Comprehensive Guide to Eczema: Key Symptoms, Root Causes, and Effective Treatment Strategies
Eczema is a prevalent chronic skin condition characterized by inflammation, redness, and itching. This comprehensive guide explores its causes, symptoms, and effective management techniques. While there is no cure, understanding triggers and implementing proper skincare routines can significantly reduce flare-ups and improve skin health. The article highlights the importance of personalized treatment plans, lifestyle adjustments, and advances in medical research in controlling eczema efficiently.

Comprehensive Guide to Eczema: Key Symptoms, Root Causes, and Effective Treatment Strategies
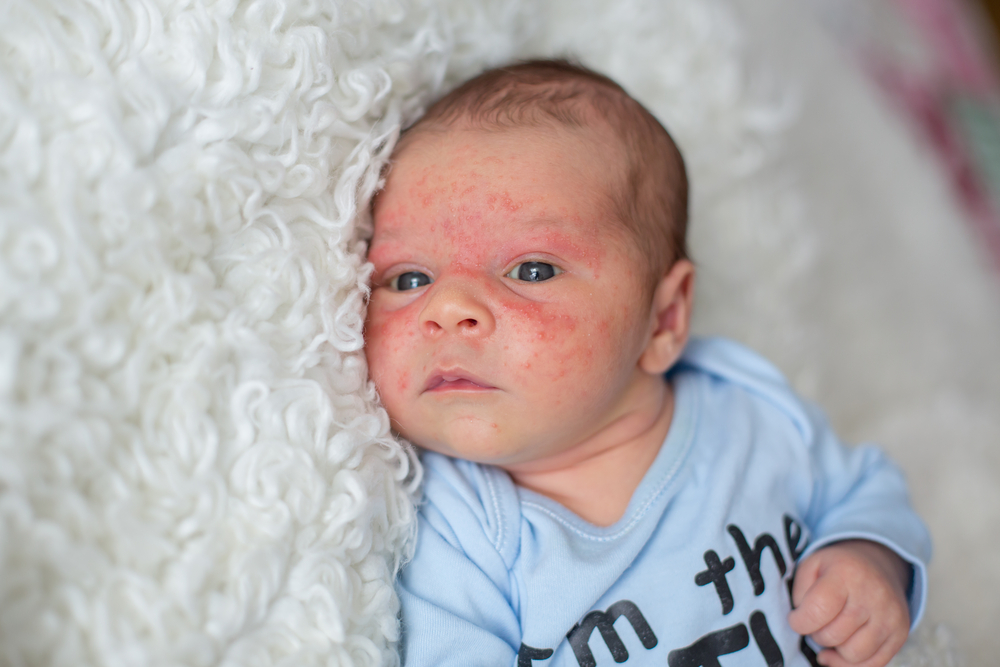
Eczema, also known as dermatitis, is a common and often persistent skin condition characterized by inflammation, redness, itching, and irritation. It affects millions worldwide, with prevalence varying across age groups and populations. In the United States alone, estimates indicate that about 10-20% of infants experience eczema during infancy, and approximately 3% of adults suffer from its symptoms. Many children tend to outgrow eczema by their tenth year, but for some individuals, the condition persists or recurs throughout their lives. The most prevalent form of eczema is atopic dermatitis, which has a strong connection to inherited allergic predispositions such as hay fever and asthma.
Understanding the Causes of Eczema
Despite extensive research, the exact cause of eczema remains elusive. However, medical studies point toward a complex interplay of genetic, immune, and environmental factors. At its core, eczema is linked to an overactive immune response to certain triggers, leading to skin inflammation. Several elements contribute to the development and exacerbation of eczema:
Defective skin barrier function: In individuals with eczema, the skin’s protective barrier is compromised, making it more susceptible to irritants, allergens, and moisture loss.
Hereditary factors: A family history of allergic conditions increases the risk of developing eczema, indicating a genetic predisposition.
Environmental influences: Exposure to environmental irritants such as harsh soaps, detergents, and chemicals can trigger flare-ups.
Stress: Emotional or physical stress can worsen symptoms by suppressing immune function.
Climate and weather changes: Cold, dry weather often aggravates eczema symptoms, while humidity may provide some relief.
