Comprehensive Guide to Preventing the Spread of Genital Herpes
This comprehensive article discusses effective strategies to prevent the transmission of genital herpes. It covers causes, spread mechanisms, and detailed preventive measures, including condom use, regular testing, and antiviral medication. Empower yourself with knowledge to minimize risks and maintain sexual health. Proper understanding and responsible practices are crucial in reducing herpes transmission and promoting safe sexual behaviors.
Comprehensive Strategies for Preventing Genital Herpes Transmission
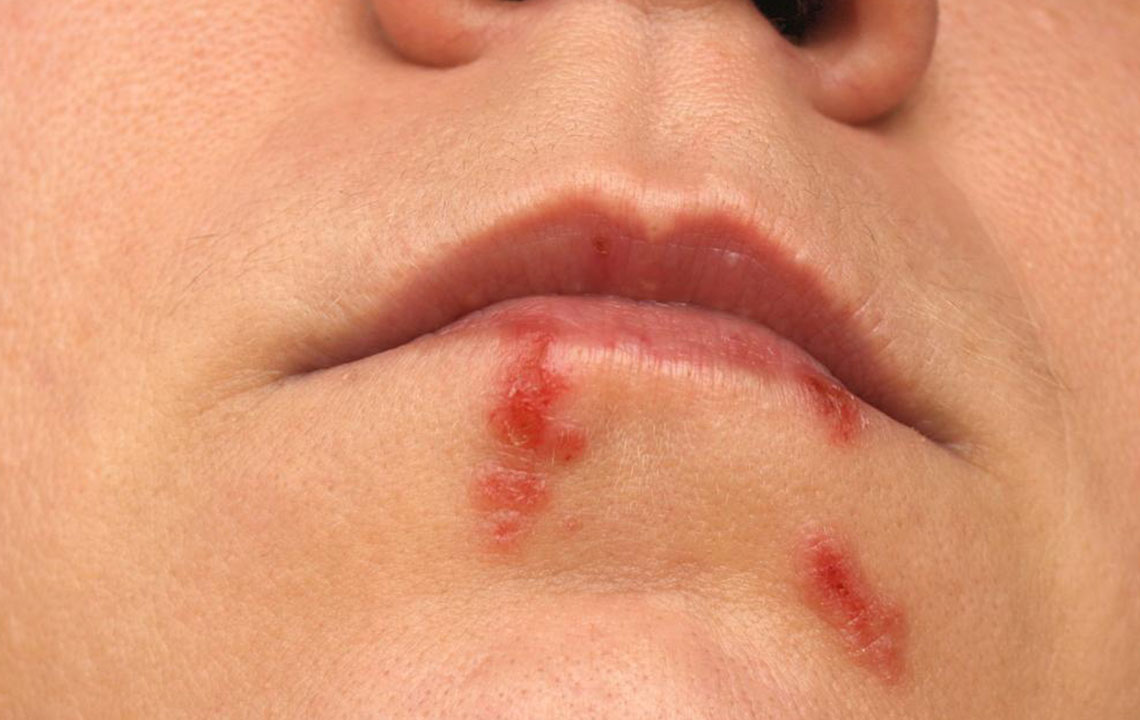
Genital herpes stands as one of the most prevalent sexually transmitted infections (STIs) worldwide, affecting millions of people regardless of age or background. This viral infection is primarily caused by the herpes simplex viruses, specifically Herpes Simplex Virus types 1 (HSV-1) and 2 (HSV-2). Both viruses can infect the genital area through various forms of sexual contact, leading to uncomfortable symptoms, including painful sores and blisters. These lesions may rupture, releasing infectious fluid that can spread the virus further, making management and prevention critical aspects of sexual health.
Understanding the nature of genital herpes and adopting effective prevention strategies can significantly reduce the risk of transmission. This comprehensive guide will delve into the causes of genital herpes, the way it spreads, and the most reliable preventive practices to safeguard yourself and your partners.
Understanding Genital Herpes and Its Causes
Herpes simplex viruses are highly contagious viruses that establish lifelong infections in their hosts. HSV-1 is traditionally associated with oral herpes, often manifesting as cold sores around the mouth, but it can also cause genital infections through oral-genital contact. HSV-2 predominantly causes genital herpes but can sometimes affect oral areas. Once infected, individuals may experience recurrent outbreaks or remain asymptomatic, unknowingly transmitting the virus.
The Spread of Genital Herpes
Genital herpes transmits primarily through sexual contact, including vaginal, oral, and anal sex. The virus can spread even when the infected person shows no symptoms, due to asymptomatic viral shedding. The highest risk occurs during active outbreaks when sores are visible, but transmission can also occur when no symptoms are present. Contact with infected skin, mucous membranes, or bodily fluids facilitates the spread. Additionally, other factors like compromised immune systems or skin abrasions increase susceptibility.
Effective Preventive Measures Against Genital Herpes
Preventing the transmission of genital herpes requires a multi-faceted approach, emphasizing safe sexual practices, open communication, and regular healthcare consultations. Here are the most effective strategies:
Consistent Condom Use: Using latex or polyurethane condoms during all forms of sexual activity greatly reduces the risk of herpes transmission. While condoms do not cover all infected areas, they significantly limit exposure to infected secretions and skin contact.
Regular STD Testing and Screening: Routine testing for STDs, including herpes, is vital, especially if you have multiple partners or new partners. Early detection allows for timely management and reduces the possibility of unknowingly infecting others.
Open Communication with Partners: Discussing sexual health history with partners helps establish trust and awareness. Knowing whether your partner has herpes or other STIs enables informed decision-making and appropriate precautions.
Limiting Number of Sexual Partners: Reducing sexual partners minimizes exposure risk. Monogamous relationships with an uninfected partner are one of the safest options.
Avoiding Contact During Outbreaks: Refraining from sexual activity when either partner shows symptoms or active sores prevents virus transmission during contagious periods.
Use of Antiviral Medication: For individuals diagnosed with herpes, antiviral drugs such as acyclovir, valacyclovir, or famciclovir can suppress outbreaks and reduce the likelihood of transmission. Consult a healthcare provider for personalized treatment options.
Applying Extra Precautions During High-Risk Times: Increased caution during outbreaks, or when symptoms are present, is crucial to prevent spreading the virus.
Additional Tips for Reducing Herpes Transmission Risks
While following the primary preventive measures is highly effective, additional practices can further diminish risk:
Avoiding Sharing Personal Items: Do not share towels, underwear, or sex toys that may be contaminated with the virus.
Maintaining Good Personal Hygiene: Proper hygiene practices help prevent additional skin abrasions that can facilitate viral entry.
Educating Yourself and Partners: Understanding herpes transmission, asymptomatic shedding, and preventive practices empowers responsible decision-making.
When to Seek Medical Advice
If you notice symptoms such as painful sores, blisters, or other unusual genital discomfort, consult a healthcare professional promptly. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential for managing outbreaks, reducing symptoms, and minimizing transmission risk. Remember, even in the absence of symptoms, regular STI screening is crucial, especially if you have multiple sexual partners or engage in unprotected sex.
Final Thoughts on Herpes Prevention
Preventing the spread of genital herpes is achievable through informed choices and responsible behavior. Using barrier protection methods like condoms, maintaining open communication with partners, and adhering to medical advice for antiviral therapy are key components of effective prevention. Educating yourself about asymptomatic viral shedding and risk factors helps you make safer sexual decisions. While herpes remains a manageable condition with proper care, consistent preventive efforts are vital to reduce its transmission and protect your health and that of your partners.