Comprehensive Guide to Effective Back Pain Management and Treatment Strategies
This comprehensive article explores various effective strategies for managing and treating back pain. Covering everything from medication options, therapy techniques, natural remedies, to preventive tips, it offers valuable insights for those suffering from back discomfort. Understanding the causes and appropriate interventions can lead to improved quality of life, making this a must-read guide for anyone seeking relief from back pain and looking to maintain a healthy spine for years to come.

Comprehensive Guide to Effective Back Pain Management and Treatment Strategies
Back pain is a common health issue that affects millions of people worldwide, significantly impacting daily life and overall well-being. The causes of back discomfort are diverse, ranging from nerve impingement, muscle strains, to degenerative diseases such as osteoarthritis, herniated discs, and spinal stenosis. Understanding these underlying causes is crucial for selecting appropriate treatment options and managing symptoms effectively. This detailed guide explores various strategies for alleviating back pain, incorporating medical interventions, natural remedies, lifestyle changes, and preventive measures.
Back pain manifests in different forms, from a persistent dull ache to sharp, shooting pains that radiate down the legs or along the spine. Recognizing the symptoms early can help in seeking timely treatment, which can prevent chronic conditions and improve quality of life. Common symptoms include stiffness or tightness along the spine, persistent discomfort after prolonged sitting or standing, and pain that may extend from the lower back toward the buttocks or legs, depending on the severity and cause.
Understanding the Causes of Back Discomfort
Before diving into treatment options, it's beneficial to understand the different factors contributing to back pain. These include:
Muscle strains caused by improper lifting, sudden movements, or overuse.
Nerve issues, such as pinched nerves or disc herniations, leading to radiating pain and numbness.
Degenerative conditions like osteoarthritis or spinal disc deterioration.
Postural problems stemming from poor ergonomics during work or daily activities.
Structural abnormalities or injuries following accidents or trauma.
Medical and Pharmacological Interventions
Various medications and clinical therapies can help manage back pain. These treatments aim to reduce inflammation, ease muscle tension, and address nerve-related issues.
Over-the-counter pain relievers: Medications such as acetaminophen are frequently used for mild to moderate pain. They provide temporary relief without significant side effects when used as directed.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Drugs like ibuprofen and naproxen help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain, but should be taken cautiously after consulting a healthcare provider due to potential gastrointestinal and cardiovascular risks.
Topical treatments: Creams, gels, and sprays containing menthol, capsaicin, or methyl salicylate can provide localized relief by cooling or warming the affected area and reducing inflammation.
Advanced Therapeutic Approaches
For persistent or severe back discomfort, non-invasive and minimally invasive medical procedures offer additional relief. These include:
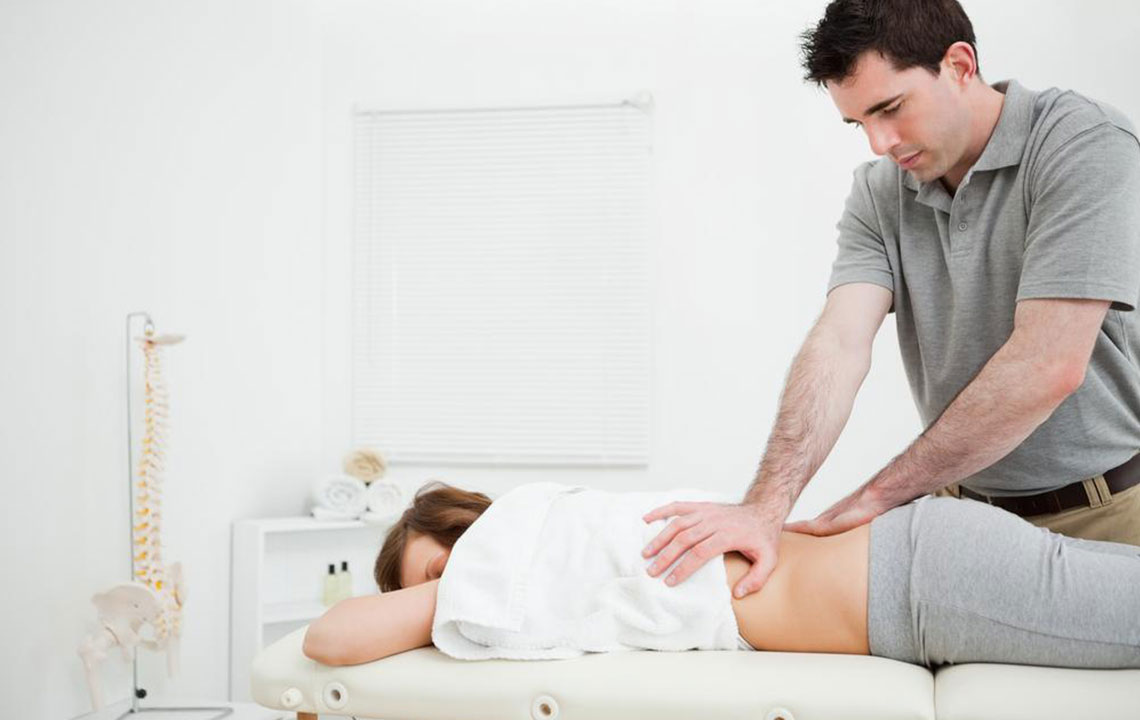
Chiropractic therapy: Focuses on spinal adjustments to restore proper alignment, reduce nerve compression, and promote natural healing pathways without surgery.
