Comprehensive Strategies for Effectively Managing Arthritis Symptoms
This comprehensive guide explores effective strategies for managing arthritis through diet, weight control, medications, and physical therapy. It emphasizes lifestyle modifications and medical treatments to alleviate joint pain and improve mobility, offering practical advice for those affected by arthritis. Early diagnosis and personalized care are central to successful management, helping individuals regain control over their condition and enhance their quality of life.

Effective Approaches to Managing Arthritis
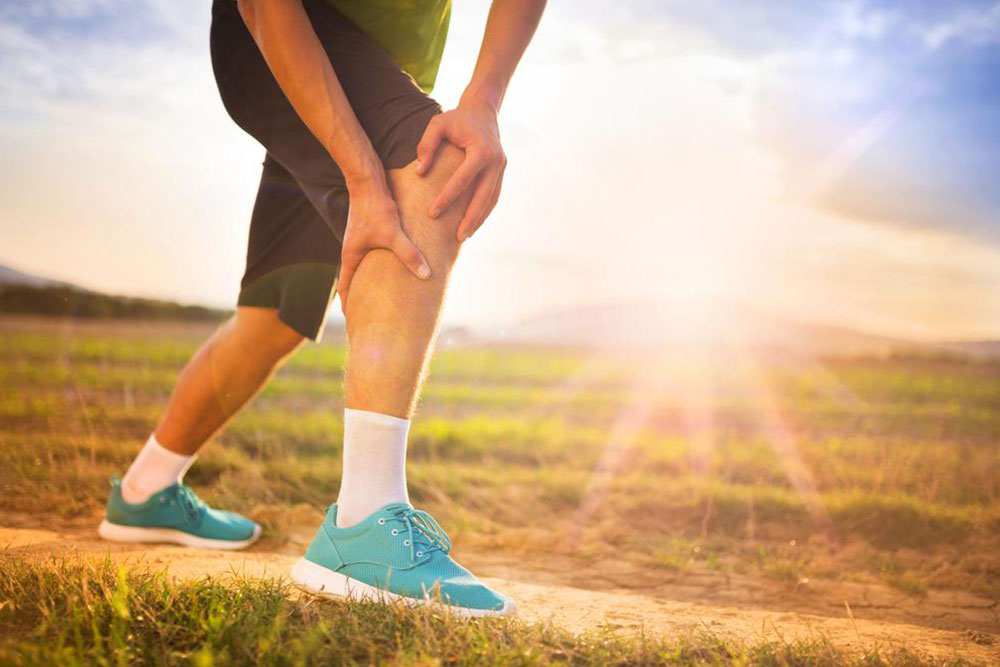
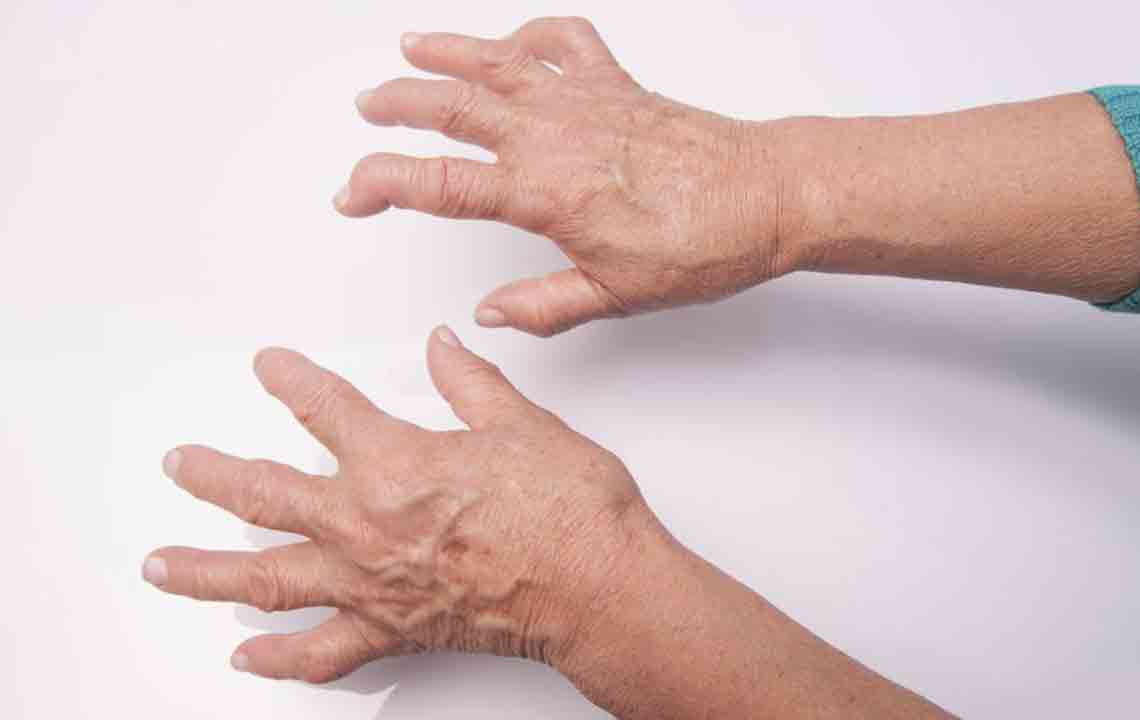
Arthritis is a common and often debilitating condition that can develop unexpectedly, leading to persistent joint pain, swelling, stiffness, and impaired mobility. Though there is no definitive cure for arthritis, numerous treatments and lifestyle modifications can significantly help in reducing symptoms, slowing disease progression, and improving quality of life. Proper management involves a comprehensive approach that includes dietary adjustments, weight control, physical activity, and medical interventions tailored to individual needs.
