Comprehensive Guide to Managing Osteoarthritis Symptoms Effectively
Discover effective strategies to manage osteoarthritis symptoms with a comprehensive guide that covers medical treatments, lifestyle modifications, and surgical options. Learn how to improve joint health, reduce pain, and maintain an active lifestyle despite OA. This detailed article provides insights for patients and caregivers seeking quality of life improvements through tailored management plans and preventative practices.
Comprehensive Guide to Managing Osteoarthritis Symptoms Effectively
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a prevalent degenerative joint disease that affects millions worldwide. Characterized by the progressive deterioration of cartilage within joints, OA leads to discomfort, stiffness, and reduced mobility. It predominantly impacts weight-bearing joints such as the knees, hips, and also affects the neck, fingers, and toes. The condition tends to worsen over time, especially in individuals aged 50 and above, with the highest incidence seen after the age of 65. Despite being a chronic condition with no definitive cure, effective management strategies can significantly minimize symptoms, improve joint function, and enhance the quality of life for those affected.
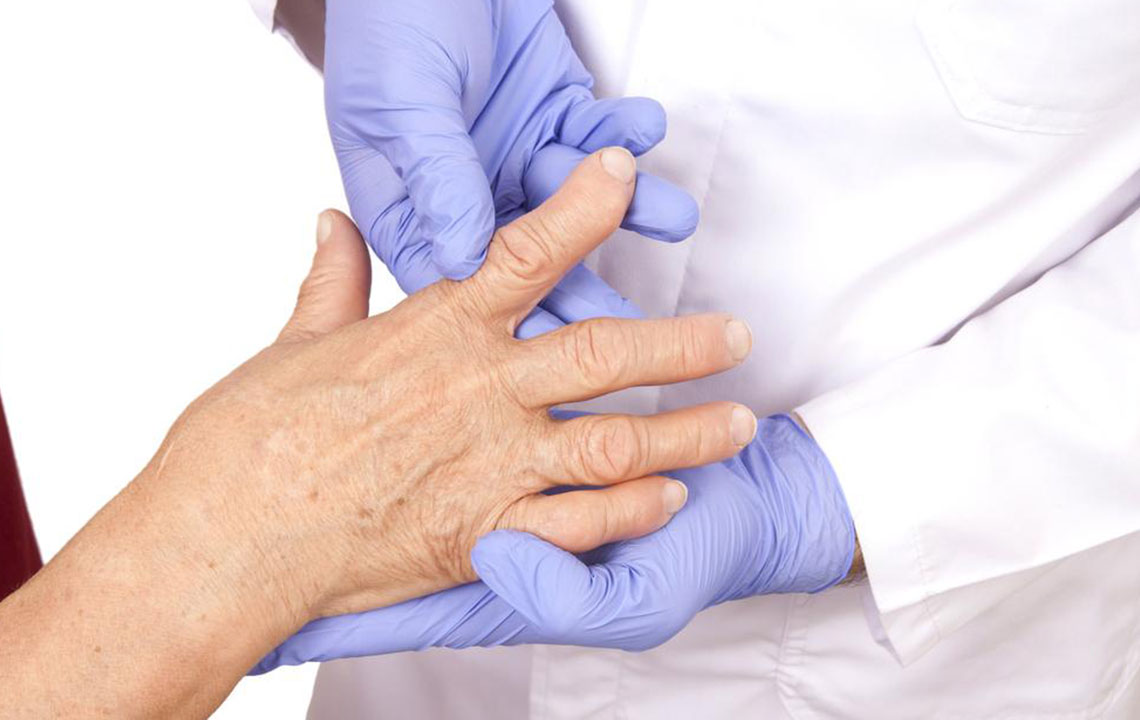
Understanding osteoarthritis involves recognition of its insidious progression. Initially, cartilage damage may be mild, producing subtle discomfort or stiffness, often misattributed to aging or overuse. As the disease advances, symptoms intensify, presenting as persistent joint pain, morning stiffness lasting less than 30 minutes, swelling, a sense of joint instability, and decreased range of motion. The intertwined nature of symptoms often impacts daily activities, mental health, and overall well-being. Counting on proper diagnosis and a comprehensive treatment approach can help manage these symptoms effectively.
Medical management forms the cornerstone of osteoarthritis treatment. Pharmacological options encompass several drug classes aimed at alleviating pain and reducing inflammation, which are essential in improving mobility and daily function. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen, naproxen, or diclofenac are commonly prescribed to control inflammation and discomfort. For severe inflammation, corticosteroid injections directly into the joint can provide powerful relief. Hyaluronic acid injections are also utilized to improve joint lubrication, decreasing friction and easing movement during activities.
