Comprehensive Guide to Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis Symptoms Effectively
This comprehensive guide explores effective strategies for managing rheumatoid arthritis symptoms. It covers early diagnosis, medication options including DMARDs and biologics, physical therapy, surgical interventions, dietary choices, and lifestyle modifications. By adopting a multi-faceted approach, patients can significantly improve their quality of life, reduce symptoms, and prevent joint damage. The article emphasizes personalized treatment plans and the importance of ongoing medical supervision, highlighting recent advancements that make RA management more effective and accessible. A must-read for those seeking to understand how to live well with RA.
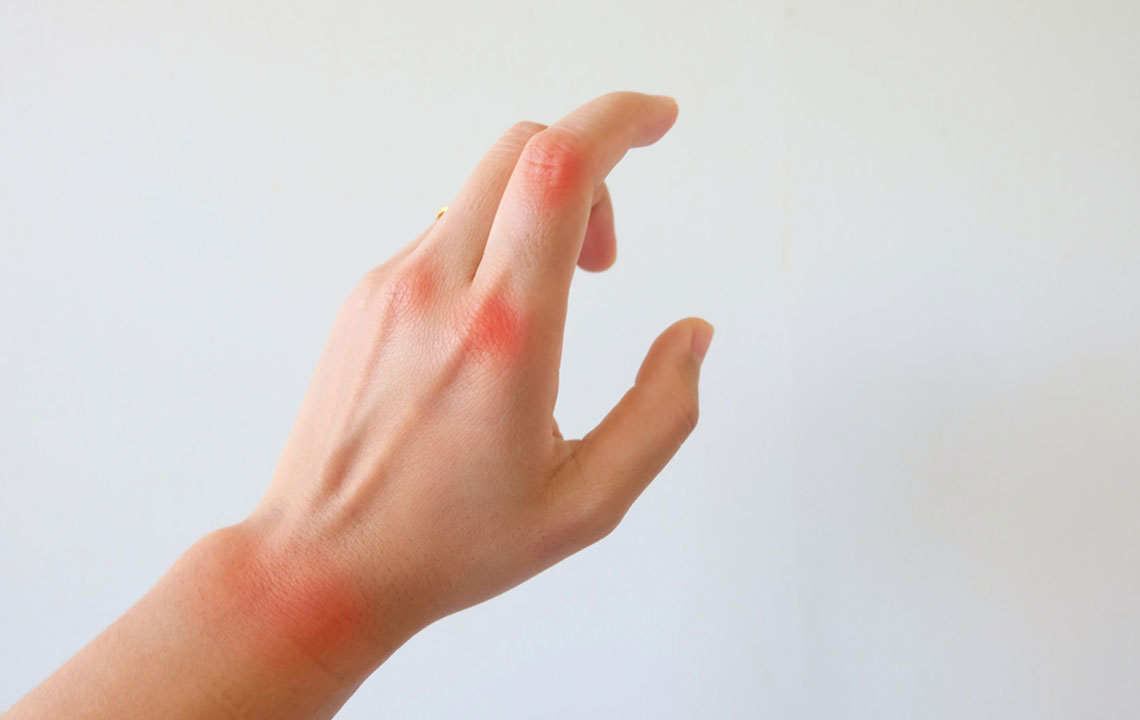
Comprehensive Strategies for Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis Symptoms
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the joints, causing inflammation, swelling, stiffness, and pain. It develops when the immune system mistakenly targets healthy joint tissues, leading to cartilage destruction and potential joint deformities if not managed properly. Although there is currently no cure for RA, early diagnosis and comprehensive management can significantly reduce symptoms, improve quality of life, and slow disease progression. Advances in medical treatments, lifestyle adjustments, and innovative therapies have transformed the outlook for individuals living with RA, enabling many to maintain active and fulfilling lives.
