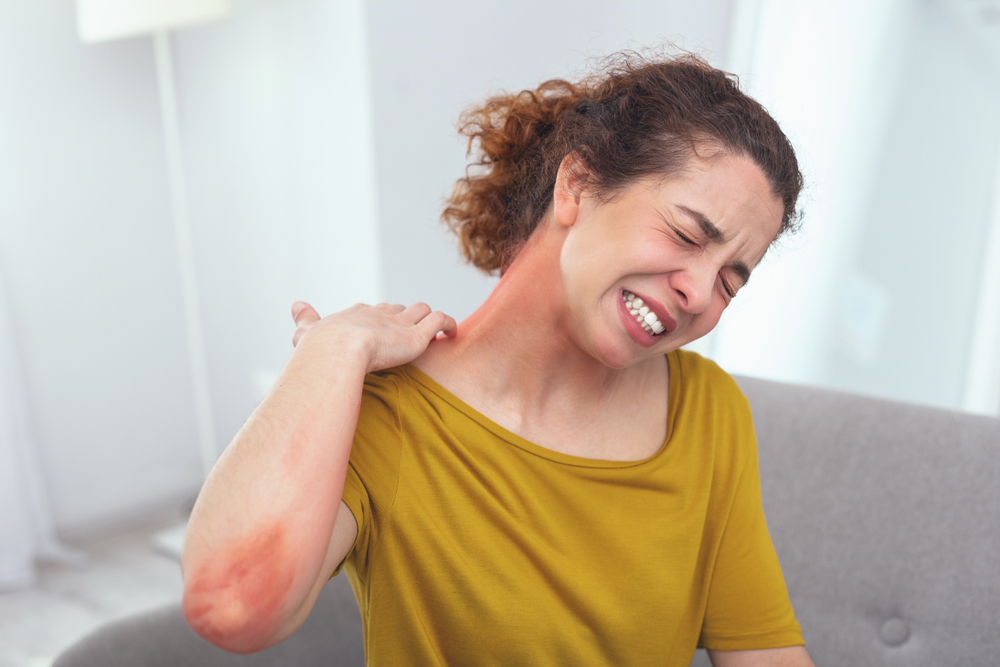
Typical symptoms of atopic dermatitis begin with dry, itchy patches that often appear on specific areas of the body. These patches can become inflamed, resulting in redness, swelling, and sometimes blistering or oozing. The pattern of symptoms varies among individuals and fluctuates over time, with episodes of exacerbation and remission. Mild cases often involve localized patches that respond well to topical treatments, while severe cases may cover large areas, cause intense discomfort, and require more aggressive therapy.
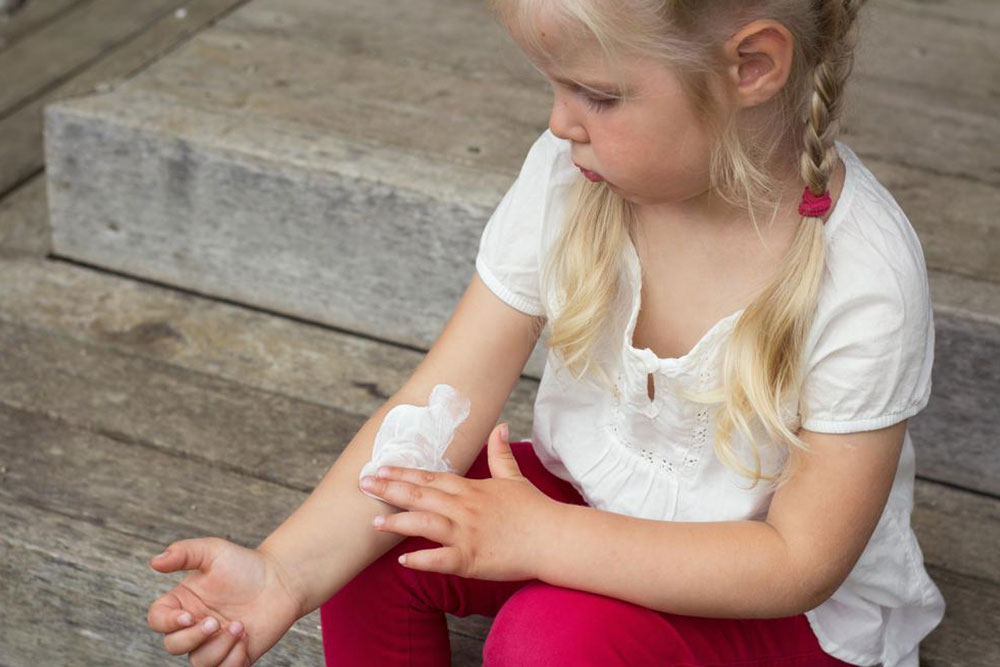
The distribution of eczema varies with age. Infants generally develop rashes on the cheeks, scalp, and the back of their elbows. Children tend to experience rashes on the legs, knees, wrists, and ankles. In adults, common sites include the neck, inner elbows, and knees. Recognizing these patterns aids in diagnosis and treatment planning.
