Comprehensive Guide to Herpes: Understanding Risks and Effective Prevention Methods
This comprehensive article explores herpes, including its symptoms, risks, and complications. It emphasizes the importance of early treatment, safe sexual practices, and effective prevention strategies to reduce transmission and manage outbreaks. The guide provides practical advice for individuals with herpes and their partners, highlighting ways to protect oneself and loved ones effectively. Understanding herpes is vital for minimizing health risks, addressing social stigma, and improving quality of life through informed decision-making and medical management.

Understanding Herpes: Key Risks, Complications, and Proven Prevention Strategies
Herpes is a widespread viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV), which affects millions worldwide. The virus primarily manifests as oral herpes (cold sores) and genital herpes, both of which can significantly impact an individual’s health and quality of life. Understanding the risks associated with herpes infections, potential complications, and effective preventive measures is crucial for managing and reducing transmission.
People infected with herpes, especially those with compromised immune systems, often experience more frequent, intense, and prolonged outbreaks. These outbreaks can lead to discomfort, stigma, and in some cases, severe health issues. For some individuals, herpes remains dormant for extended periods but can reactivate due to factors like stress, illness, immune suppression, or hormonal changes.
Herpes is not just a simple skin condition—it carries risks of serious complications. For instance, if left untreated, herpes can cause eye infections that threaten sight, and neonatal herpes acquired during childbirth can lead to life-threatening conditions in newborns. Additional complications include urinary tract issues caused by inflammation, which may require medical interventions such as catheterization. Moreover, individuals with genital herpes are at a higher risk of acquiring other sexually transmitted infections (STIs), including HIV/AIDS, because the open sores provide an entry point for the virus.
Herpes and Its Impact: Recognizing Symptoms and Risks
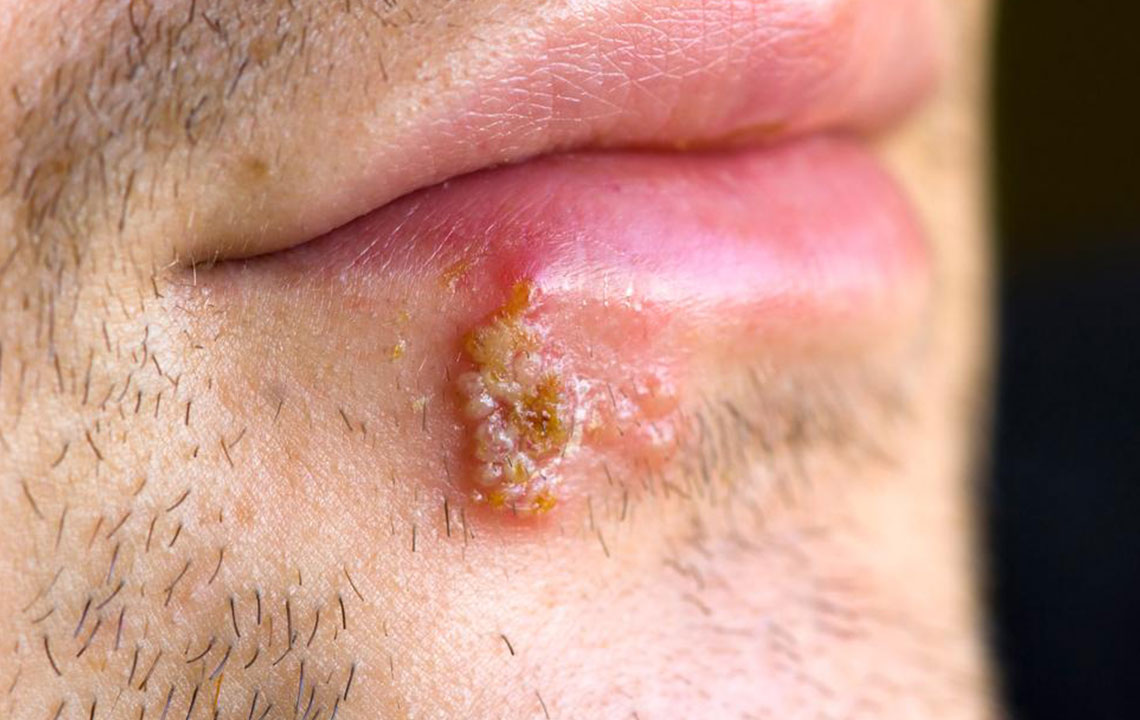
Herpes symptoms vary. Some people experience noticeable blisters, pain, and itching, while others may have mild symptoms or remain asymptomatic. Cold sores, caused predominantly by HSV-1, are common around the lips and mouth and tend to be more visible and uncomfortable. Genital herpes, caused mainly by HSV-2, affects the genital area, causing painful sores and recurrent outbreaks.
In addition to discomfort, herpes infections can have psychological impacts, such as anxiety and depression stemming from stigma and fear of transmission. The infection is lifelong, with no cure currently available, but antiviral medications can significantly reduce symptom severity, frequency, and risk of transmission.
Preventing the spread of herpes involves a combination of behavioral strategies, medical interventions, and open communication. Effectively managing herpes requires understanding these measures and acting proactively to protect oneself and others.
Effective Prevention Strategies for Herpes Transmission
Never touch herpes blisters or sores near the mouth or genital region. Hands can transfer the virus, especially if there are cuts or abrasions, making hand hygiene essential after any contact.
Initiate antiviral therapy as soon as you notice early signs of an outbreak, such as tingling or itching, to minimize severity and reduce contagiousness.
Maintain a supply of prescribed antiviral medication if you are prone to recurrent outbreaks for prompt treatment.
If pregnant and aware of a herpes infection, inform your healthcare provider immediately. Proper management can significantly reduce risks to the baby during delivery.
Practice safe sexual behaviors, including discussing STIs openly with partners before engaging in sexual activity to assess risks and agree on preventive measures.
Consistently use latex condoms during vaginal, anal, and oral sex, keeping in mind that condoms reduce but do not eliminate the risk of herpes transmission due to skin contact outside the protected area.
Avoid sexual activity during active outbreaks to prevent spreading the virus to partners.
Limit the number of sexual partners to decrease the likelihood of exposure to herpes and other STIs.
Maintain good general health through proper nutrition, stress management, and adequate sleep, which can strengthen the immune response and reduce outbreak frequency.
Understanding herpes comprehensively enables individuals to make informed decisions, adopt protective practices, and seek timely medical advice. Managing herpes infection effectively not only reduces health risks but also improves quality of life by minimizing outbreaks and preventing transmission to loved ones.
While current treatments cannot eliminate the virus, ongoing research continues to explore vaccine development and new therapies. Staying informed and proactive is key to living well with herpes.