Comprehensive Guide to Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis and Gout Effectively
This comprehensive guide explores effective strategies for managing rheumatoid arthritis and gout, emphasizing early diagnosis, medication options, and lifestyle modifications. It highlights the importance of tailored treatment plans, supportive therapies, and dietary adjustments to improve quality of life for individuals dealing with these inflammatory joint conditions. Whether dealing with acute attacks or long-term management, understanding these approaches enables better disease control and joint health preservation.
Effective Approaches to Diagnose and Treat Rheumatoid Arthritis and Gout
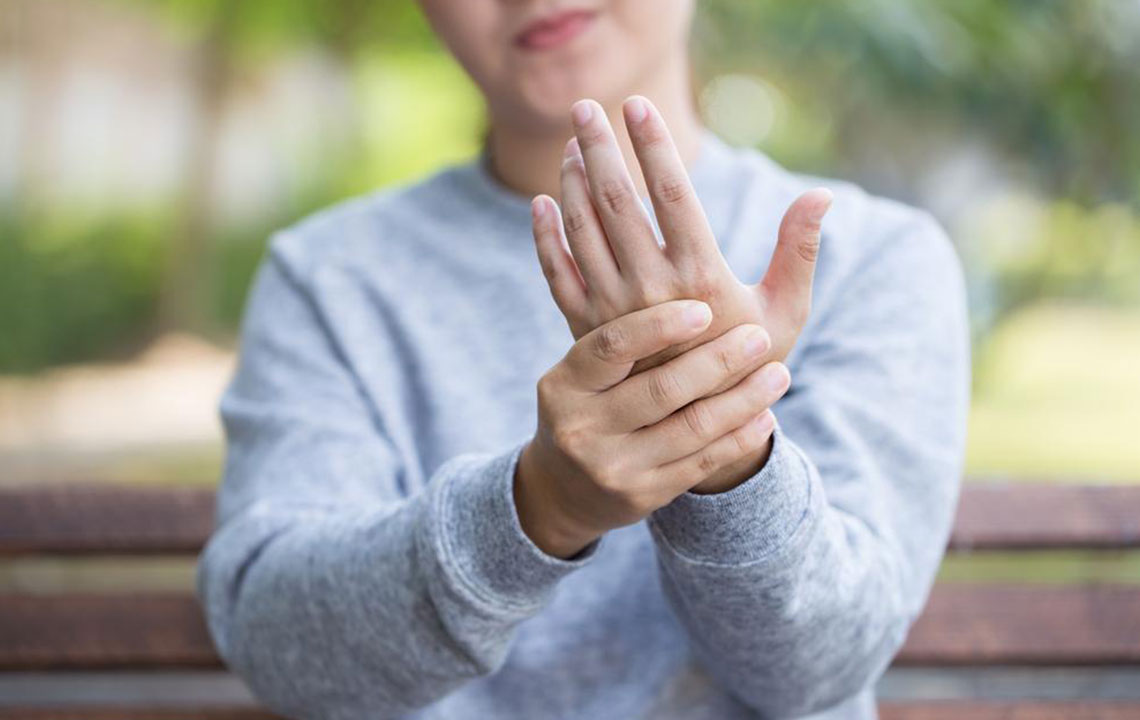
