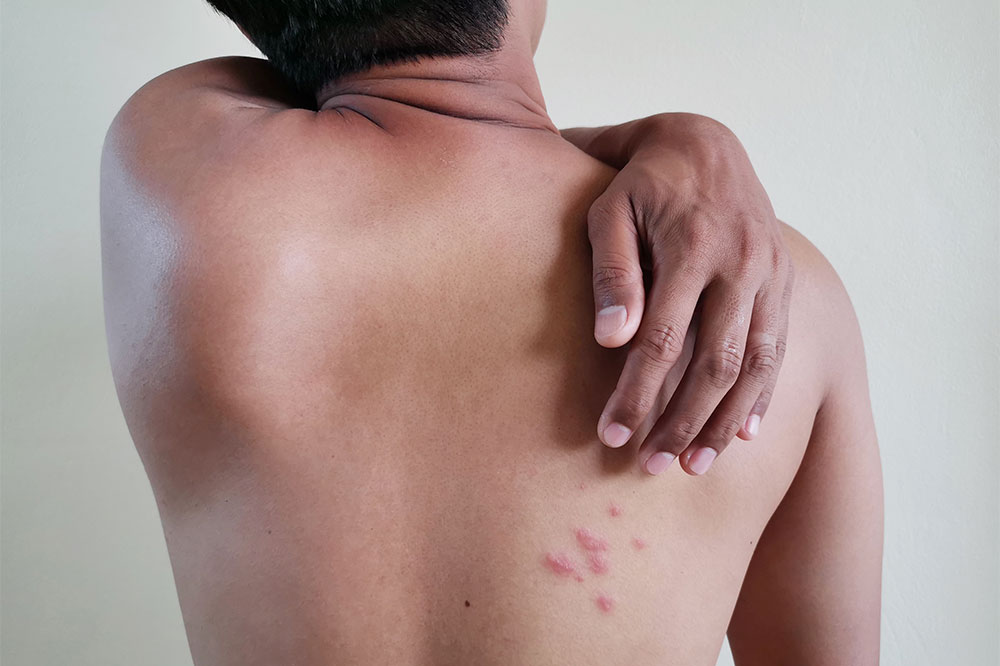
Comprehensive Guide to Managing Shingles: Conventional Treatments and Natural Therapies
This comprehensive guide offers effective strategies for managing shingles through conventional medications, home remedies, dietary tips, and natural therapies. Early treatment is vital to reduce pain, speed recovery, and prevent complications. Explore proven approaches including antiviral drugs, soothing baths, cool compresses, dietary support, and herbal supplements to enhance your recovery journey. Empower yourself with knowledge and adopt holistic methods for better shingles management and improved quality of life.
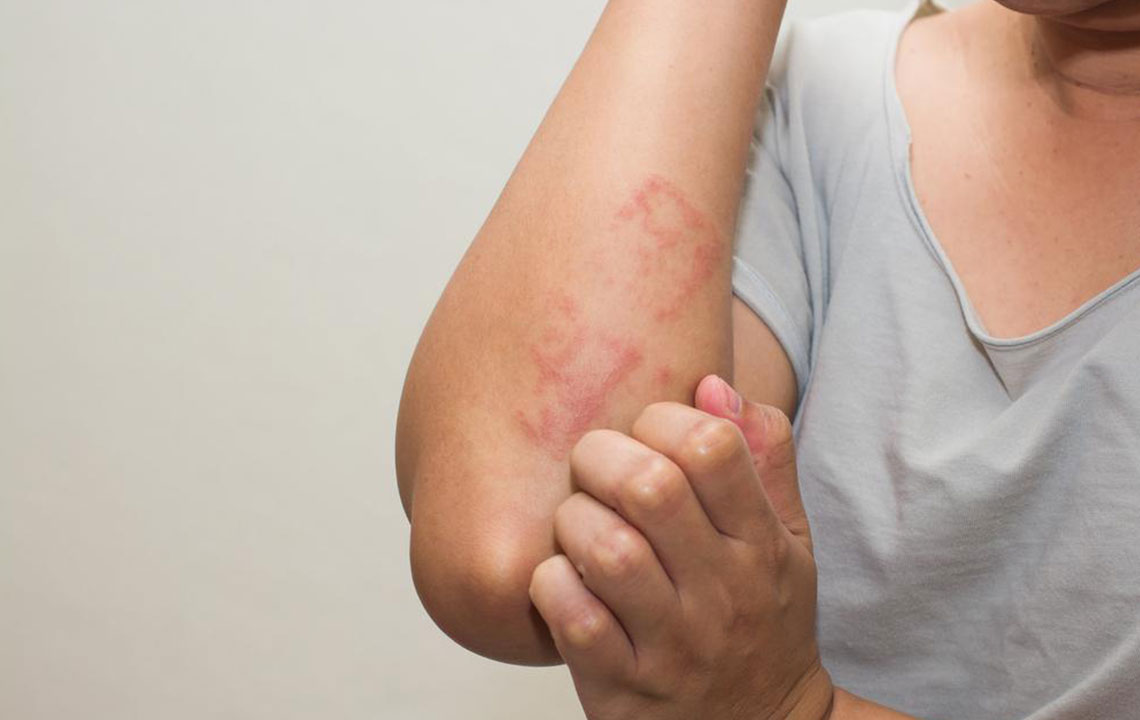
Effective Approaches for Treating Shingles: Medical and Natural Methods
Shingles, also known as herpes zoster, is a serious painful skin condition caused by the reactivation of the varicella zoster virus—the same virus responsible for chickenpox. This illness manifests through a distinctive rash, often accompanied by nerve pain that can significantly impact daily life. Although shingles commonly affects older adults and those with weakened immune systems, it can occur at any age, especially when the immune defenses are compromised due to stress, injury, certain medications, or underlying health issues. While most cases are single episodes, some individuals may experience recurrent outbreaks. The duration of shingles typically ranges from two to six weeks, and although there is no complete cure, early intervention and appropriate treatment can significantly alleviate symptoms, promote healing, and reduce the risk of complications such as postherpetic neuralgia.
