Comprehensive Dietary Strategies to Alleviate Arthritis Symptoms and Reduce Inflammation
This comprehensive guide explores dietary strategies for managing arthritis, emphasizing anti-inflammatory foods like omega-3-rich fish, garlic, ginger, and cruciferous vegetables. It highlights how regular consumption of these nutrient-packed foods can reduce joint pain, stiffness, and swelling. The article also discusses medical options like ACTEMRA®, offering a holistic approach to joint health. Ideal for arthritis sufferers seeking natural and medical solutions, this expanded content provides practical tips to improve quality of life and joint function through diet and targeted therapies.

Comprehensive Dietary Strategies to Alleviate Arthritis Symptoms and Reduce Inflammation
Arthritis is a prevalent condition that affects millions of people worldwide, characterized by joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and decreased mobility. It encompasses over 100 different types, with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis being the most common. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks joint tissues, leading to inflammation and joint damage. Osteoarthritis, on the other hand, results from the wear and tear of cartilage, often due to aging, injury, or overuse. Regardless of the type, managing symptoms effectively is crucial to maintaining a good quality of life, and diet plays a significant role in this.
Recent research highlights that certain foods possess natural anti-inflammatory properties, which can help reduce joint pain, stiffness, and swelling associated with arthritis. Making deliberate dietary choices can serve as a complementary approach alongside medical treatments. In this expanded guide, we delve into the most beneficial foods and dietary habits that can significantly impact arthritis management, bolstering joint health and easing discomforts.
Heart-Healthy Omega-3 Rich Fish
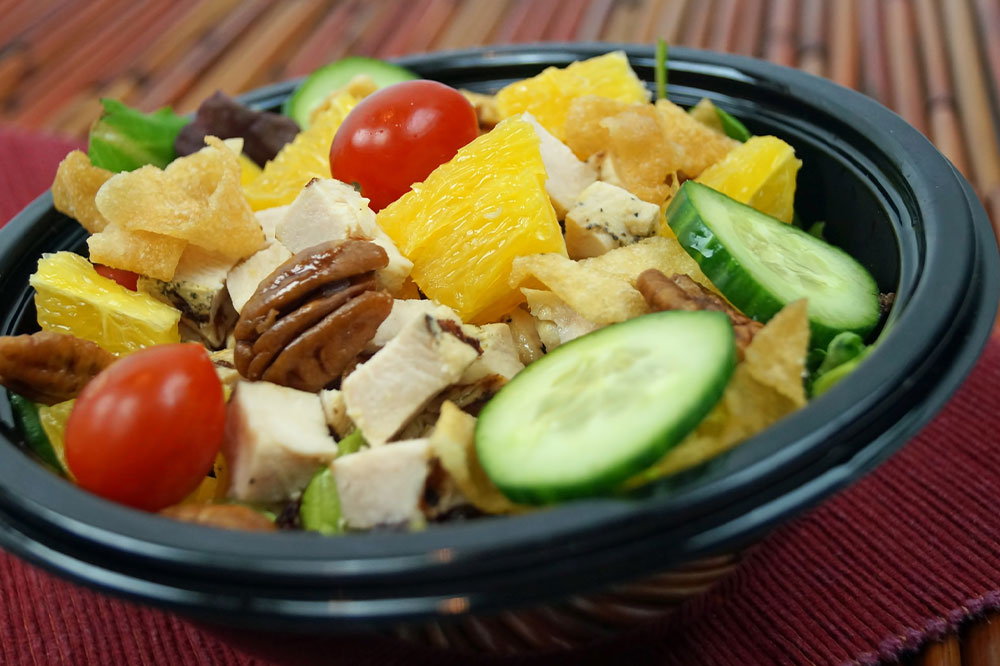
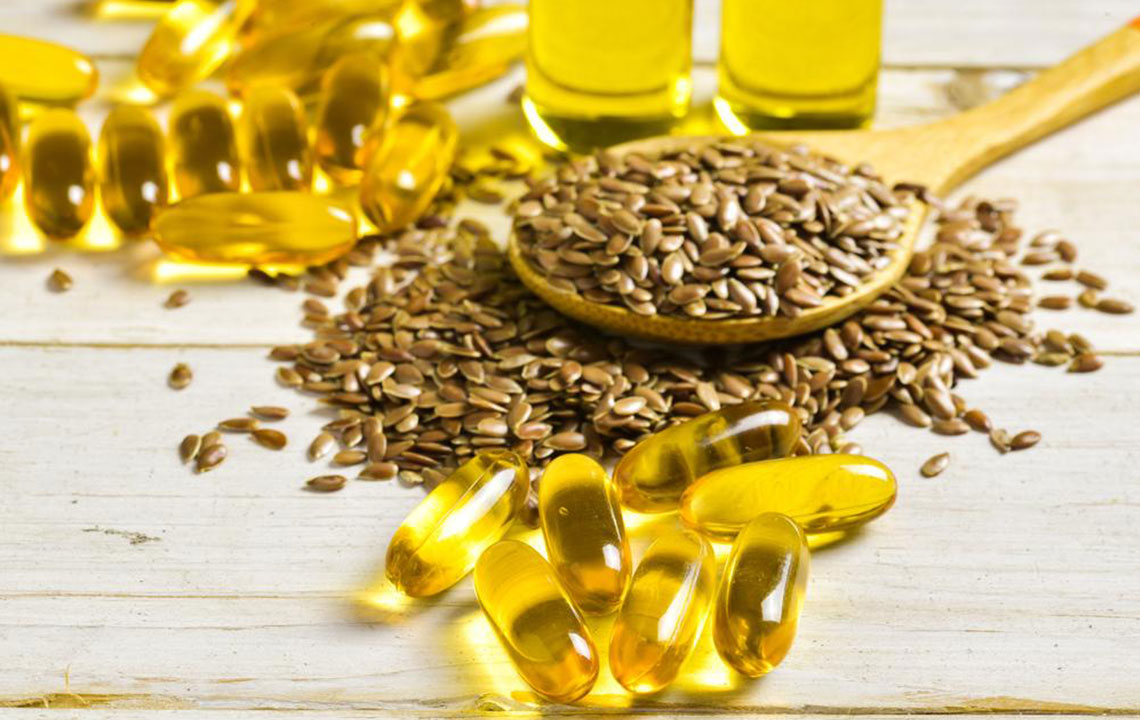
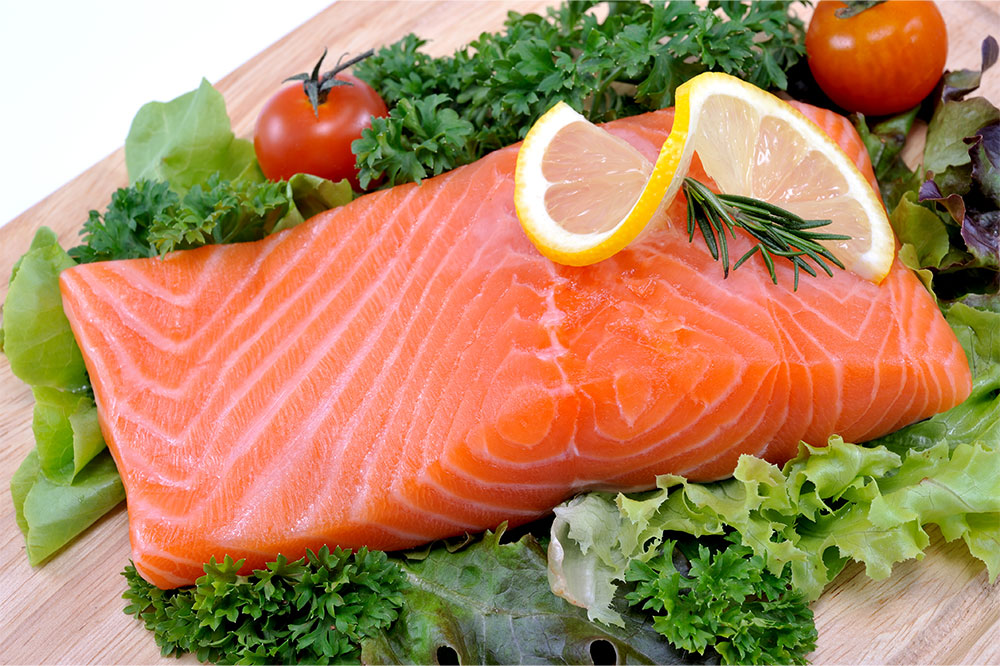
Consuming fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, sardines, and trout is one of the most evidence-backed dietary strategies for reducing inflammation related to arthritis. These fish are abundant sources of omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA, which have potent anti-inflammatory effects. Regular intake of omega-3-rich fish can lead to decreased joint stiffness, reduced pain, and lowered levels of inflammatory markers in the blood. Moreover, fish provides vitamin D, essential for healthy bones and immune regulation, which may help in preventing or alleviating rheumatoid arthritis symptoms. The American Heart Association recommends consuming at least two servings of fatty fish per week to harness these health benefits effectively. Incorporating fish into your weekly meal plan can be simple—try grilled salmon on Mondays and baked sardines on Fridays for variety and maximum effect.