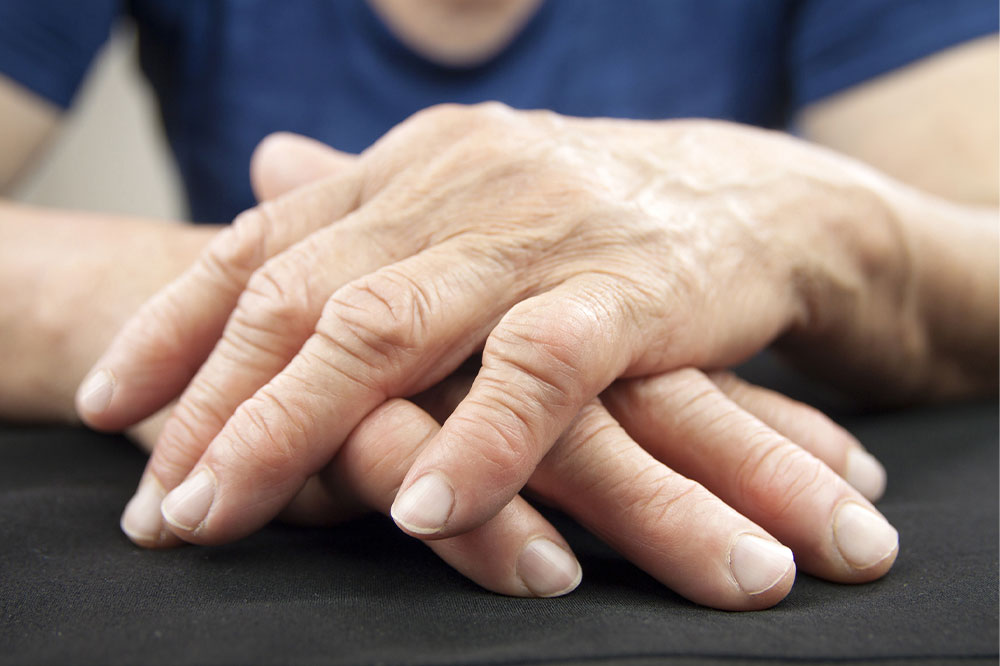
Recent medical research indicates that the simultaneous occurrence of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and gout is more prevalent than previously recognized. RA is an autoimmune inflammatory disorder that primarily targets the joints, leading to chronic pain, swelling, stiffness, and potential deformity if left untreated. Gout, on the other hand, results from an accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints, causing sudden and severe episodes of pain, redness, and swelling. Both conditions involve inflammation, often complicating clinical diagnosis, as their symptoms can overlap or differ depending on individual cases.
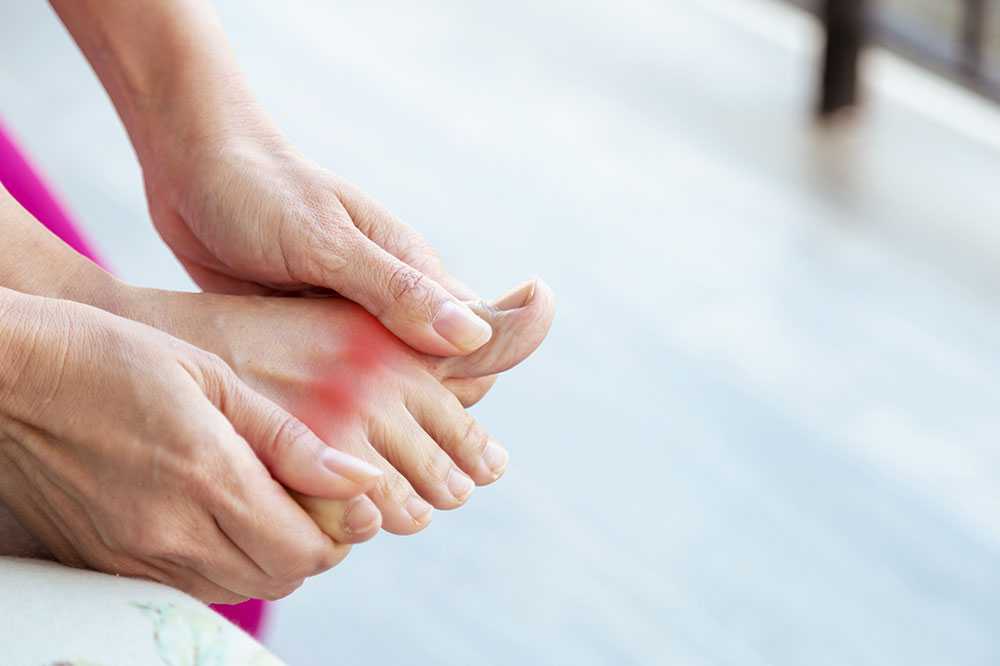
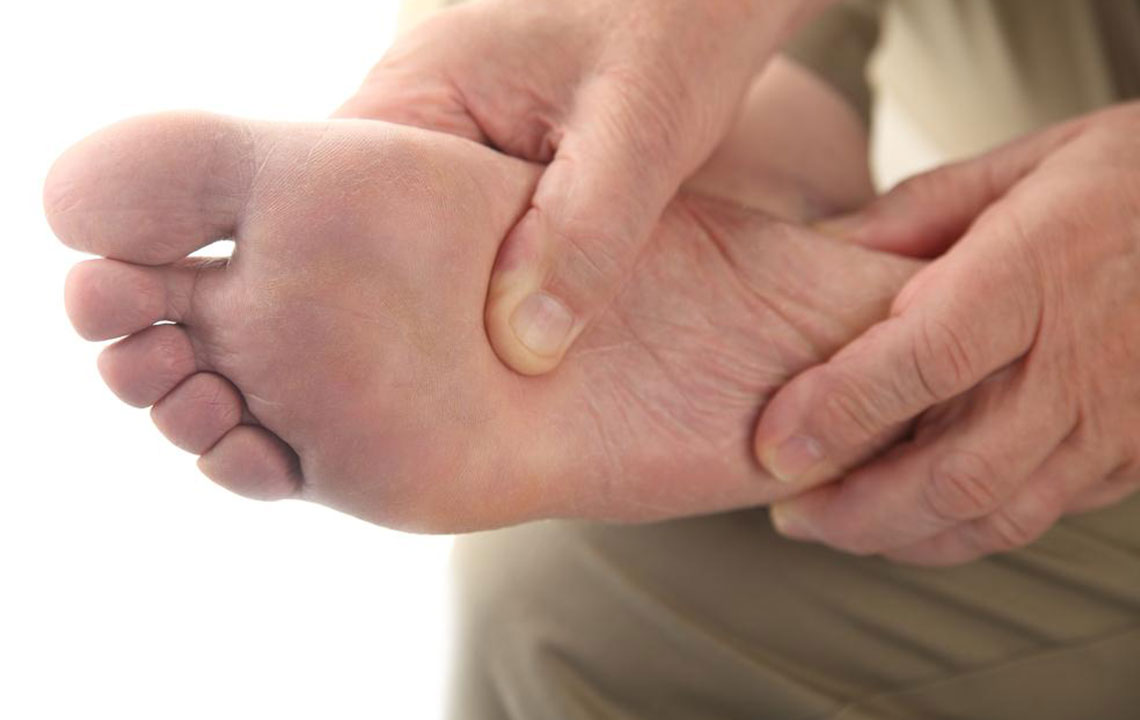
Studies have shown that men are statistically more likely to develop both rheumatoid arthritis and gout at the same time, emphasizing the importance of awareness and early detection. Recognizing subtle signs such as the deposits of uric acid crystals at the base of the big toe, wrist, or finger joints is essential for prompt diagnosis. While gout typically causes marked redness, swelling, and warmth over the affected joints, RA may present with symmetrical joint stiffness without prominent redness, especially in early stages. Accurate diagnosis involves a combination of physical examination, blood tests measuring uric acid and inflammatory markers, and joint fluid analysis to identify crystal deposits or autoimmune activity.