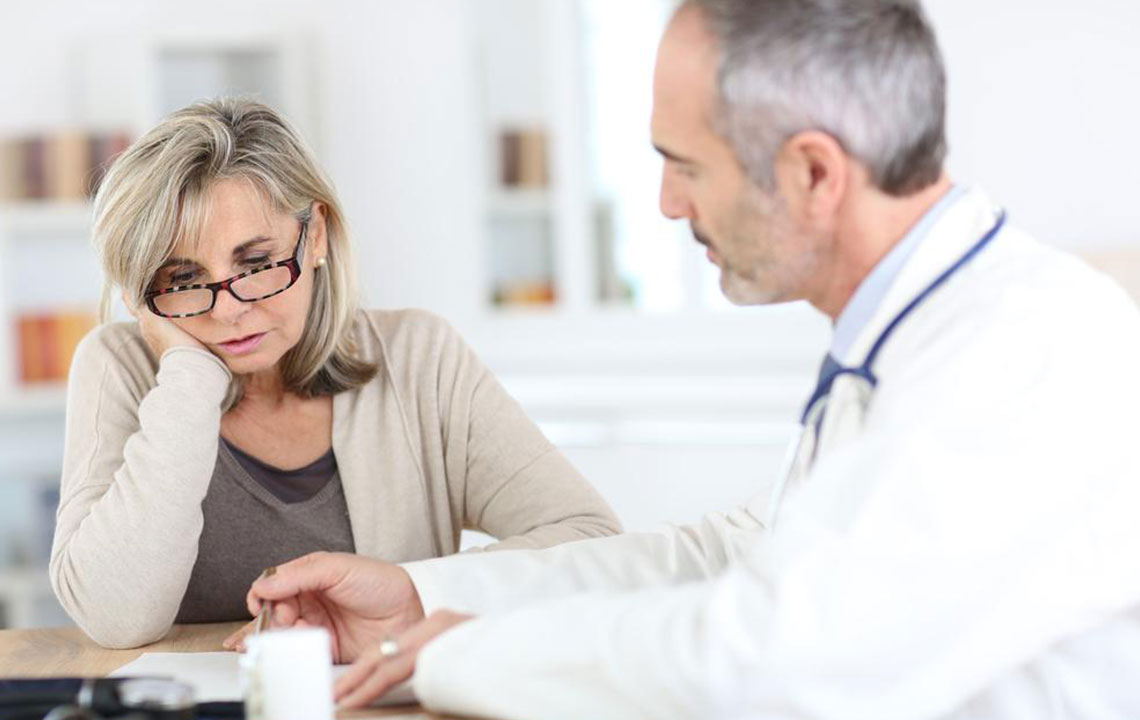
Understanding the importance of early intervention is vital. Early diagnosis allows for prompt initiation of treatment, which is crucial to prevent irreversible joint damage. The main goals of RA management include alleviating pain, reducing inflammation, maintaining joint function, and preventing deformities. This multi-faceted approach combines pharmaceutical interventions, physical therapy, surgical options in severe cases, and lifestyle modifications, all tailored to each patient's unique condition and needs.
Pharmacological treatment remains the cornerstone of RA management. Patients are generally prescribed disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), which work to slow or halt disease progression by targeting the immune system's abnormal activity. Traditional DMARDs, such as methotrexate, are often used in conjunction with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and corticosteroids to control acute symptoms. However, these medications can have side effects, including liver toxicity, increased risk of infections, or vision problems, necessitating close medical supervision.
In recent years, biologic therapies have revolutionized RA treatment. These injectable or infusion-based medications specifically target inflammatory pathways involved in RA, such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) inhibitors and interleukin blockers. Biologics often provide better symptom control, particularly for patients who do not respond adequately to traditional DMARDs. The selection of therapy depends on factors like disease severity, comorbidities, and patient preferences, making personalized treatment plans essential.
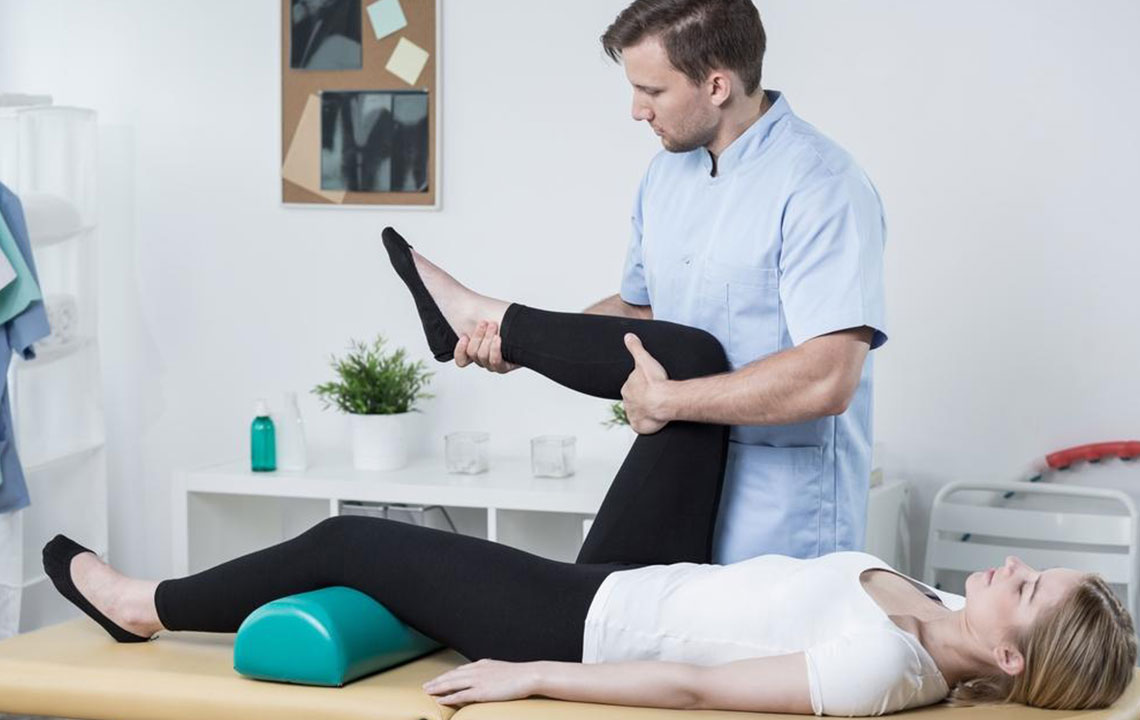
In addition to medications, physical therapy plays a key role in maintaining joint function and mobility. Rehabilitation specialists design exercise regimens that enhance flexibility, strength, and cardiovascular health while minimizing joint strain. Regular exercise, including low-impact activities like swimming, walking, and yoga, helps reduce stiffness and improve overall physical condition. Stress management techniques, such as meditation and deep-breathing exercises, can also help alleviate symptoms since emotional stress can exacerbate inflammation.
