Comprehensive Guide to Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis: Treatments and Medications
This comprehensive guide covers the latest treatments and medications for managing rheumatoid arthritis. It emphasizes the importance of combined therapies, lifestyle modifications, and surgical options for effective disease control. Early diagnosis and personalized treatment plans are crucial for improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis: Effective Treatments and Medications
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis and Its Management Strategies
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a complex, chronic autoimmune disorder characterized by persistent inflammation that primarily targets the joints but can also affect other organs and systems in the body. It is a condition in which the immune system, which normally defends the body against infections, mistakenly attacks the body's own tissues, causing joint damage, swelling, and pain. RA typically starts in small joints such as those in the hands and feet, gradually spreading to larger joints and other parts of the body over time. Although there is currently no known cure for rheumatoid arthritis, early diagnosis combined with effective management strategies can significantly curb disease progression, alleviate symptoms, and improve patient quality of life.
Strategies for Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis Effectively
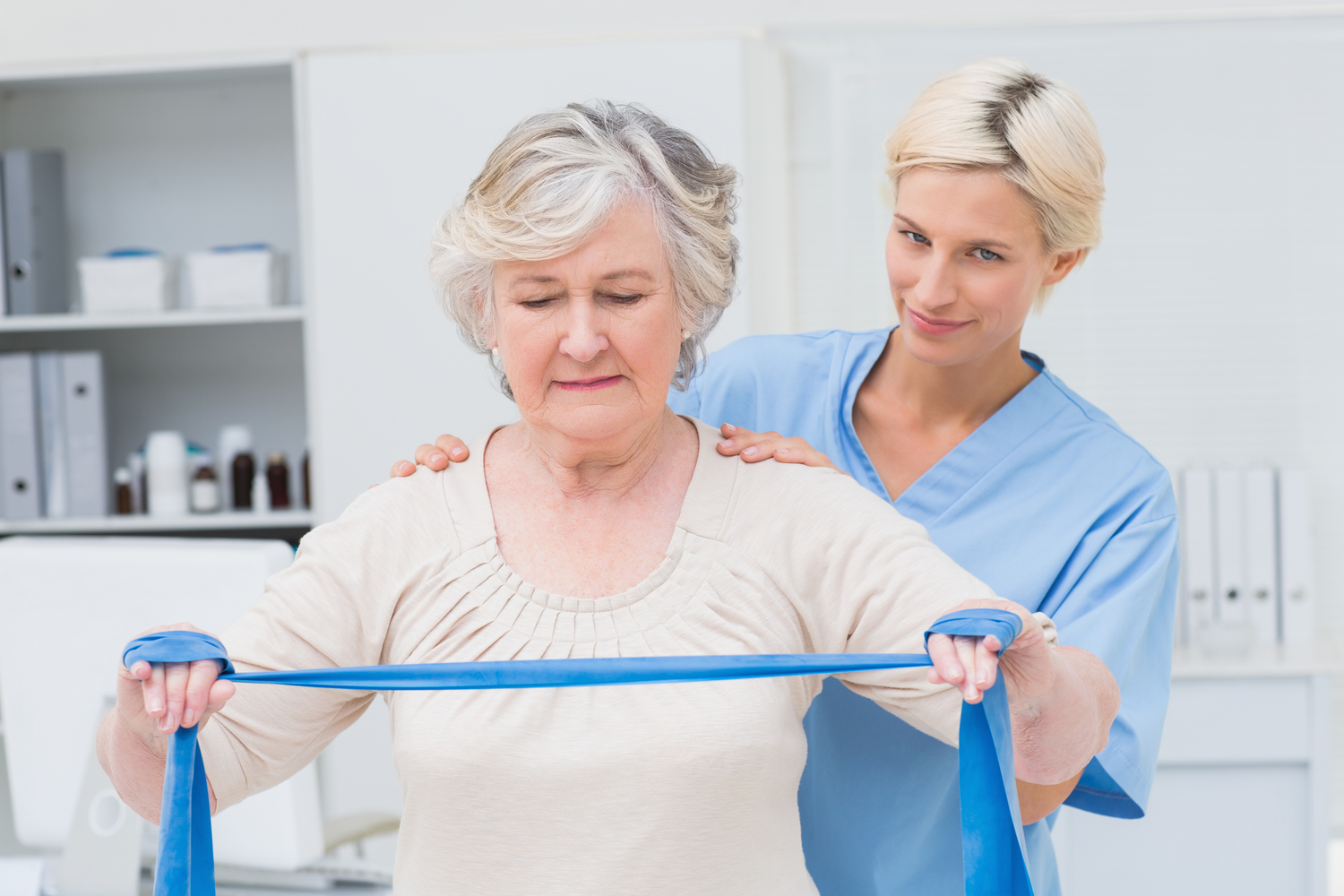
Physical Therapy: An essential component in RA management, physical therapy aims to preserve and enhance joint function and mobility. Specialized exercises are designed by licensed physiotherapists to strengthen muscles, improve joint flexibility, and reduce stiffness. Physical therapy also helps in reducing fatigue, managing pain, and preventing joint deformities. Patients often learn techniques to protect their joints during daily activities, which can significantly decrease disease impact over time.
Occupational Therapy: This therapy focuses on enabling patients to maintain independence by adapting their daily routines and environments. Occupational therapists provide tailored strategies and recommend adaptive devices to ease tasks like dressing, cooking, cleaning, and bathing. These interventions help minimize physical strain, prevent further joint damage, and improve overall well-being, especially during flare-ups or advanced stages of RA.
