Comprehensive Guide to Eczema: Types, Symptoms, and Effective Treatments
This comprehensive guide explores the different types of eczema, their symptoms, and effective treatment options. From atopic dermatitis to seborrheic dermatitis, learn how to identify and manage these common skin conditions for healthier skin and relief from discomfort. Expert insights offer practical advice on triggers, remedies, and therapies to help individuals better understand and control eczema outbreaks.
In-Depth Understanding of Eczema: Types, Causes, and Treatment Options
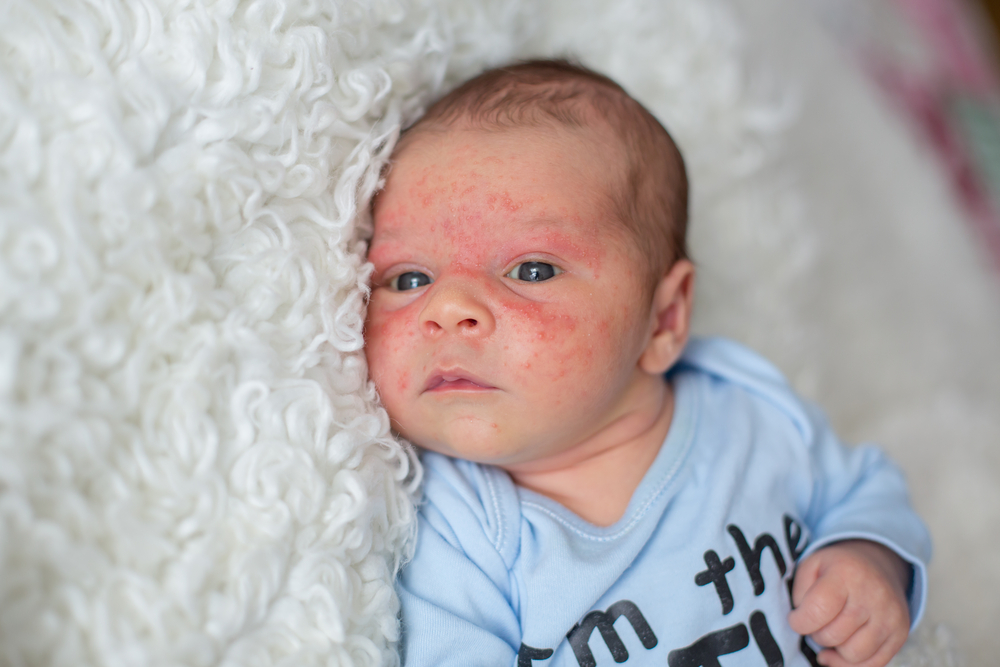
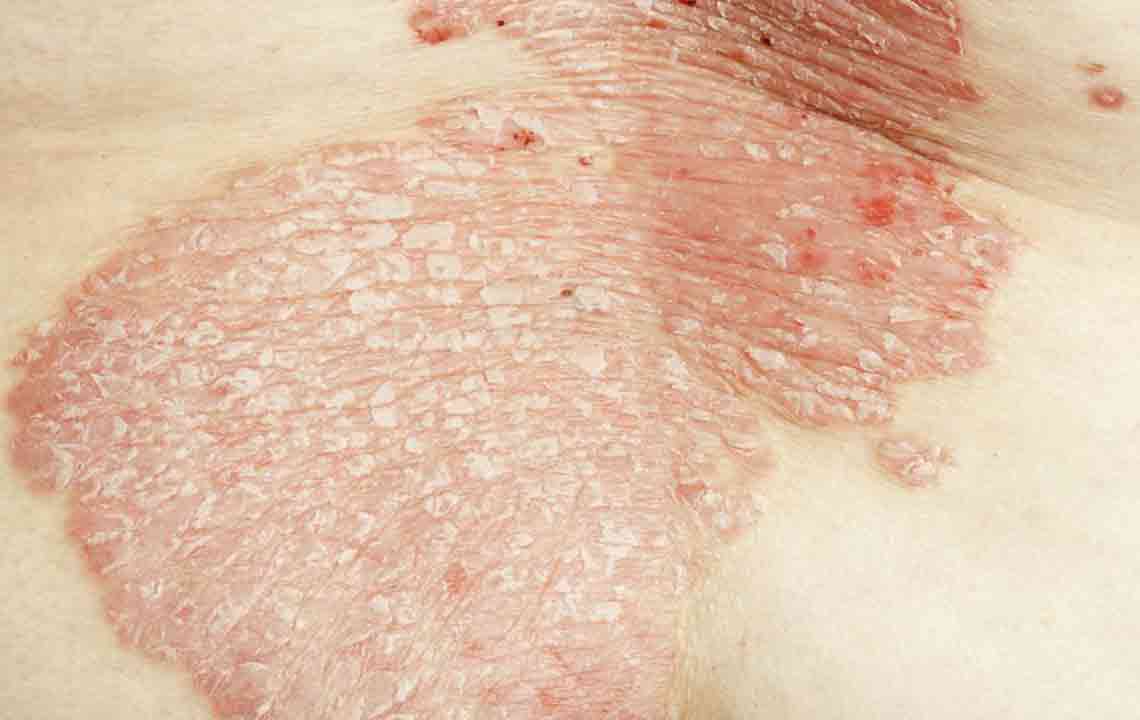
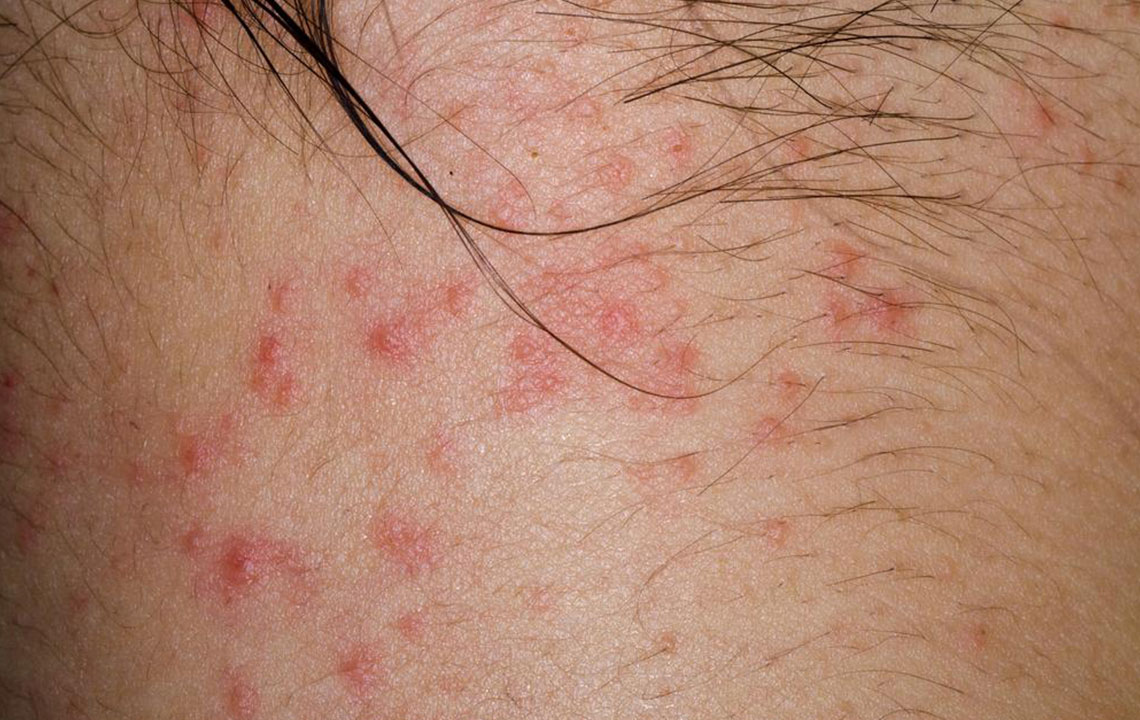
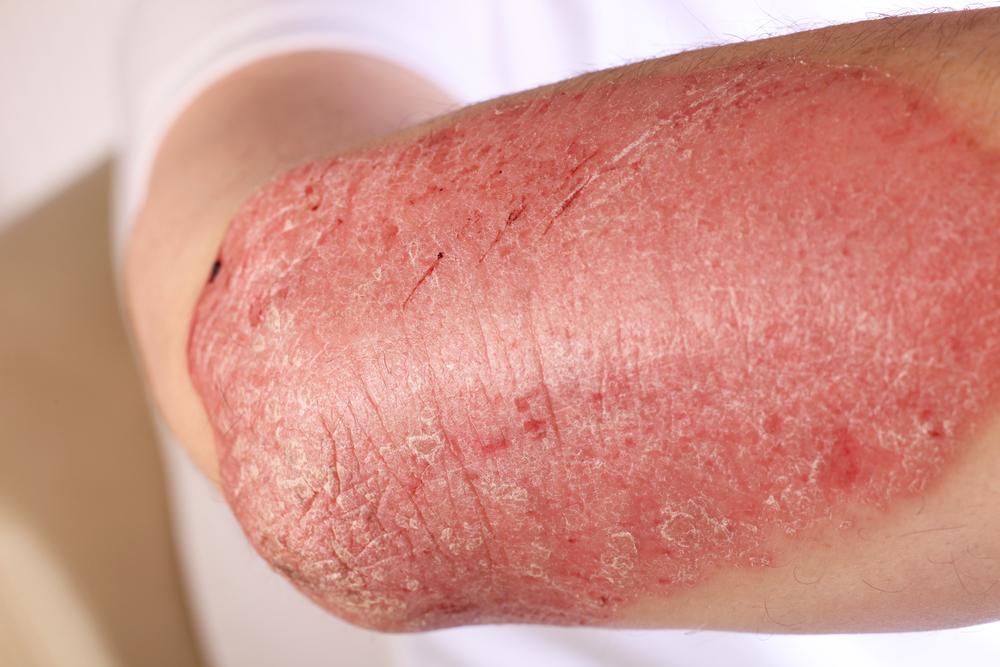
Eczema, medically known as dermatitis, is a prevalent skin disorder characterized by inflammation that affects various parts of the skin. This condition is quite common and can significantly impact an individual's quality of life due to its persistent symptoms. Eczema manifests through a variety of symptoms, including intense itching, redness, rough and flaky skin, blister formation filled with fluid or pus, as well as painful cracks or fissures on the skin surface. The severity and presentation can vary depending on the type of eczema and the individual's skin response. Scratching exacerbates the condition, often leading to further skin damage and increased risk of infection. Understanding the visual cues through online images can assist in accurate identification and early intervention.