Surgical intervention is considered when joint damage has caused severe deformities or loss of function, despite medical therapy. Procedures such as joint replacement surgeries can restore mobility and relieve pain, significantly improving patients’ quality of life. Surgical options are carefully evaluated, with the goal of providing long-term functional improvement while minimizing risks.
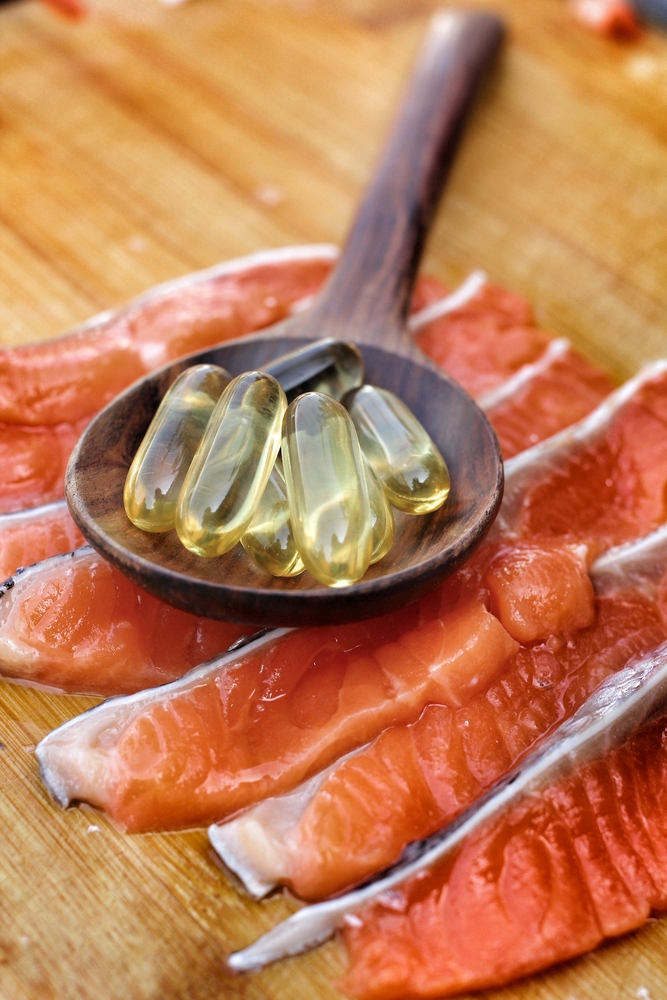
Dietary choices significantly influence joint health. A balanced, anti-inflammatory diet rich in antioxidants supports overall well-being and may help reduce disease activity. The Mediterranean diet, in particular, emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, healthy fats, and lean proteins, contributing to reduced inflammation. Nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish, have been shown to possess anti-inflammatory properties. Maintaining a healthy weight alleviates extra stress on joints, further easing symptoms.
Adopting healthy lifestyle habits is essential in managing RA effectively. Regular physical activity not only improves joint function but also boosts mood and energy levels. Adequate rest and sleep are crucial for recovery and reducing fatigue. Avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol consumption can reduce inflammation and lower the risk of comorbid conditions. Patients are encouraged to work closely with healthcare providers to develop an individualized treatment plan that includes medication, physical activity, diet, and stress management strategies.
In summary, managing rheumatoid arthritis requires a comprehensive, multi-disciplinary approach. Advancements in pharmacological therapies, personalized care, and lifestyle modifications have significantly improved patient outcomes. With early diagnosis, ongoing treatment, and proactive lifestyle choices, individuals living with RA can enjoy better pain control, improved mobility, and a higher overall quality of life. Continued research and innovation hold promise for even more effective management options in the future, making it possible for patients to lead active and healthier lives despite the challenges of this autoimmune disorder.