Comprehensive Overview of Eczema: Symptoms, Causes, Types, and Effective Treatments
This comprehensive guide explores eczema in detail, covering symptoms, causes, types, and modern treatment options. It emphasizes understanding triggers, proper skin care, and personalized management strategies to improve quality of life for sufferers. Valuable insights help individuals control their condition effectively and reduce flare-ups.

Understanding Eczema: A Detailed Guide to Symptoms, Causes, Variations, and Management Strategies
Eczema is an umbrella term for a diverse group of inflammatory skin conditions that often present with distinctive symptoms such as redness, bumps, dryness, and intense itching. It affects millions worldwide, impacting quality of life and requiring effective management. Recognizing the different types and understanding their unique characteristics is essential for proper treatment and alleviation of discomfort.
This comprehensive guide aims to shed light on eczema’s various forms, underlying causes, typical symptoms, and the most recent and effective treatment options. Armed with this knowledge, individuals suffering from eczema can implement personalized strategies to control flare-ups, prevent complications, and live more comfortably.
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms of Eczema
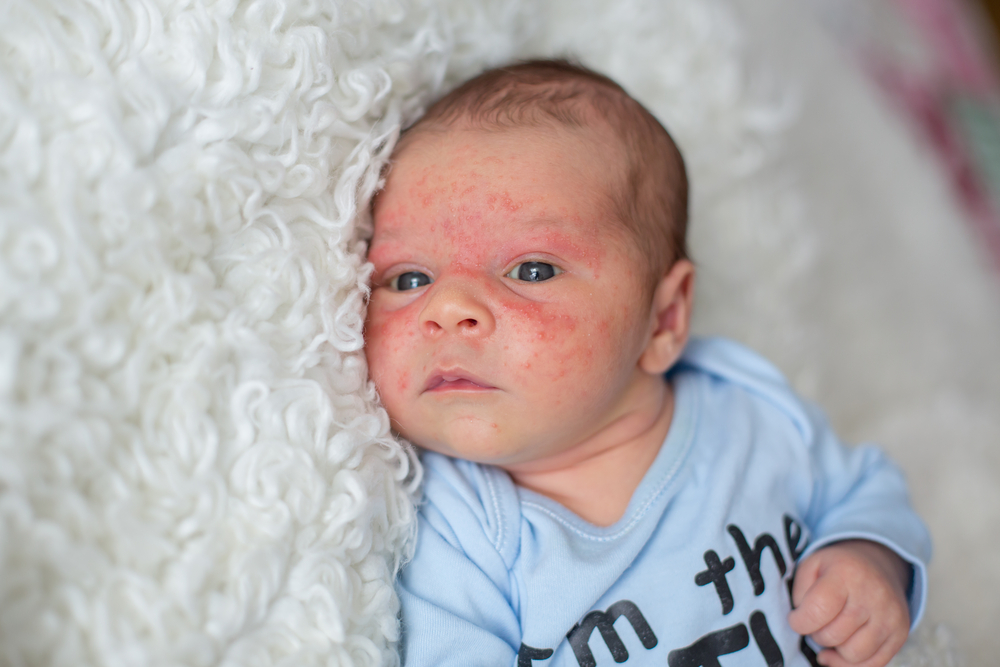
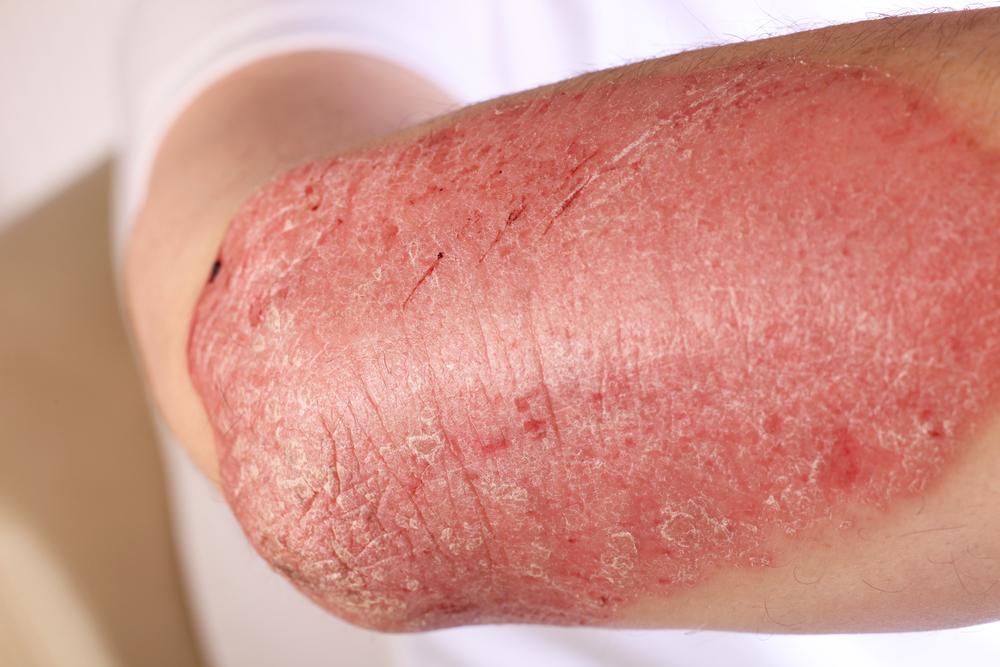
Eczema initially manifests as inflamed, red patches on the skin that can be dry, itchy, and sometimes thickened or scaly. These patches are often itchy, leading to scratching that exacerbates skin irritation and increases the risk of infection. Depending on skin tone, the coloration of affected areas may differ. In lighter skin tones, the rash appears vividly red, whereas in darker skin, it may present as darker or lighter patches.