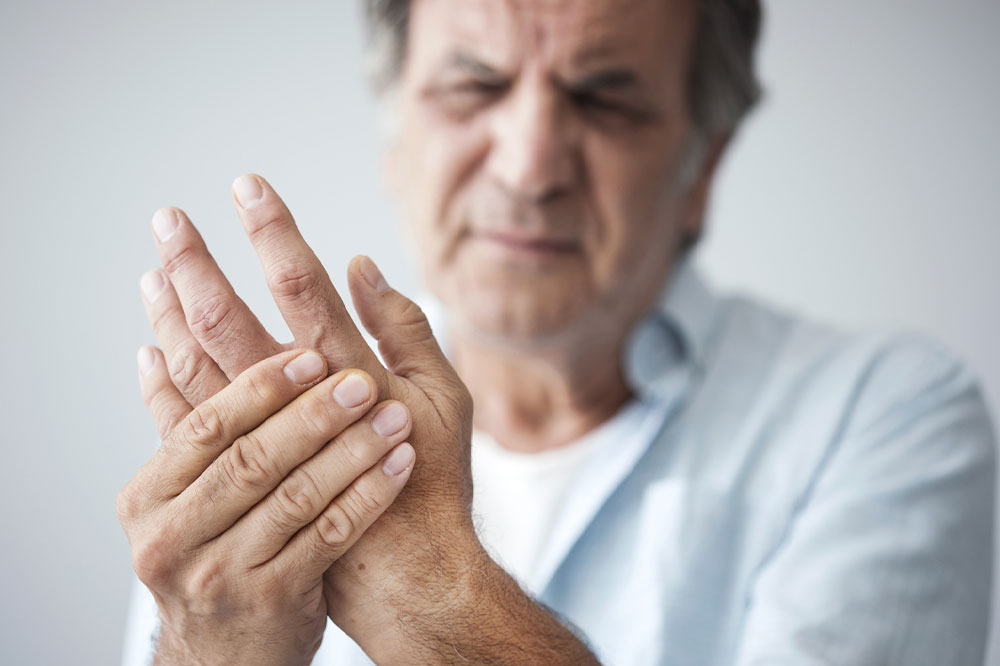
Effective management hinges on proper identification of symptoms and tailored treatment plans. The approach to treatment varies according to whether the patient is dealing with gout, RA, or both. Gout affects approximately 4% of the population and requires immediate intervention during acute attacks. Medications are often categorized into short-term relief agents and long-term preventive drugs. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen and naproxen are frontline options used to alleviate pain and inflammation during flare-ups, especially when taken at the first sign of symptoms. Corticosteroids can be administered externally or systemically under medical supervision to rapidly reduce joint inflammation and swelling.
Another cornerstone of gout treatment includes colchicine, a plant-derived medication with a long history of use in managing gout attacks. It effectively reduces pain and prevents the formation of new uric acid crystals, helping break the cycle of recurring episodes. For long-term management, urate-lowering therapies like allopurinol or febuxostat are prescribed to maintain uric acid levels below the crystal-forming threshold and prevent future gout attacks.
Rheumatoid arthritis management involves disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) such as methotrexate, sulfasalazine, and biologic agents like TNF inhibitors, which aim to slow disease progression, reduce joint damage, and improve functional capacity. NSAIDs are also used to control symptoms and provide symptomatic relief, but they do not prevent joint destruction. Early initiation of comprehensive treatment is vital to preserve joint integrity and enhance quality of life for RA patients.
Complementary and Lifestyle Strategies for Better Disease Control
Beyond medication, various supportive therapies and lifestyle modifications play an essential role in managing rheumatoid arthritis and gout effectively. Physiotherapy, including tailored exercises, helps improve joint mobility, strength, and flexibility. Massages can provide relief from muscular tension caused by joint pain. Practices like yoga, tai chi, and meditation reduce stress, which is known to exacerbate inflammatory conditions, thereby helping manage flare-ups.
Low-impact exercises such as swimming, walking, or cycling strengthen muscles around affected joints without putting excessive strain on them. Applying heat packs can relax stiff joints, while cold therapy helps diminish swelling and reduce pain during acute flare-ups. Maintaining a balanced diet that emphasizes healthy fats—like omega-3 fatty acids from fish oils, nuts, and seeds—supports overall joint health and reduces inflammation.
Individuals affected by gout should limit high-purine foods such as red meats, seafood, and alcohol, which elevate uric acid levels. Hydration is equally crucial; drinking plenty of water helps flush out excess uric acid. Weight loss, when necessary, can significantly decrease joint stress and lower uric acid levels, further reducing attack frequency and severity.
Combining these lifestyle modifications with appropriate medical management provides a holistic approach that can significantly improve patients' quality of life. Regular monitoring with healthcare providers ensures treatment plans are adjusted to achieve optimal outcomes and minimize long-term joint damage.