Surgical Interventions: When conservative treatments are insufficient to control joint damage or pain, surgical options may be considered. Surgeries such as joint repair, synovectomy (removal of inflamed joint lining), or joint replacement (arthroplasty) can restore joint function and relieve persistent pain. Surgical procedures are generally reserved for cases with severe joint destruction or deformity, and they are performed after thorough assessment and consideration of potential risks and benefits.
Medications Used in Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment
H.P. Acthar® (Corticotropin): A hormone-based therapy that stimulates natural steroid production to reduce inflammation and symptoms. While effective for symptom relief, it is not a cure for RA but often used during flares or as an adjunct treatment.
CUPRIMINE® (Azathioprine): An immunosuppressant drug reserved for severe or refractory cases. It helps modulate the immune response to prevent joint damage but is typically not approved for juvenile rheumatoid arthritis due to its potent immunosuppressive effects.
REMICADE® (Infliximab): A biologic therapy that targets tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), a substance involved in systemic inflammation. Administered via infusion, Remicade is often used when traditional DMARDs (Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs) fail to control symptoms.
HUMIRA® (Adalimumab): Another anti-TNF biologic that neutralizes TNF-α to reduce inflammation and joint destruction. While highly effective, it carries an increased risk of infections due to immune suppression and requires careful monitoring.
Enbrel® (Etanercept): A biologic agent similar to Humira, it inhibits TNF-α and helps improve joint symptoms. Enbrel is also approved for treating psoriasis and other autoimmune conditions, including in pediatric patients older than 4 years.
SIMPONI® (Golimumab): A biologic drug used in combination with methotrexate to suppress inflammatory mediators. Like other biologics, it can increase susceptibility to infections, necessitating vigilant healthcare supervision.
In addition to pharmaceutical treatments, lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular low-impact exercise, and avoiding joint stress, can enhance overall management. Some patients find relief through complementary therapies and home remedies, but these should always complement, not replace, professional medical advice. Regular consultations with healthcare providers are crucial for personalized treatment plans, ongoing assessment, and adjustment of therapies to optimize outcomes. While rheumatoid arthritis long-term remission remains a challenge, a comprehensive approach combining medications, therapy, and lifestyle adjustments can considerably improve daily functioning and quality of life. Always seek guidance from healthcare professionals before starting new treatments or alternative remedies.