Other common symptoms include persistent dryness and roughness, darkening of affected skin, leathery or hyperkeratotic patches, and occasionally blistering that may ooze or bleed. The severity varies, and itching can be intense enough to disrupt daily activities or sleep. Excessive scratching may cause cuts or openings in the skin, making it vulnerable to bacterial infections such as impetigo.
Furthermore, flare-ups can be triggered or worsened by environmental irritants, allergens, and irritants like soaps, detergents, fabrics, and extreme weather conditions. While eczema is non-contagious, its symptoms can significantly affect self-esteem and mental health, making effective management crucial.
Understanding the Different Types of Eczema
Atopic Dermatitis: The most common form, often seen in children and individuals with a personal or family history of allergies such as asthma or hay fever. It frequently affects areas like the face, neck, elbows, and behind the knees. Symptoms include persistent itching, dryness, and redness that may become thickened over time.
Stasis Dermatitis: Usually occurs in individuals with circulatory issues, such as chronic venous insufficiency. The skin on the lower legs becomes swollen, reddened, and may develop ulcers or crusting. It is often accompanied by aching or heaviness in the legs.
Scabies (Mite Infestation): Caused by an infestation of mites, scabies presents with intense itching, especially at night, and a rash that mimics eczema but requires specific treatment.
Fungal Dermatitis: Fungal infections, such as those caused by dermatophytes, can resemble eczema and often require laboratory testing (like skin scrapings) to confirm the presence of fungi before treatment.