Different Types of Eczema: An Overview
Each type of eczema has distinct causes, symptoms, and treatment approaches. Recognizing these differences is crucial for effective management and relief.
1. Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis is the most common form of eczema, especially affecting infants and children, though it can also develop in adults. It is often linked to other allergic conditions such as asthma and hay fever. The hallmark symptoms include red, irritated, thickened skin, primarily on the face, hands, feet, elbows, and knees. The skin may appear inflamed and can become crusty or lichenified due to chronic scratching. Triggers for atopic dermatitis include exposure to soaps, harsh detergents, rough fabrics, dust mites, pet dander, certain foods, and environmental allergens. Managing atopic eczema involves a comprehensive approach: regular moisturizing with emollients to restore skin barrier function, applying topical corticosteroids or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents like crisaborole, and in more severe cases, immune-modulating treatments such as dupilumab injections. Light therapy, including ultraviolet (UV) light, has also been effective for some patients.
2. Contact Dermatitis
This type results from direct skin contact with irritants or allergens. It can be irritant contact dermatitis caused by substances like detergents, solvents, or acids, or allergic contact dermatitis triggered by specific allergens such as nickel in jewelry, cosmetics, or sprays. The hands are the most commonly affected area due to frequent exposure. Symptoms typically include redness, swelling, burning sensation, and blistering. Management emphasizes avoiding known triggers, using gentle skin cleansers, and applying moisturizers. Steroid creams help reduce inflammation, and antibiotics may be necessary if secondary bacterial infection develops.
3. Dyshidrotic Dermatitis
This form of eczema usually targets the hands and feet. Its exact cause remains unknown, but it appears to be associated with stress, allergies, or moist environments. Symptoms include intense itching, small blisters, and cracking skin that can become infected if scratched or damaged. Treatments focus on symptom relief through cold compresses to reduce itching, corticosteroid ointments, and ultraviolet therapy when appropriate. Managing moisture and avoiding irritants are also key to preventing flare-ups.
4. Nummular Dermatitis
Predominantly seen in men, nummular dermatitis manifests as coin-shaped, red, itchy patches that commonly appear on the legs, arms, and hands. Exposure to dry air, cold weather, or contact with chemicals like formaldehyde and nickel can trigger these lesions. The affected skin may become inflamed, scaly, and cracked. Treatment strategies include applying steroid creams to reduce inflammation, using emollients for hydration, and sometimes administering oral medications to control persistent symptoms.
5. Neurodermatitis
This type appears as intensely itchy, thickened patches that often develop on the neck, back, genitals, scalp, or wrists. It frequently results from persistent scratching due to stress or anxiety. If scratched excessively, the skin can become infected, leading to further complications. Treatment involves resisting the urge to scratch, using topical steroids to alleviate inflammation, and in some cases, oral corticosteroids like prednisone to manage severe inflammation and itching.
6. Seborrheic Dermatitis
Sharing similarities with dandruff, seborrheic dermatitis affects the eyebrows, sides of the nose, ears, chest, and groin. Symptoms include itchiness, dryness, and greasy-looking, thickened skin. While the exact cause is not fully understood, it is believed to involve yeast overgrowth and immune responses. Effective treatments include medicated dandruff shampoos containing ingredients like ketoconazole or selenium sulfide, topical steroid creams, and antifungal agents. Managing stress and maintaining good skin hygiene can help mitigate flare-ups.
Understanding the various types of eczema, their triggers, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for effective management. If you suspect you have eczema or experience persistent skin issues, consulting a healthcare professional or dermatologist is recommended for a tailored treatment plan that can significantly improve skin health and quality of life.