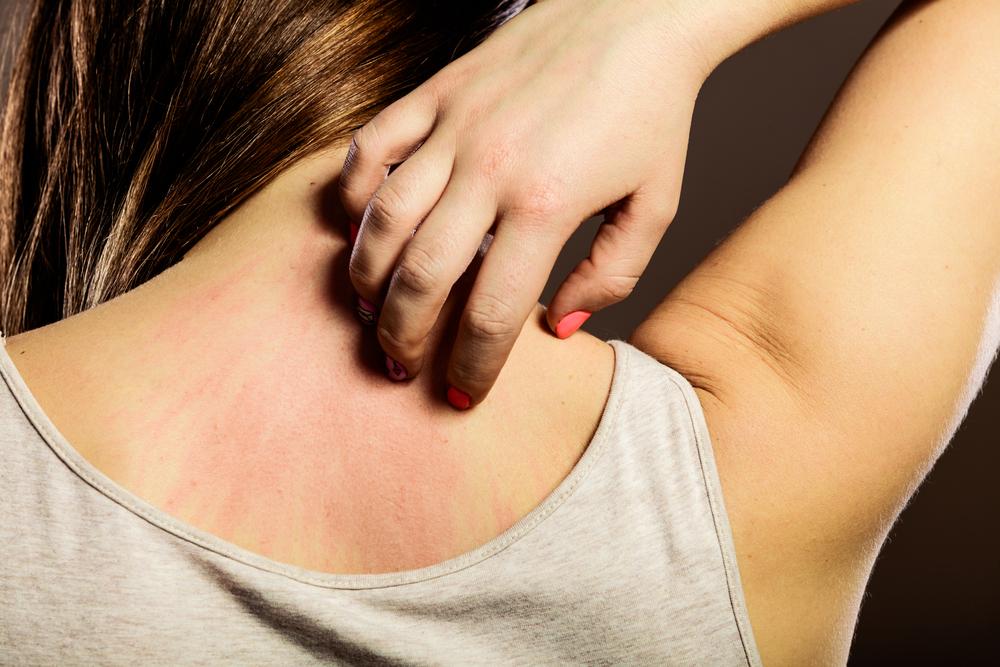
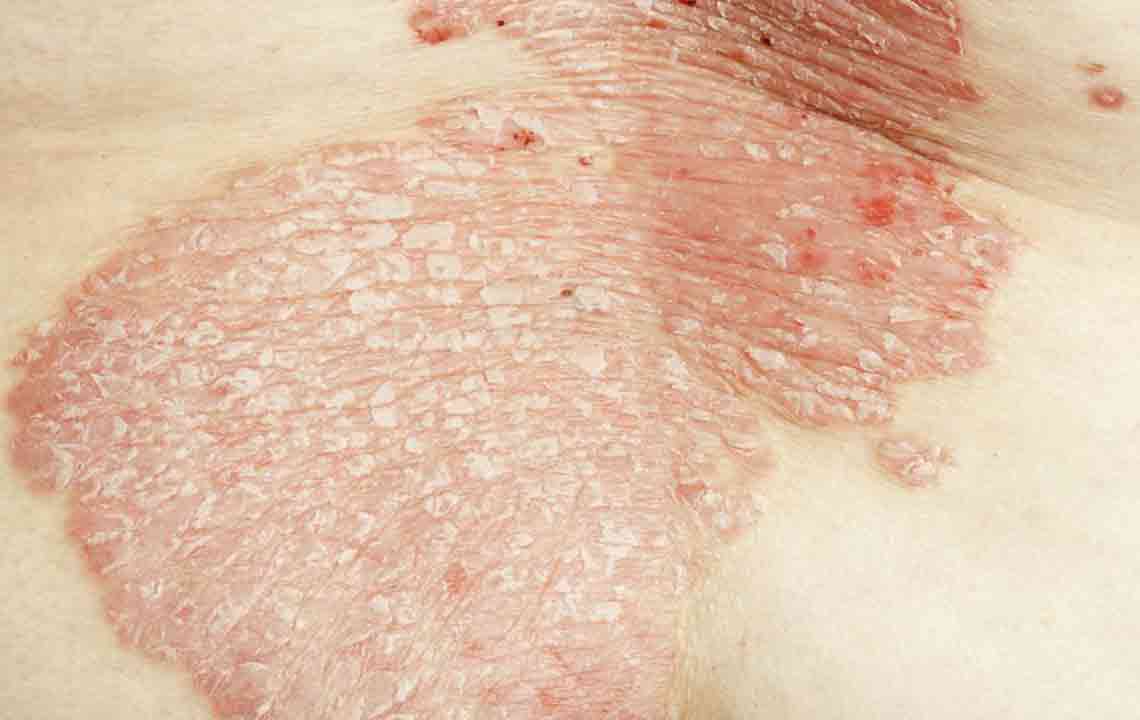
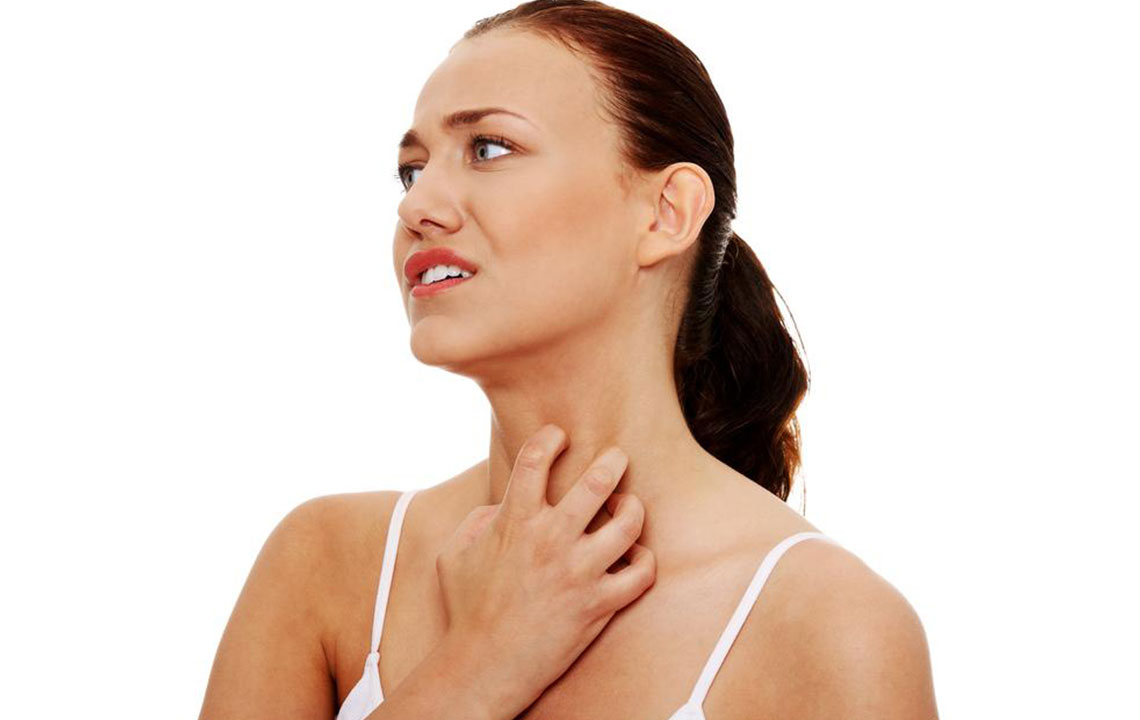
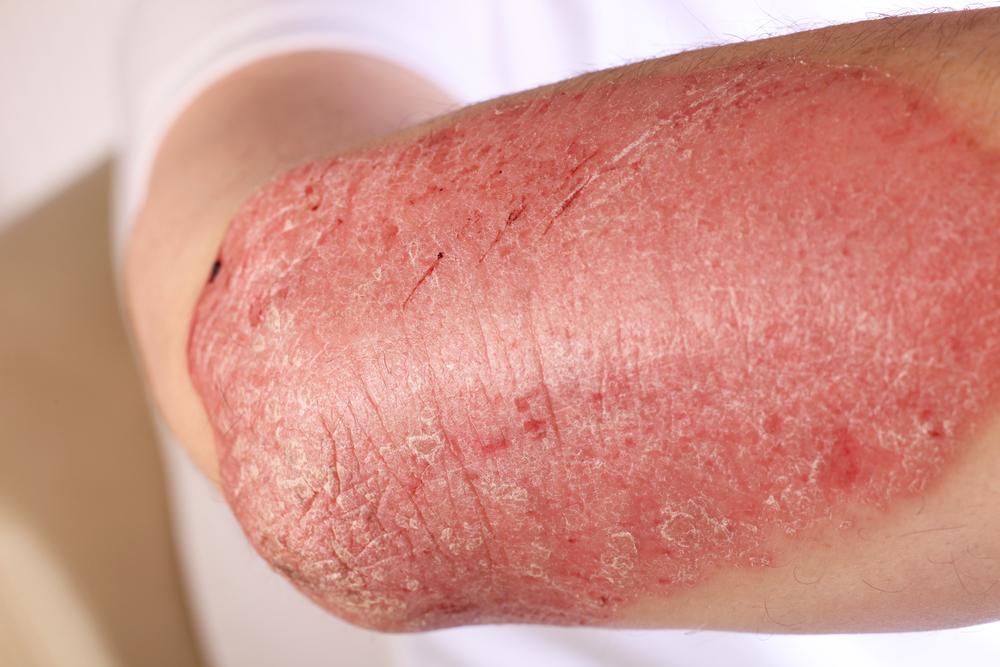
Symptoms of eczema are diverse but predominantly marked by intense itching, redness, and skin rashes. These manifestations commonly appear on areas such as the face, hands, feet, behind the knees, and inside the elbows. The skin affected by eczema tends to become dry, rough, and scaly over time. In individuals with lighter skin tones, redness may initially be prominent and can sometimes turn into brownish pigmentation after inflammation subsides. Conversely, those with darker skin may notice hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation, resulting in darker or lighter patches that can persist even after other symptoms diminish.