Garlic – The Natural Anti-Inflammatory
Beyond its culinary uses, garlic is renowned for its medicinal properties. The compounds present in garlic, such as allicin, have demonstrated anti-inflammatory and immune-boosting effects. Regular garlic consumption may help reduce joint inflammation and mitigate symptoms of arthritis. Studies suggest that garlic can support cardiovascular health, which is often compromised in individuals with chronic inflammatory conditions. Incorporating fresh garlic into salads, stir-fries, or roasted dishes can easily enhance flavor while providing potent health benefits. Consistency is key; even small daily amounts can contribute to reducing joint pain over time.
Ginger – Nature’s Pain Reliever
Ginger has a long history of use in traditional medicine for treating inflammatory conditions. Scientific evidence indicates that ginger contains bioactive compounds like gingerol and shogaol, which inhibit substances responsible for pain and inflammation, such as prostaglandins and leukotrienes. Consuming ginger, whether fresh, dried, or powdered, can be particularly effective in alleviating knee pain, one of the most common complaints among arthritis sufferers. Adding freshly grated ginger to teas, smoothies, or Asian stir-fry dishes is an easy way to leverage its anti-inflammatory properties. Consider brewing ginger-infused teas or supplementing with ginger capsules after consulting your healthcare provider.
Cruciferous Vegetables Boosting Joint Health
Vegetables like broccoli, Brussels sprouts, cauliflower, and kale are rich in phytochemicals such as sulforaphane, which play a vital role in reducing inflammation. These vegetables also contain antioxidants that combat oxidative stress, a contributor to joint degradation. Regular intake of cruciferous vegetables may help lower inflammation levels and support joint repair mechanisms. Incorporating these vegetables in salads, soups, and stir-fries not only enhances dietary variety but also provides crucial nutrients for overall health. Cooking lightly can preserve their beneficial compounds, making them more bioavailable for your body.
Walnuts – Nourishing Your Joints with Healthy Fats and Antioxidants
Walnuts are a powerhouse of nutrients, particularly omega-3 fatty acids and polyphenols, which exert anti-inflammatory effects. Multiple studies link walnut consumption to decreased markers of inflammation and improved joint swelling and pain in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Snack on a handful of walnuts daily or add chopped walnuts to oatmeal, yogurt, or salads to integrate their benefits effortlessly into your diet. Their rich antioxidant content also helps combat free radicals that damage cells and tissues, contributing to joint degeneration over time.
Antioxidant-Rich Berries for Joint Restoration
Berries such as blueberries, strawberries, raspberries, and blackberries are packed with vitamins C and K, fiber, and plant antioxidants like rutin and quercetin. These compounds have demonstrated the ability to reduce inflammatory markers considerably. Consuming at least two servings of berries weekly has been associated with a 14% reduction in systemic inflammation, which can translate into fewer flare-ups and less joint pain. Adding berries to smoothies, cereals, or enjoying them as a snack provides a delicious way to support joint health and overall immunity.
In addition to dietary measures, certain medical treatments play a role in managing arthritis inflammation. For example, ACTEMRA® (tocilizumab) is an FDA-approved medication that targets interleukin-6 (IL-6), a cytokine involved in inflammation processes. This medication can be administered via weekly or bi-weekly injections or infusions, often self-injected at home. Such targeted therapies can significantly reduce joint swelling and pain, especially in moderate to severe cases of rheumatoid arthritis. Combining appropriate medical therapies with a nutrient-rich diet offers a comprehensive approach to managing arthritis effectively. Always consult your healthcare provider before making dietary or medication changes to ensure they suit your individual health needs.