The Importance of Nutrition and Lifestyle Choices
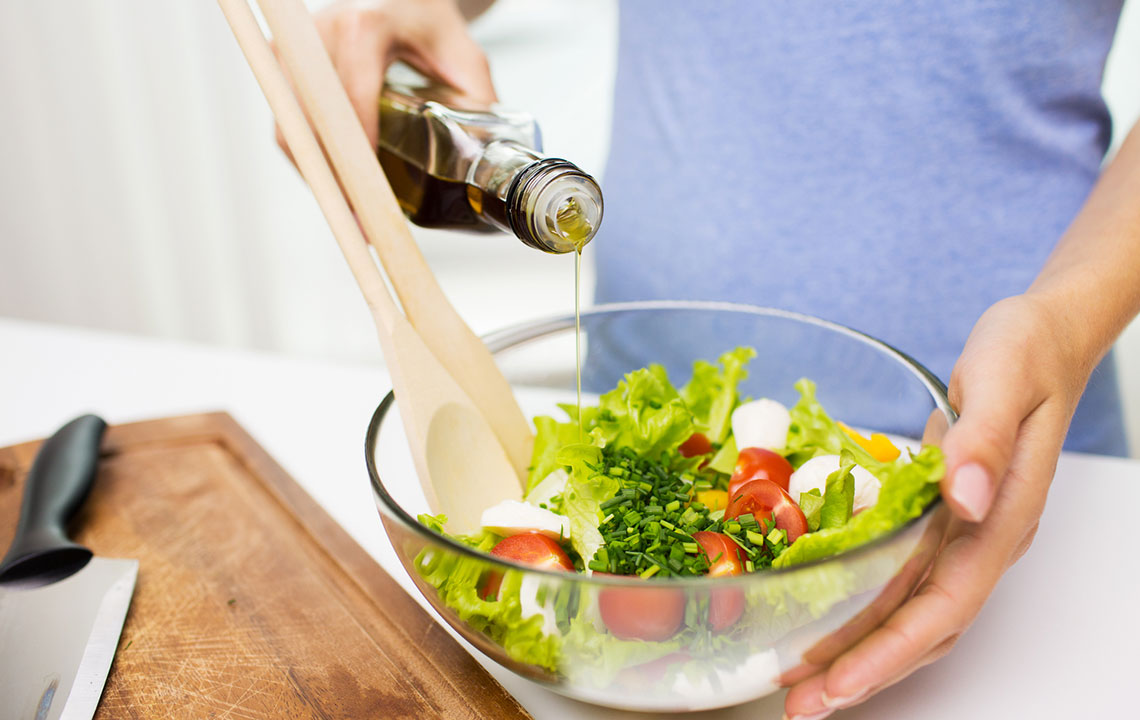
Maintaining an optimal diet and a healthy weight are vital components in managing arthritis symptoms. Excess body weight puts additional stress on weight-bearing joints such as the knees, hips, and spine, exacerbating pain and accelerating joint damage. Therefore, adopting dietary habits that support joint health is essential. Consuming foods rich in anti-inflammatory properties, such as omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish, nuts, and seeds, can help reduce joint inflammation and pain. Conversely, it’s prudent to limit foods high in purines—including certain types of fish, red meats, and some vegetables—which can lead to uric acid buildup, worsening gouty arthritis symptoms.
They should also minimize processed foods, fried items, and foods high in advanced glycation end products (AGEs), as these contribute to systemic inflammation. Incorporating fresh fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins into your diet may promote overall joint health. Additionally, staying well-hydrated can aid in maintaining joint lubrication and function.
Maintaining a healthy weight is equally vital. Studies have consistently shown that even a modest weight loss can significantly decrease joint stress, reduce pain, and improve mobility. Combining a balanced diet with gentle exercise routines helps in achieving and maintaining optimal body weight.
Consult your healthcare provider or a registered dietitian before making any significant dietary changes. Accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plans are crucial for effective arthritis management.
Medical and Pharmacological Treatments for Arthritis
Managing arthritis effectively often involves a combination of medications and physical therapies. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen and naproxen, are among the most commonly prescribed drugs to alleviate pain and decrease inflammation. They are effective in reducing daily discomfort but should be used under medical supervision to avoid potential side effects like gastrointestinal issues or cardiovascular risks.
Analgesics, like acetaminophen (paracetamol), primarily focus on pain relief without reducing inflammation. For localized pain relief, topical agents containing capsaicin or menthol can be applied directly to affected joints. These products work by blocking pain signals and providing temporary relief.
For managing rheumatoid arthritis, a more aggressive approach may be necessary. Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), such as methotrexate, are used to slow disease progression and prevent joint damage. Biologic therapies—targeting specific immune system proteins—are often combined with DMARDs for better control of inflammation. Corticosteroids, administered orally or via injections, are reserved for short-term use during flare-ups or severe symptoms, as long-term use can cause significant side effects.
In addition to medications, physical therapy plays a pivotal role in improving joint function. Therapists can recommend exercises and techniques to enhance joint mobility and strengthen surrounding muscles, which helps reduce pain and prevent further joint deterioration. Supportive devices like braces, splints, or cushions can also provide stabilization and relieve stress on affected joints.
Furthermore, adopting regular low-impact exercise routines such as swimming, walking, or cycling can support joint flexibility and overall health. Proper rest, managing stress, and avoiding activities that worsen joint pain are also critical components of arthritis management.
In conclusion, effective management of arthritis requires a multifaceted approach involving lifestyle changes, medications, and physical therapies tailored to individual conditions. Early intervention and consistent treatment adherence are key to maintaining joint function and improving quality of life for those living with arthritis.