Effective Treatment Options for Eczema
While there is currently no cure for eczema, many treatment strategies focus on controlling symptoms, reducing flare-ups, and protecting the skin barrier. A personalized approach, often supervised by a healthcare professional, is essential for managing this chronic condition effectively.
Common treatment methods include:
Topical medications: Prescription corticosteroid creams and ointments are frequently prescribed to reduce inflammation and itching. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory topical agents, such as calcineurin inhibitors, may be used for sensitive areas like the face.
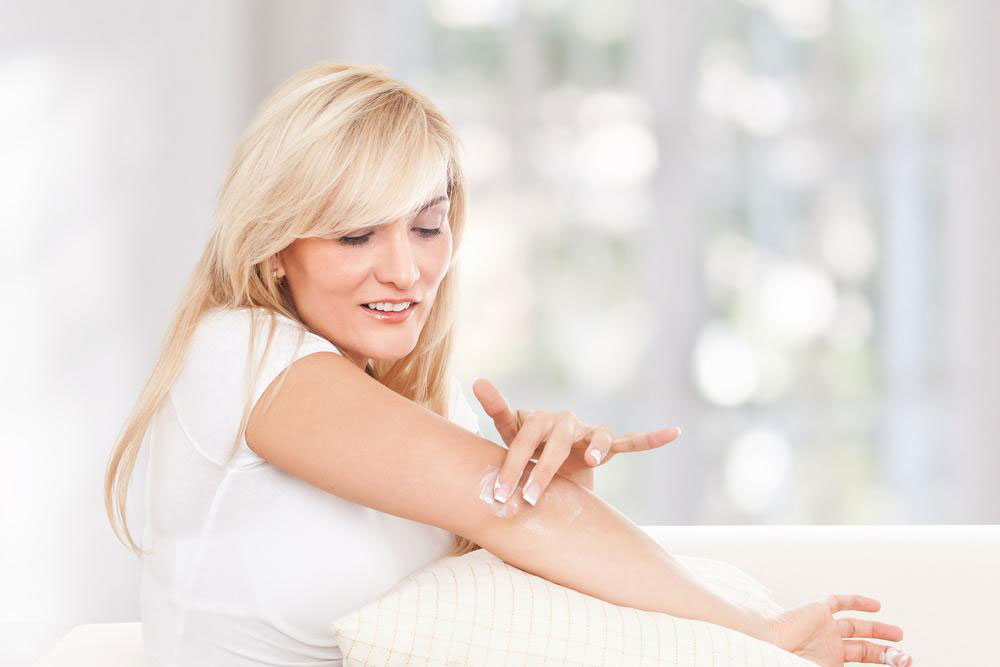
Barrier repair moisturizers: Using emollients regularly helps restore the skin’s protective barrier, keeping it hydrated and preventing irritant penetration.
Antibiotics: If an eczema flare-up becomes infected due to scratching, topical or oral antibiotics might be necessary to treat bacterial infections.
Antihistamines: These can help reduce itching and improve sleep quality during flare-ups.
Phototherapy: Controlled exposure to ultraviolet light under medical supervision can sometimes help reduce severe symptoms.
In addition to medication, lifestyle modifications play a pivotal role in managing eczema:
Skincare routines: Regular bathing with lukewarm water, gentle cleansers, and thorough moisturization are fundamental.
Avoiding triggers: Identifying and steering clear of specific irritants, allergens, and stressors is crucial for preventing flare-ups.
Wearing comfortable clothing: Loose, breathable fabrics like cotton minimize skin irritation.
Stress management: Techniques such as meditation, yoga, and adequate sleep can help reduce flare frequency.
In conclusion, while eczema is a lifelong condition for some, understanding its causes, recognizing symptoms early, and adopting comprehensive management strategies can vastly improve quality of life. Continuous research is opening new avenues for promising treatments, bringing hope to millions impacted by this chronic skin ailment.