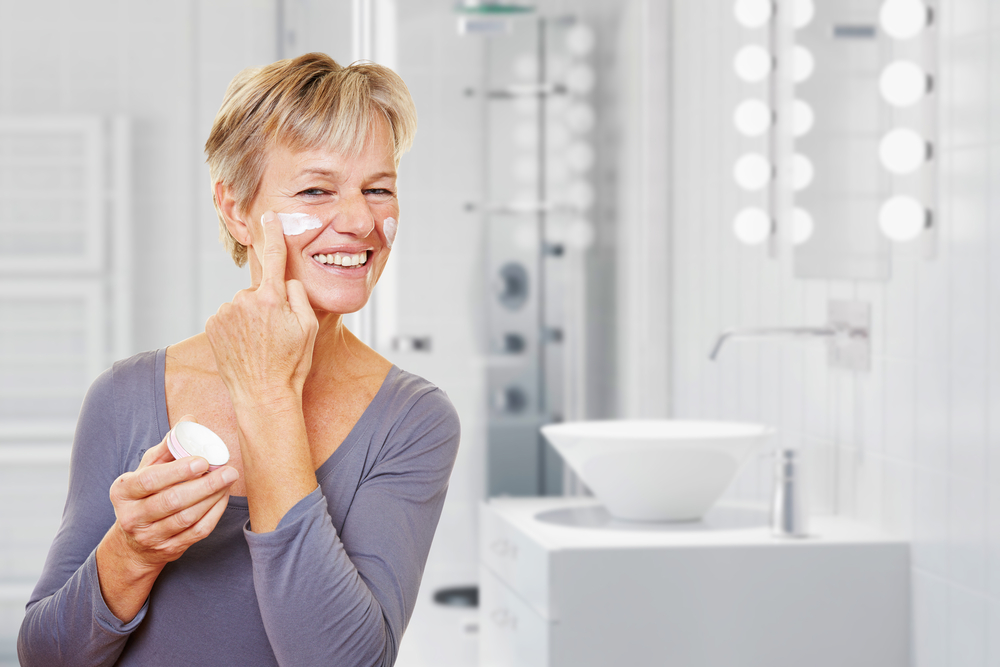
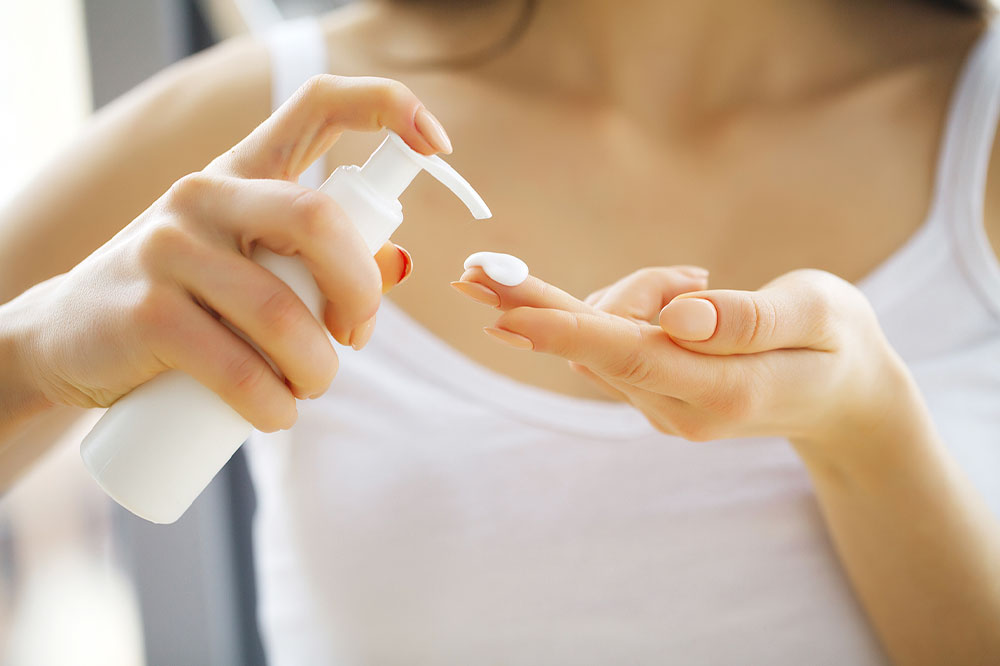
Managing atopic dermatitis comprehensively requires a combination of lifestyle adjustments and medical interventions. Regular application of moisturizers—preferably fragrance-free and barrier-repair formulations—is essential to restore and maintain skin hydration. Anti-itch creams containing corticosteroids or non-steroidal alternatives help reduce inflammation and relieve discomfort. In more severe cases, physicians may prescribe oral medications such as antihistamines to control itching or immunosuppressants for persistent inflammation.
Additional steps include taking warm (not hot) baths to hydrate the skin, using humidifiers to add moisture to indoor air, and avoiding known triggers such as harsh soaps, irritants, and allergens. Patients are encouraged to identify specific food allergies through testing, as certain foods like peanuts, dairy, soy, fish, and wheat can exacerbate symptoms. Stress management techniques, such as mindfulness and relaxation exercises, also play a role in reducing flare-ups.
Consultation with dermatologists is crucial for personalized treatment plans. They can recommend appropriate topical therapies, prescribe effective medications, and suggest lifestyle modifications tailored to individual needs. Early diagnosis and proactive management can significantly improve symptoms, prevent complications, and enhance overall quality of life.
If you notice persistent skin issues such as rashes, persistent itching, or skin thickening, seek medical advice promptly. Early intervention helps prevent secondary infections and facilitates better control over the condition, allowing individuals to lead healthier, more comfortable lives.