Comprehensive Guide to Managing Osteoarthritis: Strategies for Pain Relief and Improved Joint Health
This detailed guide provides comprehensive strategies for managing osteoarthritis, emphasizing medical treatments, lifestyle changes, home remedies, and surgical options. Learn how to alleviate joint pain, reduce inflammation, and maintain mobility through expert-recommended methods tailored for long-term joint health. The article covers causes, symptoms, and effective ways to improve quality of life with osteoarthritis.
Comprehensive Guide to Managing Osteoarthritis: Strategies for Pain Relief and Improved Joint Health
Osteoarthritis, a common form of joint disease, is characterized by the gradual breakdown of cartilage that cushions the ends of bones within joints. It often leads to persistent joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and decreased mobility, significantly impacting quality of life. As the most prevalent type of arthritis, osteoarthritis affects millions worldwide, particularly in aging populations. Effective management of this condition requires a combination of medical treatments, lifestyle modifications, and home remedies tailored to individual needs.
Understanding osteoarthritis involves recognizing its primary causes, affected areas, symptoms, and available treatment options. While it predominantly affects weight-bearing joints such as the knees, hips, and the spine, it can also influence smaller joints like fingers and toes, particularly at the base of the thumb and big toe.
Healthy joints are protected by a smooth, elastic cartilage that allows bones to glide smoothly against each other during movement. In osteoarthritis, this cartilage gradually deteriorates, becoming rough and thin, which exposes underlying bone surfaces, leading to pain, swelling, and reduced mobility. The progression of osteoarthritis varies among individuals but generally worsens over time if not managed properly.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to the development of osteoarthritis, including age, genetic predisposition, joint injuries, obesity, and repeated stress or overuse of specific joints. Excess weight increases the load on weight-bearing joints, accelerating cartilage deterioration. Additionally, joint injuries sustained through accidents or sports can predispose individuals to osteoarthritis later in life.
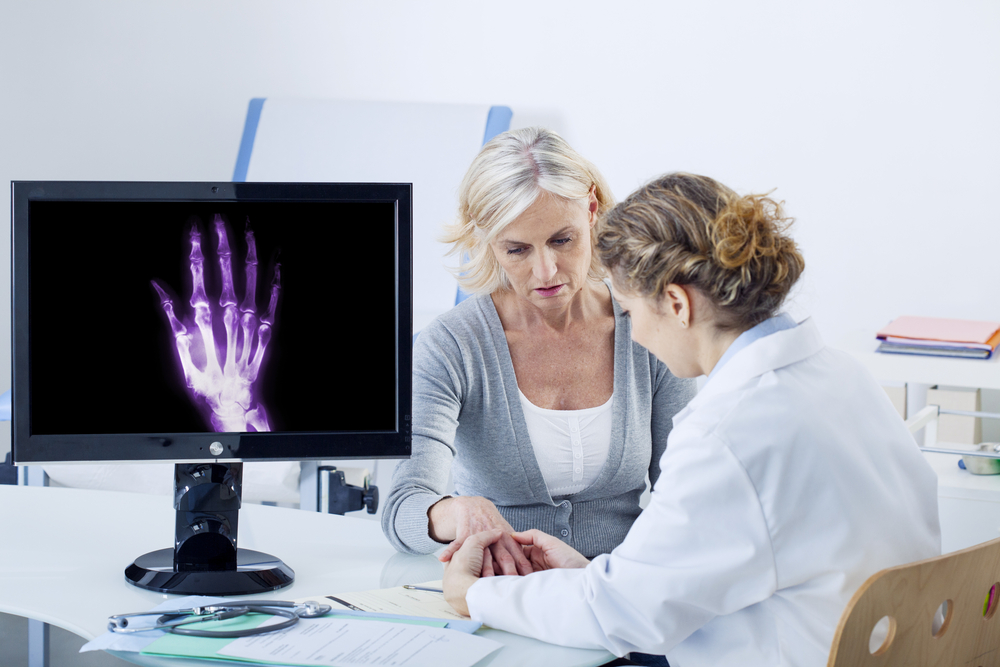
Symptoms Facilitating Diagnosis
Common symptoms include joint pain, stiffness, swelling, decreased range of motion, and sometimes crepitus—the sensation of crackling or grating sounds during movement. These symptoms tend to worsen with activity and improve with rest, although chronic symptoms may persist even at rest in advanced stages.
Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial to manage symptoms effectively and slow disease progression.
Medical Treatments and Lifestyle Adjustments
Medical interventions aim to reduce symptoms, improve joint function, and slow the degenerative process. These include various medications such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroid injections, and hyaluronic acid injections. In some cases, visco-supplementation or enzyme-based treatments are considered. However, medication alone cannot fully address osteoarthritis; accompanying lifestyle changes are essential for optimal management.
Key lifestyle modifications include maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular low-impact exercises, and adopting joint-friendly habits. Proper nutrition supports joint health—foods rich in anti-inflammatory compounds, vitamins, and minerals can bolster cartilage repair and reduce inflammation.
In addition to clinical treatments, home remedies and self-care strategies offer significant relief and improve joint function.
Heat and Cold Therapy - Applying warm or cold compresses during flare-ups can reduce pain and stiffness. Warm packs help relax muscles and increase blood flow, easing chronic discomfort, while cold packs numb nerve endings and diminish inflammation during acute episodes.
Epsom Salt Soaks - Soaking in warm water with Epsom salts, which contain magnesium, provides soothing benefits. Magnesium absorbs through the skin and may help reduce joint inflammation and muscle soreness. For best results, immerse in water heated to approximately 102°F with two cups of Epsom salt for about 30 minutes several times a week.
Natural Anti-Inflammatory Foods and Beverages - Incorporating foods with natural anti-inflammatory properties can aid symptom management. Green tea, rich in polyphenols, helps protect cartilage and reduce inflammation. Turmeric, containing curcumin, has been shown to decrease pain and swelling by modulating inflammatory pathways. Ginger is another beneficial ingredient for pain relief and long-term joint health; however, moderation is advised to prevent gastrointestinal side effects.
Exercise and Physical Therapy - Gentle, low-impact exercises such as swimming, cycling, and walking strengthen muscles around affected joints, improve flexibility, and reduce stiffness. Physical therapy exercises tailored to individual needs can help maintain joint mobility and prevent further deterioration.
Weight Management - Maintaining a healthy weight lessens the stress on weight-bearing joints, slowing disease progression and alleviating symptoms. Combining calorie-controlled diets with regular activity is effective in achieving and maintaining optimal weight.
Proper Footwear and Joint Protection Techniques - Using supportive shoes and employing joint protection strategies during daily activities can prevent excessive strain on vulnerable joints. Using assistive devices like braces or canes can also provide relief and improve mobility.
Advanced Medical Interventions
In cases where conservative management fails, surgical options such as joint replacement or osteotomy may be considered. These procedures aim to restore joint function, relieve pain, and improve quality of life. The decision for surgery depends on the severity of joint damage, overall health, and patient preferences.
Regular follow-up with healthcare providers is essential to monitor disease progression and adjust treatment strategies accordingly.
In conclusion, managing osteoarthritis effectively involves a comprehensive approach combining medical treatment, lifestyle modifications, and home remedies. Maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in safe physical activity, using heat and cold therapy, and incorporating anti-inflammatory foods into your diet can significantly improve joint health and quality of life. Early intervention and personalized care are key to slowing disease progression and maintaining joint function for years to come.