Comprehensive Guide to Humira: Uses, Administration, and Safety Insights
Humira, also known as adalimumab, is a biologic medication widely used to treat autoimmune diseases such as Crohn’s disease and rheumatoid arthritis. Delivered via self-injection, it helps control inflammation and manage symptoms. This comprehensive guide covers its uses, administration methods, potential side effects, and safety considerations, providing essential information for patients and healthcare providers alike. Proper adherence and medical oversight are key to maximizing benefits and ensuring safe treatment outcomes with Humira. Discover everything you need to know about this advanced biologic therapy.

Comprehensive Guide to Humira: Uses, Administration, and Safety Insights
Understanding What Humira Is
Humira, scientifically known as adalimumab, is a groundbreaking biologic medication formulated to mitigate pain and ease inflammation stemming from a variety of autoimmune diseases. Since its approval, Humira has become a cornerstone in managing conditions such as Crohn’s disease, juvenile idiopathic arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and psoriatic arthritis. Despite not offering a cure, Humira effectively controls symptoms and improves quality of life for many patients. It functions by specifically targeting proteins integral to the immune response, thereby reducing abnormal inflammation.
The advanced nature of Humira involves biotechnological processes where living organisms are genetically engineered to produce the medication. This makes Humira a sophisticated form of biologic therapy, distinguished from traditional pharmaceuticals by its complexity and targeted mechanism. Unlike oral medications that are broken down in the digestive system, Humira's design necessitates alternative delivery methods to preserve its effectiveness.
Methods of Humira Administration
Since Humira cannot be taken orally, it is administered through subcutaneous injections. Patients typically receive injections from prefilled syringes or pen devices, which they can self-administer at home after receiving proper training. The dosing schedule is usually once biweekly or monthly, depending on the specific condition and doctor’s prescription. The length of treatment varies, with some patients experiencing noticeable symptom relief within two weeks, while others may require up to three months for significant improvements.
Adherence to the prescribed injection schedule is vital for optimal disease control. Skipping doses or discontinuing treatment abruptly can impair immune function and potentially lead to disease flares. Regular injections help maintain steady medication levels, thereby controlling inflammation and alleviating pain more effectively.
Potential Side Effects and Safety Considerations
As a powerful immunosuppressant, Humira carries certain risks that need to be carefully managed. The suppression of immune activity means that users are more prone to infections, including respiratory, sinus, or urinary tract infections. It is important to monitor for signs of infection and consult healthcare providers promptly if symptoms arise.
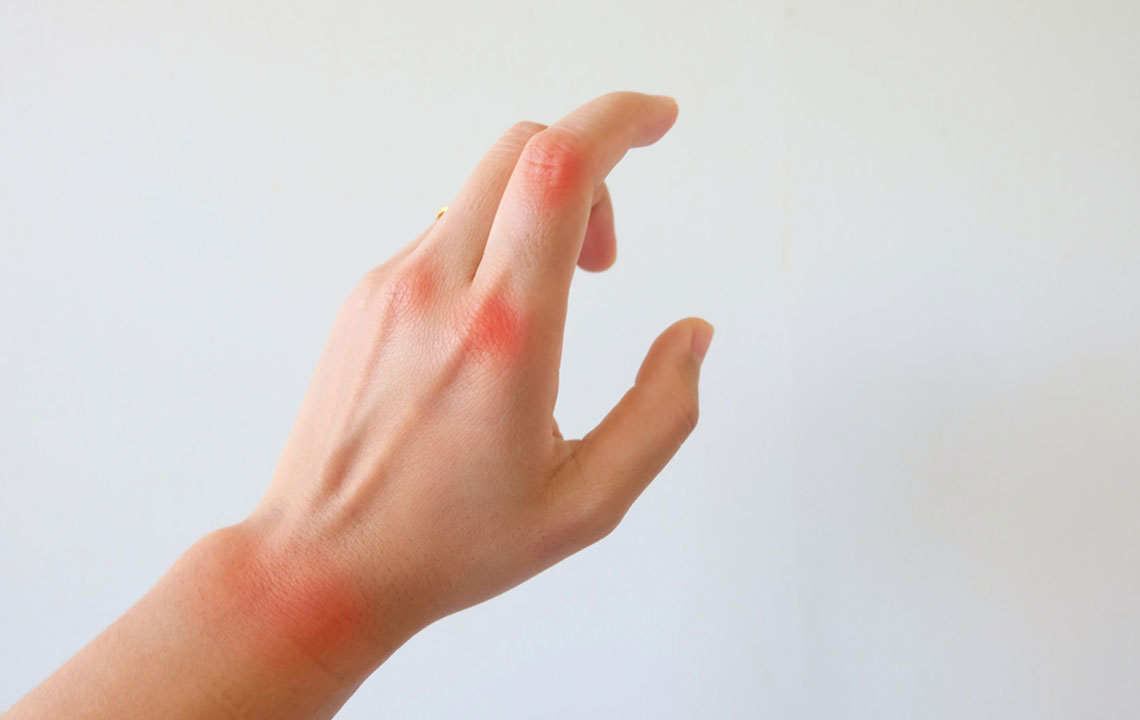
Injection site reactions are among the most common side effects, often presenting as redness, swelling, rash, bruising, or itching. These reactions typically resolve on their own but can occasionally require medical attention. Some individuals may also experience systemic side effects such as headaches or nausea during treatment.
Before starting Humira, patients should undergo thorough medical evaluation to determine suitability. Healthcare professionals will assess underlying health conditions and potential drug interactions to minimize risks. Regular monitoring throughout treatment ensures early detection of adverse effects and safe management of therapy.
In conclusion, Humira remains a vital therapy for many autoimmune conditions, providing effective symptom relief and disease management. However, understanding its administration methods, potential side effects, and safety considerations is crucial for optimizing outcomes and ensuring patient safety. Continuous communication with healthcare providers helps tailor treatment plans to individual needs, maximizing benefits while minimizing risks.