Bioelectric therapy: Utilizes electrical signals to interfere with pain transmission and stimulate the body to produce more endorphins, the natural painkillers.
Intradiscal electrothermal therapy (IDET): Applies controlled heat to damaged intervertebral discs to shrink fibers and deactivate nerve endings, thereby reducing pain.
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS): Delivers low-voltage electrical currents through electrodes placed on the skin to block pain signals, particularly effective for neuropathic symptoms.
Radiofrequency nucleoplasty: Uses electrical probes to disintegrate parts of a herniated disc, decreasing pressure on adjacent nerves and alleviating associated pain.
Surgical options: Procedures like laminectomy involve removing parts of the vertebra to decompress nerve roots. More advanced surgeries may include spinal fusion or artificial disc replacement based on severity.
Complementary and Natural Remedies
Incorporating natural treatment options can enhance overall recovery and provide ongoing relief. These include:
Heat and cold therapy: Applying ice packs in the initial 48 hours reduces swelling and numbs nerves, easing acute pain. After this period, moist heat such as warm compresses increases blood flow, relaxes muscles, and diminishes spasms.
Posture improvement: Ergonomic adjustments at workstations and proper posture during daily activities prevent undue strain on the back muscles and spine, reducing the risk of chronic pain.
Physical activity: Regular low-impact exercises like walking, swimming, or yoga strengthen back muscles, enhance flexibility, and support spinal health.
Diet and supplements: Maintaining a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, like fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids, can help reduce inflammation. Supplements such as glucosamine or chondroitin may support joint health.
Capsaicin application: Derived from hot peppers, capsaicin topical creams deplete substance P, a neurochemical involved in transmitting pain signals, providing prolonged relief for some sufferers.
Preventive Tips and Lifestyle Changes
Prevention is always better than cure. Adopting healthy habits and lifestyle changes can help prevent future back problems:
Engage in regular physical activity to keep muscles strong and flexible.
Maintain a healthy weight to reduce strain on your lower back.
Practice good ergonomics at work, including adjustable chairs and proper computer placement.
Avoid prolonged periods of sitting or standing without movement.
Lift heavy objects correctly by bending knees and keeping the back straight.
Invest in supportive mattresses and pillows to maintain proper spinal alignment during sleep.
When to Seek Professional Help
If back pain persists for more than a few weeks, worsens, or is accompanied by additional symptoms such as numbness, tingling, weakness in the legs, or loss of bladder or bowel control, it is vital to consult a healthcare provider promptly. Early diagnosis and tailored treatment plans can prevent the progression to chronic conditions and significantly improve outcomes.
Conclusion
Managing back discomfort requires a comprehensive approach that combines medical treatments, natural remedies, lifestyle modifications, and preventive strategies. Recognizing the signs early, understanding potential causes, and employing a combination of therapies can significantly enhance recovery and improve overall spinal health. Always consult healthcare professionals before starting new treatment modalities, especially if pain persists or worsens. Prioritizing back health today ensures mobility and comfort well into the future.