Understanding the treatment options available—both conventional and natural—is crucial in managing this condition effectively. This comprehensive guide explores prescription medications, pain management strategies, home remedies, lifestyle modifications, dietary suggestions, and alternative therapies that support recovery and improve quality of life during shingles outbreaks.
Conventional Medical Treatments for Shingles
The cornerstone of shingles management involves antiviral medications that hinder viral replication, minimizing severity and duration. Common antiviral drugs include:
Valacyclovir (Valtrex): Often prescribed for early-stage shingles to reduce pain and healing time.
Acyclovir (Zovirax): An effective antiviral to slow virus progression and decrease complications.
Famciclovir (Famvir): Another antiviral option used for treating shingles outbreaks.
Aside from antivirals, managing nerve pain is equally important. Pain relief strategies include:
Anticonvulsants like gabapentin (Neurontin): Help reduce nerve pain significantly.
Capsaicin topical creams: Provide localized pain relief by desensitizing nerve endings.
Numbing agents such as lidocaine patches, gels, or sprays: Offer immediate relief from itching and pain.
Tricyclic antidepressants like amitriptyline: Used for persistent nerve pain even after rash resolution.
Injections combining corticosteroids and local anesthetics: For severe neuralgia cases.
Narcotic-based medications such as codeine: Used cautiously for severe pain management under medical supervision.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Strategies for Shingles Relief
While medications are essential, various home remedies and lifestyle adjustments can complement treatment and improve comfort during shingles episodes. Here are some proven approaches:
1. Soothing Baths and Skin Care
Maintaining proper skin hygiene is vital to prevent secondary infections. Gently cleansing blisters with mild soap and cool water helps keep the area clean. Taking lukewarm baths infused with colloidal oatmeal or cornstarch for about 15-20 minutes can soothe skin irritation and reduce itching. Avoid hot water, as it can exacerbate blister formation and discomfort. After bathing, carefully pat the skin dry with a clean, soft towel to prevent irritation and virus spread.
2. Applying Cool Compresses
Applying damp, cool cloths or compresses to affected areas can diminish pain and itching significantly. It is recommended to do this several times a day, but avoid ice packs or prolonged exposure to extreme cold, which might aggravate skin sensitivity.
3. Natural Remedies for Itching and Discomfort
A simple and effective natural remedy involves creating a paste by mixing two parts baking soda or cornstarch with one part water. Applying this paste directly onto rashes for 10-15 minutes can help calm irritated skin and reduce itching. Repeating this as needed offers ongoing relief without the use of chemical agents.
4. Topical Lotions and Creams
Topical treatments like calamine lotion can provide immediate relief by soothing the skin. Capasaicin ointments, although less pleasant in scent, are effective in reducing nerve-related pain over time. It is advisable to avoid scented or perfumed products, which can further irritate sensitive skin.
5. Nutritional Support to Boost Immunity
Your immune system plays a critical role in fighting shingles. Consuming a nutrient-rich diet that includes foods abundant in vitamins A, C, E, B1 (thiamine), and the amino acid lysine can promote faster healing. Incorporate colorful fruits and vegetables, leafy greens, lean meats like chicken or turkey, eggs, dairy products, fish such as salmon, legumes like lentils, and whole grains into your meals. Simultaneously, it’s important to limit foods rich in arginine—such as chocolate, nuts, seeds, and gelatin—as they can potentially trigger outbreaks by facilitating viral replication. Reducing intake of sugar, saturated fats, and highly processed carbohydrate foods can also bolster immunity and reduce inflammation.
6. Homeopathic and Herbal Complementary Therapies
Some individuals find additional relief through homeopathic remedies, which should be administered under the supervision of a qualified practitioner. Common homeopathic medicines for shingles include Ranunculus bulbosus, Rhus Tox, Graphites, Arsenicum album, Cantharis, Hypericum, and Mezereum. Furthermore, herbal supplements like lemon balm, echinacea, oregano oil, melatonin, essential fatty acids (like omega-3s), and St. John’s Wort can support immune function and help manage symptoms. However, prior consultation with a healthcare provider is essential before adding any herbal or supplement therapies to ensure safety and appropriateness.
In conclusion, managing shingles effectively requires a multidisciplinary approach combining medical treatment, home remedies, dietary modifications, and natural therapies. Early intervention is crucial to prevent complications like postherpetic neuralgia and to speed up the recovery process. Staying informed about available options empowers patients to make educated decisions and adopt strategies that enhance comfort and healing during outbreaks. Remember, always consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice tailored to your health condition.