Comprehensive Guide to Preventing Herpes Transmission and Protecting Your Health
Learn comprehensive strategies to prevent herpes transmission effectively. This detailed guide covers hygiene practices, safe sexual behavior, medication options, and communication tips to help individuals minimize the risk of spreading herpes and protect their health and loved ones. Whether you have herpes or want to prevent its spread, adopting these proven measures ensures safety and peace of mind.
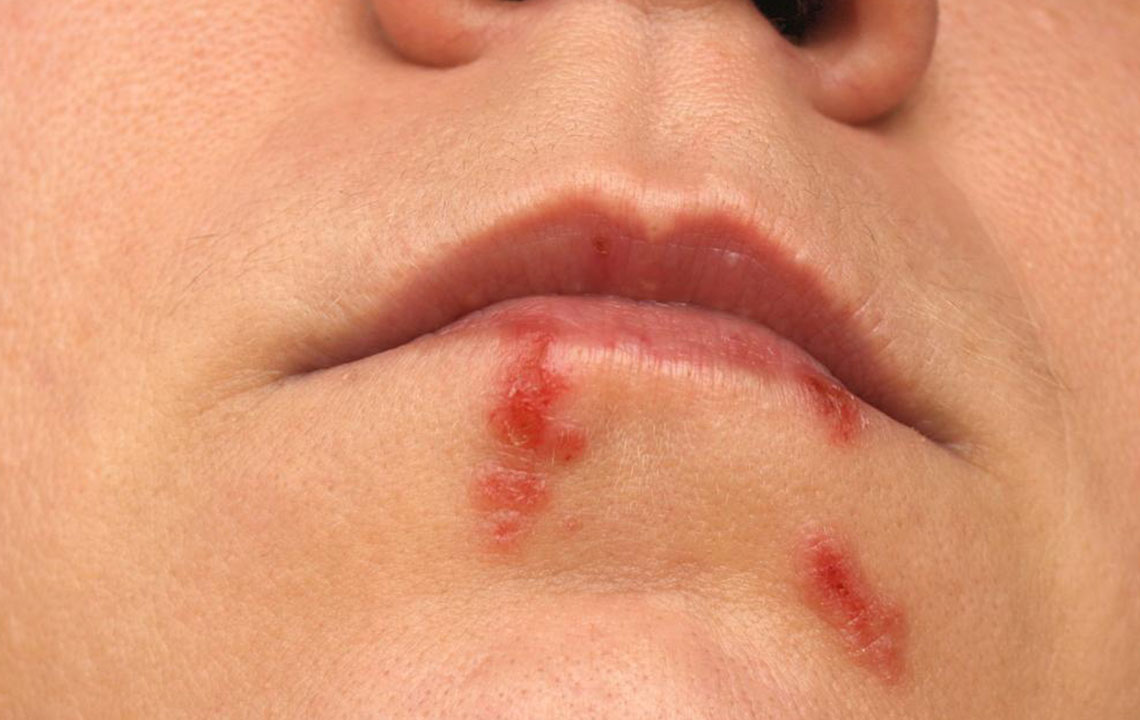
Comprehensive Strategies to Effectively Prevent Herpes Transmission
Herpes simplex virus (HSV) is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections worldwide, affecting millions of individuals across all age groups. Despite its prevalence, many people remain unaware of the effective methods to prevent its transmission. Living with herpes requires a combination of awareness, responsible behavior, and proactive health measures to minimize the risk of spreading the virus to partners, children, or others in your environment. In this detailed guide, we will explore proven strategies, practical tips, and hygiene practices that can significantly reduce the chances of HSV transmission, ensuring you maintain good health and safeguard those around you.
Understanding Herpes and Its Transmission
Herpes is caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV), which exists in two main types: HSV-1, primarily responsible for oral herpes, and HSV-2, mostly causing genital herpes. The virus is highly contagious and can be transmitted through direct contact with infected skin, mucous membranes, or bodily fluids. HSV can spread even when sores are not visible, making precautionary measures essential at all times.
Sometimes, herpes can be spread through casual contact, such as kissing, oral sex, or genital contact with an infected partner. The virus is resilient, and droplets of saliva, skin contact, or contact with contaminated surfaces can all facilitate transmission. Being aware of these transfer routes is vital for effective prevention.
Effective Prevention Strategies
1. Avoid Sexual Contact During outbreaks: The most straightforward way to prevent spread is to abstain from any sexual activity when experiencing active herpes sores or symptoms such as tingling, burning, or pain. Herpes is most contagious during outbreaks, but it can still be transmitted when no symptoms are present. Waiting until sores are fully healed decreases the risk significantly.
2. Use of Barrier Protection: Consistently using barrier methods such as latex or polyurethane condoms and dental dams during sexual contact provides a reliable layer of protection. While not foolproof, barriers greatly reduce exposure to infected skin or mucous membranes, especially in areas that are difficult to cover, such as the genital and oral regions.
3. Regular Communication with Partners: Being open about your herpes status with sexual partners fosters honesty and shared responsibility. Educate your partners about herpes transmission, signs, and preventive measures. Encourage testing and mutual understanding to minimize unintentional transmission.
4. Daily Antiviral Medication: If diagnosed with herpes, your healthcare provider may recommend daily antiviral medication, such as acyclovir, valacyclovir, or famciclovir. These medications help lower the frequency of outbreaks and reduce viral shedding, thereby decreasing the risk of transmission.
5. Proper Hygiene and Care of Sores: Maintaining impeccable hygiene is crucial. Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water after touching sores or lesions. Avoid touching or scratching herpes blisters to prevent spreading the virus to other parts of your body or to others. Covering sores with breathable clothing or dressings can also prevent accidental contact.
6. Avoiding Saliva Exchange: Herpes can be transmitted through saliva, so avoid kissing or sharing utensils, lip balms, or drinks when you or your partner has oral herpes. Special caution should be exercised during outbreaks or when symptoms are present.
7. Stay Informed and Monitor Symptoms: Familiarize yourself with herpes symptoms so you can detect outbreaks early. Early intervention with antiviral medication can reduce the severity and duration of outbreaks, further decreasing the risk of transmission.
Additional Precautions and Considerations
Herpes transmission is influenced by several factors. For example, individuals infected with herpes are twice as likely to acquire HIV due to compromised skin integrity and inflammation. Conversely, co-infection with HIV can increase the infectiousness of herpes outbreaks. To safeguard your health, it is essential to consider comprehensive measures, including regular health checkups, STI testing, and safe sexual practices.
In situations involving close contact, such as with children or vulnerable populations, minimize physical contact during active outbreaks or when symptoms are present. This prevents inadvertent transmission, especially in households or caregiving environments.
Lastly, remember that herpes is a manageable condition. With appropriate precautions, medication, and communication, individuals living with herpes can lead healthy, fulfilling lives without transmitting the virus to others.
Protecting yourself and loved ones from herpes requires consistent effort and awareness. By understanding the transmission routes and implementing effective preventive strategies, you can greatly reduce your risk and promote safer sexual and social behaviors. Remember, open communication, proper hygiene, and medical support are key components in managing herpes responsibly and avoiding unintentional spread. Stay informed, stay safe, and prioritize your health and the well-being of those around you.