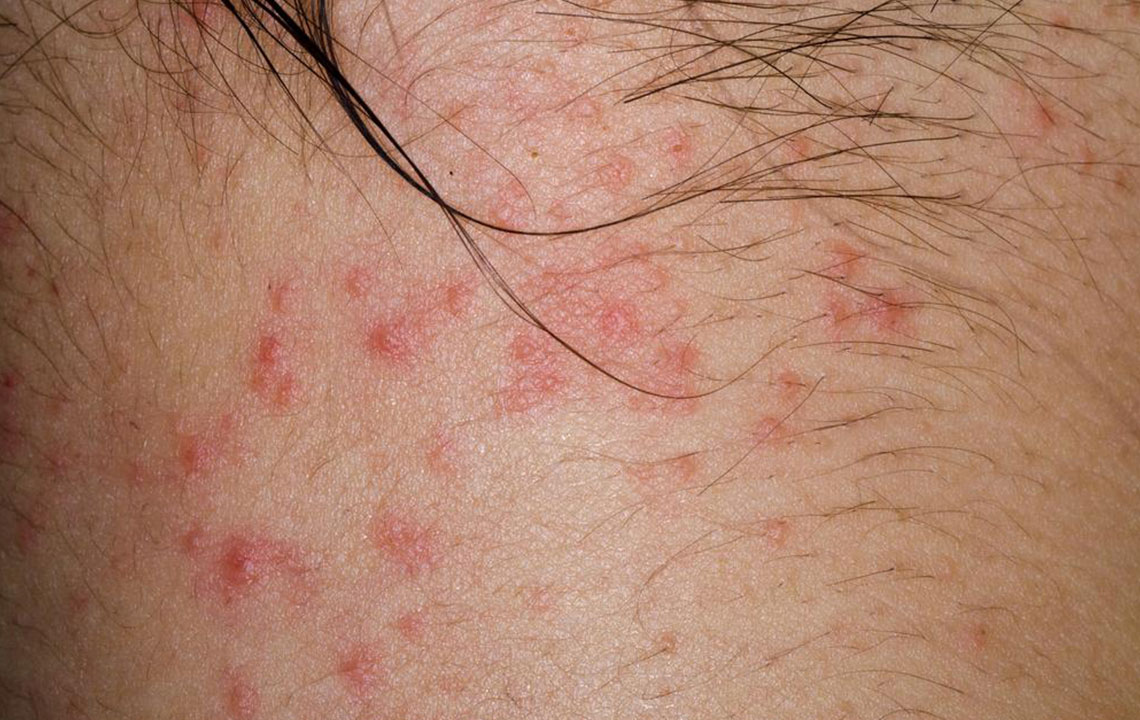
Pompholyx (Dyshidrotic Eczema): Characterized by itchy blisters on palms, soles, or sides of fingers and toes. It often occurs in response to stress, allergies, or humid weather.
Nummular Eczema: Typically affects older adults, presenting as coin-shaped patches that are scaly, inflamed, and sometimes crusted, mainly on the lower legs or arms.
Lichen Simplex Chronicus: Results from persistent scratching or rubbing, leading to thickened, leathery skin, primarily on the neck, wrists, and shins.
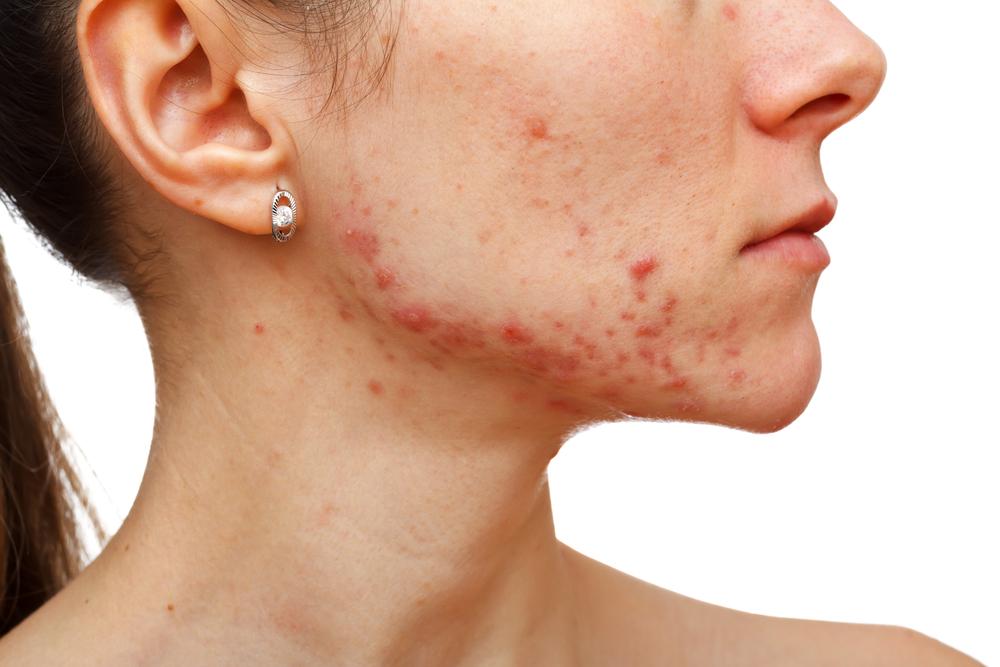
Seborrheic Dermatitis: Affects areas rich in oil glands, like the scalp, face, and chest, causing greasy, flaky patches and dandruff; can be seen in infants as cradle cap.
