Comprehensive Guide: Effective Strategies to Manage Rheumatoid Arthritis Symptoms and Improve Quality of Life
This detailed guide explores effective strategies for managing rheumatoid arthritis symptoms, emphasizing medication, physiotherapy, natural remedies, and lifestyle adjustments. Tailored treatment plans, regular monitoring, and healthy habits are critical for improving quality of life and preventing joint damage. Understanding and implementing these comprehensive approaches can help patients control pain, reduce inflammation, and maintain mobility, fostering a healthier, more active lifestyle despite the chronic nature of RA.
Comprehensive Strategies for Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis Symptoms
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by inflammation that primarily targets the joints. It is a complex condition that affects millions of people worldwide, leading to joint pain, swelling, stiffness, and potential disability if not managed effectively. While a permanent cure for RA has not yet been discovered, advances in medical treatments and lifestyle strategies have made it possible for patients to significantly reduce symptoms, maintain joint function, and enjoy a better quality of life. Understanding various management techniques and combining them appropriately can make a substantial difference in managing this debilitating disease.
In this comprehensive guide, we explore the most effective strategies to control rheumatoid arthritis symptoms, including medical treatments, physiotherapy, natural remedies, and lifestyle adjustments. The goal of these approaches is to alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, prevent joint damage, and support overall well-being.
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis and Its Impact
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system mistakenly attacks the synovial membrane— the lining of the joints. This attack leads to inflammation that causes swelling, pain, and eventually joint destruction if left untreated. RA can also affect other organs, such as the skin, eyes, lungs, and blood vessels, making it a systemic disease requiring comprehensive management.
The severity and progression of RA vary among individuals. Some people experience mild symptoms with periods of remission, while others face persistent and disabling joint deterioration. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment are crucial to control disease activity and prevent long-term damage.
Most Effective Strategies to Manage Rheumatoid Arthritis Symptoms
Successfully managing RA involves a multidisciplinary approach involving medication, therapy, lifestyle modifications, and supportive care. Here, we delve into each aspect in detail.
1. Pharmacological Treatments
Medications remain the cornerstone of RA management. They are designed to reduce inflammation, relieve pain, and slow disease progression. The choice of medications depends on disease severity, patient response, and existing health conditions.
NSAIDs (Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs): These are commonly used to provide quick relief from joint pain and inflammation. Examples include ibuprofen and naproxen. While effective for short-term relief, long-term use should be monitored due to potential gastrointestinal and cardiovascular side effects.
Analgesics: Pain relievers such as acetaminophen can be used to manage discomfort without affecting inflammation.
DMARDs (Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs): These drugs are key in controlling disease activity and preventing joint damage. Methotrexate is the most widely prescribed DMARD. Other options include sulfasalazine, leflunomide, and biologic agents like TNF inhibitors. DMARDs typically take several weeks to months to become effective and require regular monitoring for side effects.
Corticosteroids: Drugs like prednisone can sharply reduce inflammation and are often used during flare-ups or as a bridge therapy until DMARDs take effect. Long-term corticosteroid use should be minimized due to side effects such as osteoporosis and blood sugar imbalances.
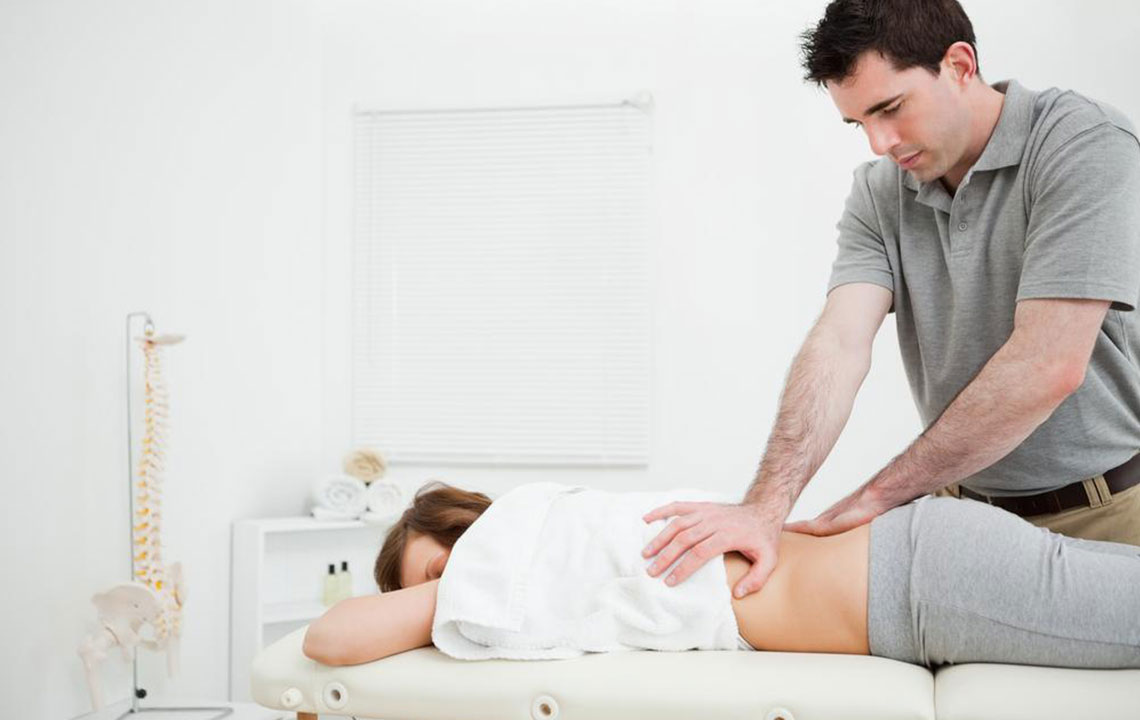
2. Physiotherapy and Supportive Care
Physical therapy plays a vital role in maintaining joint flexibility, strength, and function. Specific therapies include:
Hydrotherapy: Exercising in warm water helps reduce joint pain and stiffness while supporting gentle movement.
