Comprehensive Guide to Nutritional Strategies for Alleviating Arthritis Pain
This comprehensive guide explores the top five nutritional strategies to help alleviate arthritis pain and improve joint health. Highlighting foods like turmeric, garlic, fatty fish, vitamin C-rich fruits, and berries, the article provides scientific insights and practical tips for incorporating these anti-inflammatory foods into daily routines. Combining dietary choices with medical advice can significantly enhance quality of life for arthritis sufferers, emphasizing a natural, holistic approach to managing joint discomfort and inflammation effectively.
Comprehensive Guide to Nutritional Strategies for Alleviating Arthritis Pain
Managing arthritis effectively involves a combination of medical treatment, lifestyle changes, and dietary adjustments. Emerging research and opinions from leading rheumatologists consistently highlight the crucial role nutrition plays in controlling symptoms like joint inflammation, stiffness, and chronic discomfort. While no diet can completely cure arthritis, incorporating specific nutrient-rich foods into your daily routine can significantly reduce inflammation, improve joint health, and enhance overall well-being.
Understanding which foods contain anti-inflammatory and joint-supporting compounds is essential for those seeking natural ways to combat arthritis symptoms. A well-balanced diet targeting inflammation reduction can also contribute to strengthening bones, boosting immune function, and preventing further joint deterioration. In this article, we delve into the top five foods backed by scientific evidence that can help manage arthritis symptoms effectively.
Here are five key nutritional choices that can play a pivotal role in easing arthritis pain and promoting healthier joints.
Turmeric: Nature’s Anti-Inflammatory Powerhouse
Turmeric, a golden-yellow spice originating from South Asia, has been used for centuries in traditional medicine due to its potent medicinal properties. Its primary active compound, curcumin, possesses strong anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. Numerous studies have demonstrated that curcumin can help reduce joint swelling, stiffness, and pain associated with both osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Incorporating turmeric into your diet can be as simple as adding it to curries, smoothies, or teas. For more potent and consistent results, many people opt for turmeric supplements containing concentrated extracts, which can deliver higher doses of curcumin. When choosing supplements, look for formulations that include black pepper extract (piperine) to enhance absorption. Regular consumption of turmeric has shown promise in managing chronic inflammation typical in arthritis.
Garlic: A Natural Anti-Inflammatory Ally
Belonging to the allium family, garlic has long been valued not only as a culinary flavor enhancer but also as a medicinal remedy. It contains sulfur compounds like diallyl disulfide, which exhibit anti-inflammatory properties and can help alleviate joint pain. Consuming fresh, raw garlic tends to offer maximum health benefits, whereas processed or cooked garlic may lose some of its active compounds. Incorporating freshly chopped garlic into salads, dressings, or dishes can provide ongoing benefits for joint health. Additionally, garlic's immune-boosting effects may help reduce the frequency and severity of arthritis flare-ups driven by systemic inflammation.