Xerotic Eczema: Usually occurs in arid or dry climates, leading to cracked, dry skin prone to oozing or bleeding.
Allergic Contact Dermatitis: Develops after skin contact with allergens like certain metals, fragrances, or preservatives, resulting in localized eczema reactions.
Modern Approaches to Managing and Treating Eczema
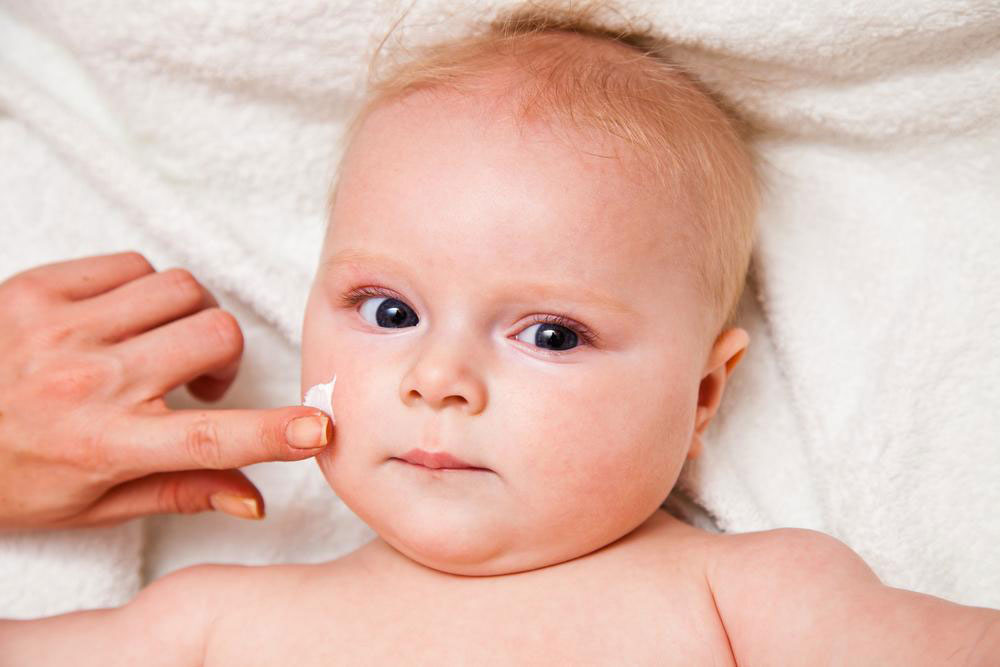
Effective eczema management focuses on minimizing triggers, maintaining skin hydration, and controlling inflammation. The cornerstone of treatment is consistent skin care routines, including gentle cleansing, use of emollients, and avoiding known irritants.
Regularly moisturizing with thick creams or ointments helps restore the skin barrier and prevent dryness and cracking. Topical corticosteroids are often prescribed to reduce inflammation during flare-ups, with potency tailored to severity and affected areas. For infected eczema, physicians may recommend antibiotics or antifungal medications.
In cases where itchy symptoms are severe, antihistamines may be used to provide relief. Additionally, phototherapy (light therapy) can be beneficial for chronic, stubborn cases. Other treatments, such as coal tar applications or immunosuppressive drugs like cyclosporine, are reserved for resistant cases under medical supervision.
Identifying and avoiding triggers are paramount. Common triggers include harsh soaps, synthetic fabrics (like wool), extreme cold or heat, stress, and certain foods. Keeping a diary of flare-ups can help pinpoint personal triggers, enabling more precise management strategies.
Consulting healthcare professionals is essential for personalized treatment planning. Dermatologists can offer tailored advice, prescribe medications, and suggest lifestyle modifications to improve the quality of life for eczema sufferers.
Living comfortably with eczema requires a proactive approach, consistent skin care, and a clear understanding of individual triggers. With proper management, individuals can significantly reduce flare-ups, minimize discomfort, and maintain healthy skin.