Occupational Therapy: Therapists assist in modifying daily activities, recommend ergonomic tools, and suggest splints to support weak joints, especially wrists and hands.
Stretching and Strengthening Exercises: Tailored exercises help preserve muscle strength around affected joints, improving stability and reducing strain.
Supportive devices like braces, orthotics, and custom footwear can also alleviate pain and prevent deformities.
3. Embracing Natural and Complementary Remedies
Alongside conventional medicine, natural remedies can help manage symptoms and improve overall well-being:
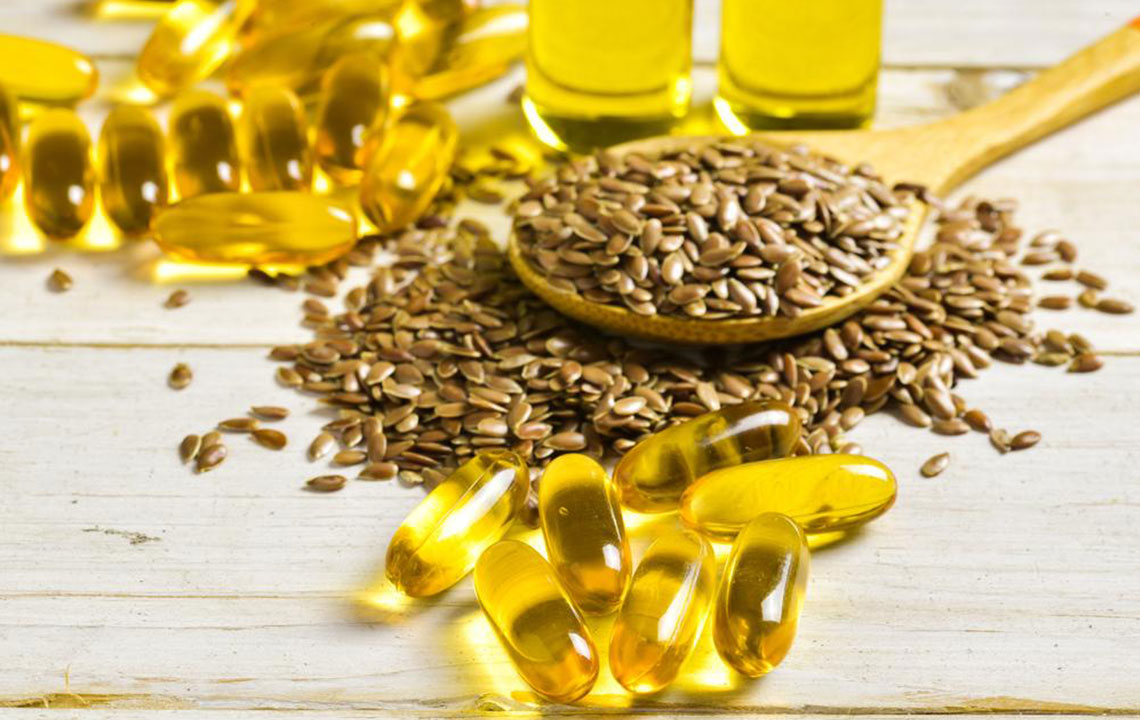
Supplements: Omega-3 fatty acids found in fish oil have anti-inflammatory properties that may support joint health. Other supplements like turmeric and ginger also have potential benefits, though scientific evidence varies.
Thermal Therapies: Hot packs or warm baths can relax stiff joints, while cold packs help reduce swelling and numb pain during flare-ups.
Massage Therapy: Gentle massages can alleviate muscle tension and promote relaxation around affected joints.
Always consult your healthcare provider before starting any natural supplement or therapy to ensure safety and compatibility with your medications.
4. Prioritizing Rest and Lifestyle Adjustments
Rest is crucial for managing RA effectively. Adequate sleep helps reduce inflammation, support immune function, and facilitate tissue repair. While rest is essential, moderate physical activity is also beneficial, helping to maintain joint mobility and prevent muscle atrophy.
Strategies for lifestyle modifications include:
Avoiding overexertion, which can exacerbate symptoms and cause fatigue.
Implementing a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods such as fruits, vegetables, nuts, and omega-3-rich fish.
Managing stress through mindfulness practices, meditation, or yoga, as stress can aggravate symptoms.
Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce stress on weight-bearing joints.
Pairing medication with these lifestyle changes ensures a holistic approach to managing joint health and enhancing overall quality of life.
The Importance of Personalized Treatment Plans
Since rheumatoid arthritis presents differently in each individual, a personalized treatment plan crafted in collaboration with rheumatologists, physiotherapists, and other healthcare professionals is essential. Regular monitoring and adjustments to therapy are necessary to adapt to disease progression and responses to treatment.
Patients should be proactive in communicating with their healthcare team, tracking symptoms, side effects, and functional ability. Early intervention during flare-ups can prevent significant joint damage, while long-term management focuses on maintaining mobility and reducing disability.
Conclusion
While rheumatoid arthritis remains a challenging condition, a comprehensive, individualized approach combining pharmaceutical treatments, physiotherapy, natural remedies, and lifestyle changes can significantly improve patient outcomes. Consistent management, regular medical follow-ups, and healthy habits empower patients to lead active, fulfilling lives despite the challenges of RA. Educating oneself about the disease and actively participating in treatment decisions is key to achieving optimal health and well-being.