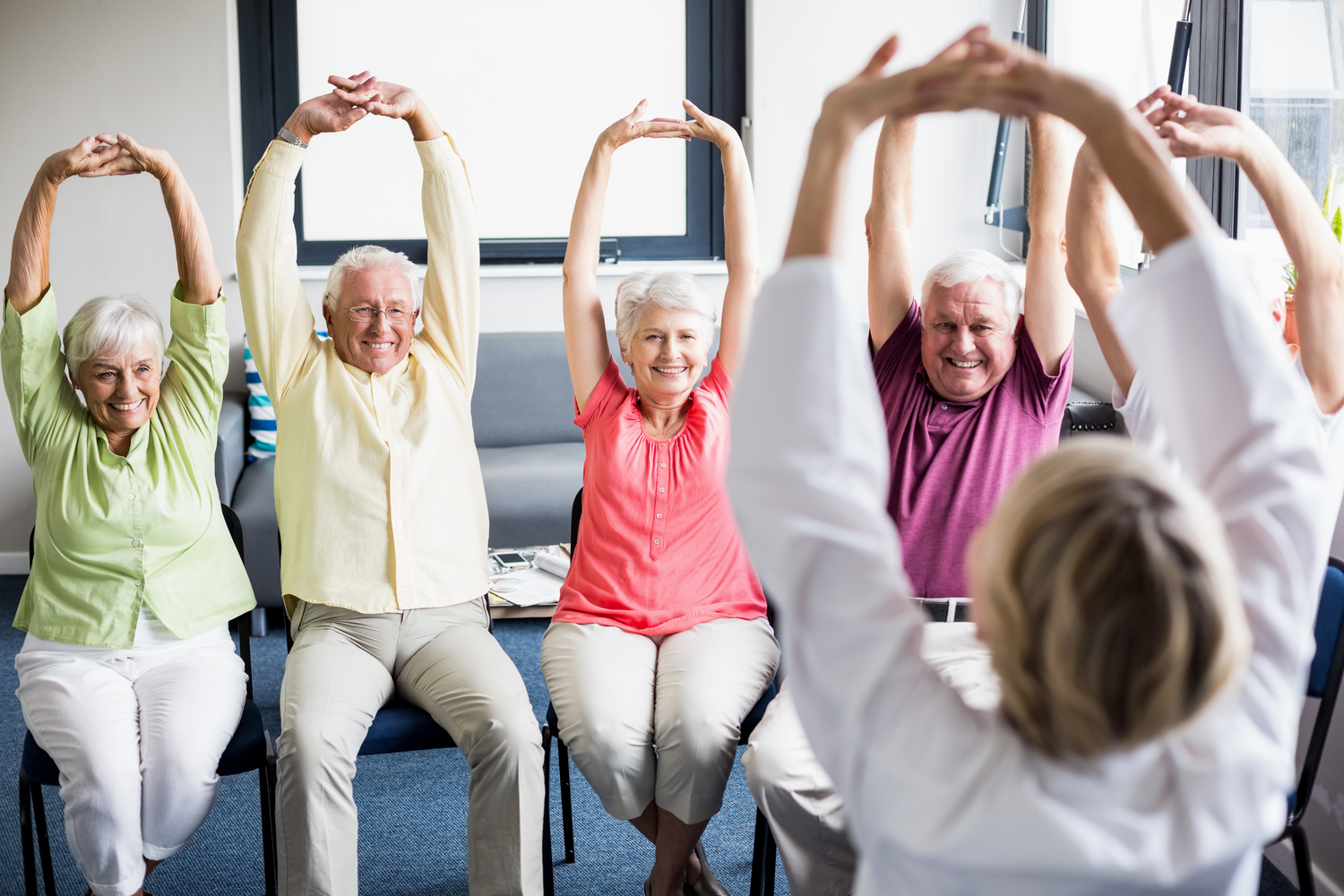
Beyond medications, physical therapy plays a vital role in OA management. Therapeutic exercises designed to strengthen periarticular muscles help stabilize joints, reduce pain, and enhance overall mobility. Physical therapists also recommend modalities such as heat and cold therapy — applying ice packs to reduce swelling and warmth to improve circulation and relax muscles. Assistive devices, including braces, orthotics, or walking aids, can support joint stability and decrease stress during movement. Lifestyle modifications hold equal importance, with patients encouraged to maintain a healthy weight to reduce joint load, avoid repetitive movements that strain affected joints, and incorporate low-impact activities like swimming or cycling that promote joint health without causing further damage.
For individuals with advanced osteoarthritis that significantly impairs quality of life, surgical interventions may be necessary. Joint replacement surgeries, particularly of the hips and knees, have been highly successful in restoring joint function and relieving pain. Arthroscopic procedures can be employed for less severe cases to remove loose cartilage or repair damaged tissues. Postoperative rehabilitation, including physiotherapy, is crucial to regain strength and function.
Preventative measures and early intervention are key to managing osteoarthritis effectively. Regular check-ups, imaging diagnostics such as X-rays or MRI scans, and close monitoring of symptoms enable healthcare providers to tailor treatments. Patients must adopt a proactive approach, including weight management, dietary considerations rich in anti-inflammatory foods, and engagement in joint-friendly exercises. Consulting healthcare professionals—rheumatologists, orthopedic surgeons, physical therapists—is essential in designing individualized management plans that optimize outcomes. Although OA is a chronic condition, a comprehensive, multidisciplinary approach can significantly improve daily functioning, reduce pain, and help individuals lead active, fulfilling lives despite their diagnosis.