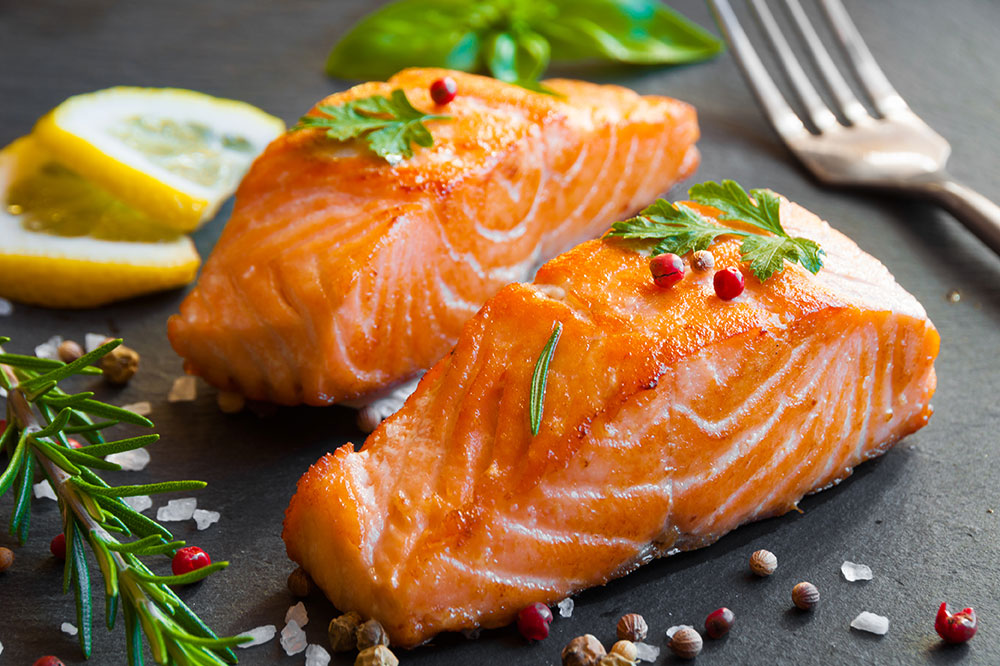
Fatty Fish: Omega-3 Rich Foods for Joint Health
Fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, sardines, and tuna are excellent sources of omega-3 fatty acids. Omega-3s are renowned for their ability to suppress inflammatory pathways, thereby reducing joint pain and stiffness common in arthritis conditions. For optimal benefits, it’s advisable to include these fish in your diet at least twice a week. If you’re vegetarian or allergic to fish, plant-based sources like soybeans, walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds serve as good alternatives, providing alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), a type of omega-3 fatty acid. Omega-3 fatty acids not only help diminish inflammation but may also slow disease progression and improve joint mobility in arthritis patients.
Vitamin C: Essential for Joint Cartilage and Bone Health
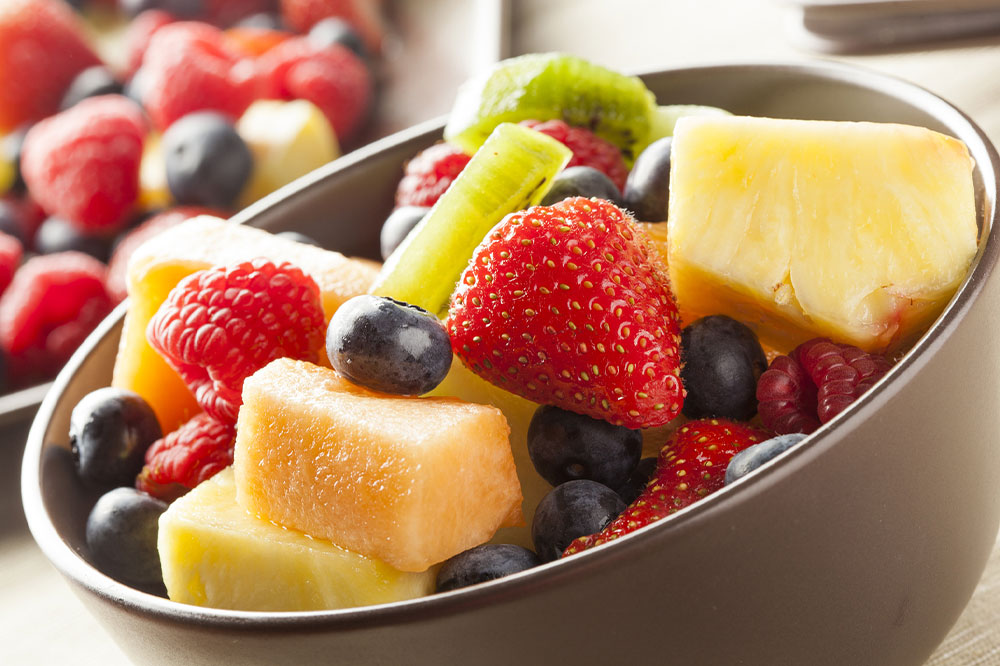
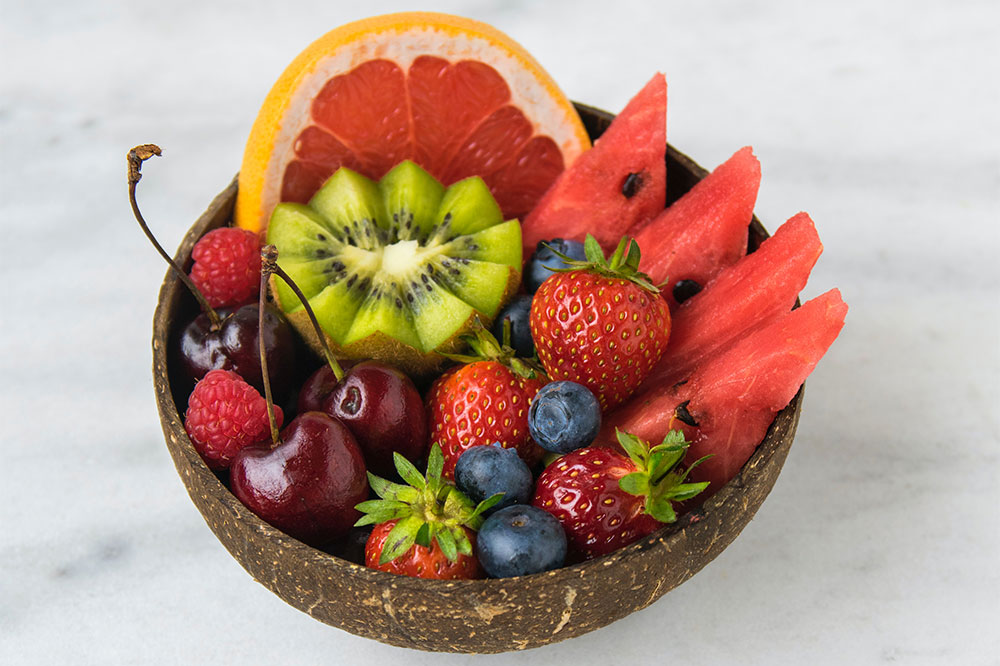
Vitamin C, a potent antioxidant, plays a vital role in collagen synthesis, which is crucial for maintaining the integrity of joint cartilage and bone strength. Regular intake of vitamin C-rich fruits and vegetables has been linked to a slower progression of osteoarthritis. Fruits such as pineapples, kiwis, strawberries, and citrus fruits are abundant sources of vitamin C. Consuming these foods daily can help lower osteoarthritis risk by up to 11%. While vitamin C supplements are available, it’s recommended to keep daily intake between 65–85 mg to prevent adverse effects like kidney stones. Adequate vitamin C intake supports joint tissue repair and enhances immune function, both vital for managing arthritis effectively.
Cherries and Other Berries: Natural Remedies for Joint Comfort
Tart cherries are rich in anthocyanins, plant compounds with strong anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. Clinical studies have indicated that drinking tart cherry juice can reduce joint pain, stiffness, and gout flare-ups. The high antioxidant content helps neutralize free radicals responsible for joint tissue damage. Alongside cherries, other berries such as strawberries, raspberries, blueberries, and blackberries contain similar compounds that help combat inflammation. Regular consumption of these berries, whether fresh or in smoothies, provides natural relief from joint discomfort and may decrease the frequency of arthritis episodes. Their inclusion in a balanced diet can enhance overall health and contribute to the long-term management of joint issues.
Adopting a diet rich in these five nourishing foods, complemented by medical guidance and lifestyle modifications like regular exercise and weight management, can dramatically improve symptoms of arthritis, boosting quality of life and functional capacity. While dietary strategies alone may not entirely eliminate symptoms, they form a critical component of a holistic approach to arthritis management.
Tags: arthritis management, anti-inflammatory diet, joint health, nutritional therapy, chronic pain relief





