Comprehensive Approaches to Managing Atopic Dermatitis Effectively
This article provides a detailed guide on managing atopic dermatitis effectively through lifestyle changes, skincare routines, and medical treatments. It covers over-the-counter remedies, prescription options, and tips for long-term control, helping patients improve their quality of life and reduce flare-ups. Essential for those living with eczema, this comprehensive resource offers practical insights and personalized strategies for skin health and comfort.

Comprehensive Approaches to Managing Atopic Dermatitis Effectively
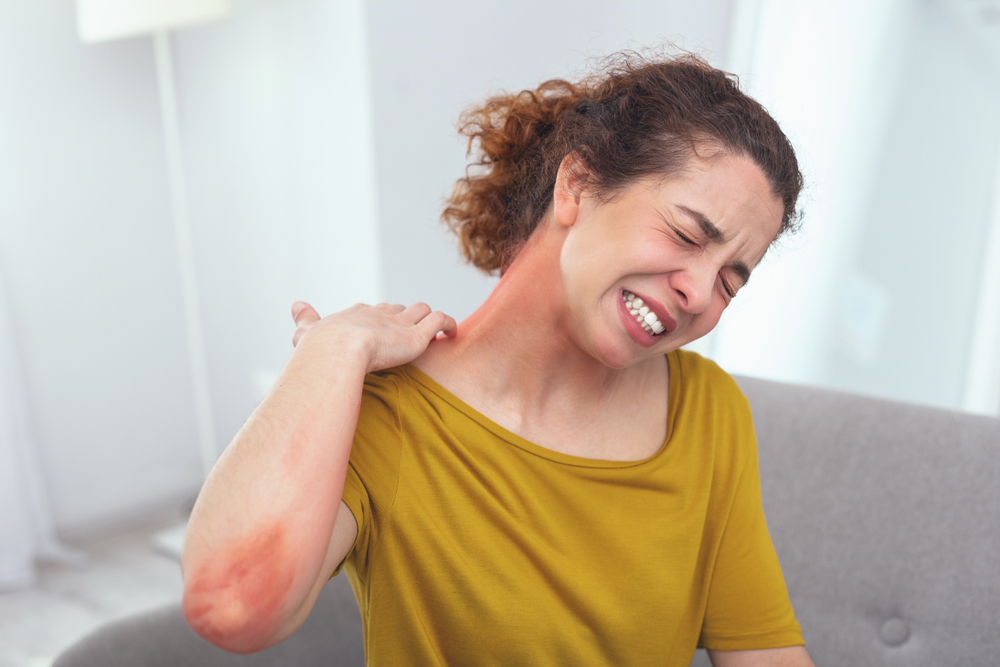
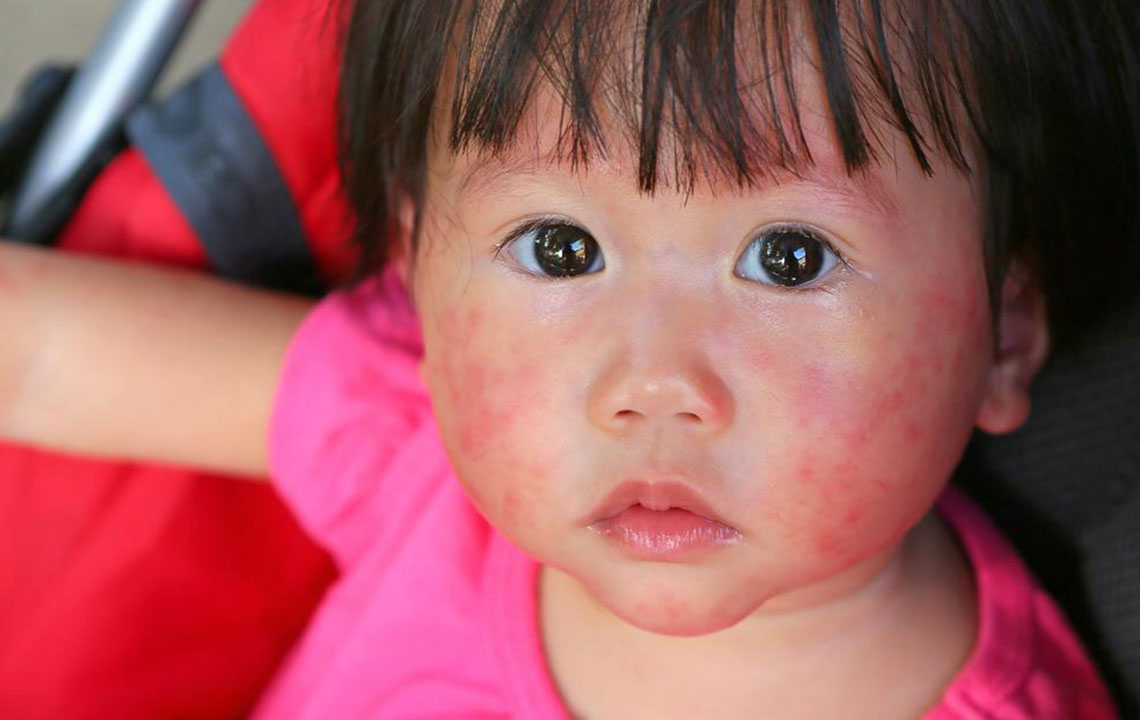
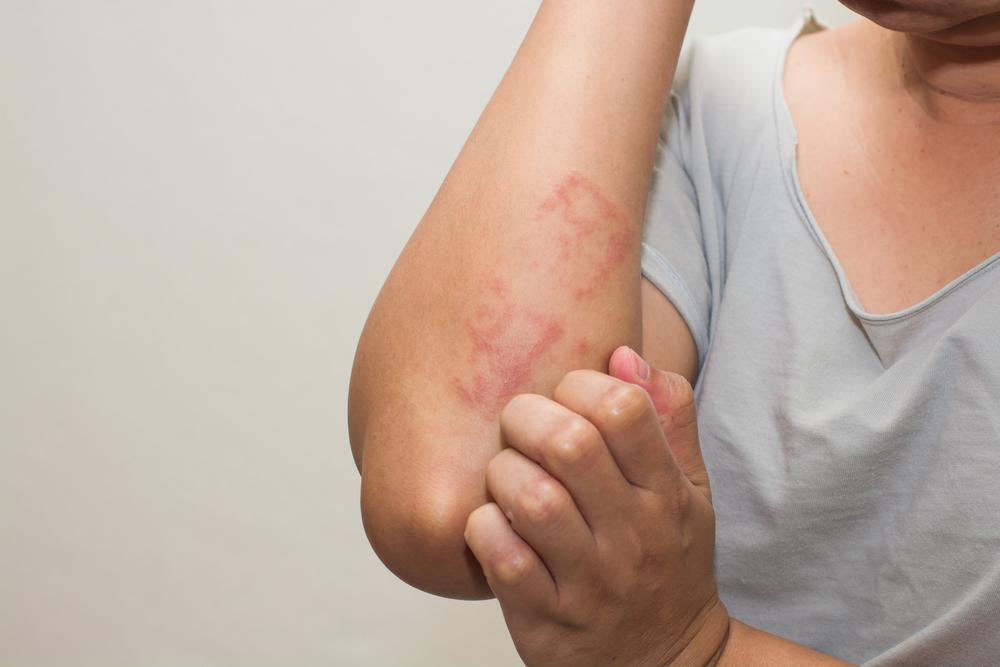
Atopic dermatitis, commonly known as eczema, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that affects a significant portion of the population worldwide. Approximately 18 million individuals suffer from this persistent and often frustrating skin disorder, which manifests through symptoms such as relentless itching, dry patches, redness, and inflammation. The condition can severely impact daily life, disrupting sleep patterns and leading to emotional distress. Understanding the best management practices is crucial for controlling symptoms, preventing flare-ups, and improving overall quality of life. Failure to manage atopic dermatitis properly can result in continuous discomfort, increased risk of skin infections from scratching, and further skin damage. Therefore, adopting effective treatment strategies is vital for those living with this condition.
Effective dermatitis management involves a combination of lifestyle adjustments, skincare routines, and medical interventions. When properly managed, individuals can experience relief from symptoms, better sleep, and enhanced well-being. This detailed guide explores various treatment options, from over-the-counter remedies to prescription medications, as well as daily habits that can help mitigate flare-ups and manage symptoms over the long term.
Over-the-Counter (OTC) Treatments for Atopic Dermatitis
Many people seeking relief from atopic dermatitis start with OTC products designed to soothe irritated skin, reduce inflammation, and restore the skin barrier. These accessible options are often the first line of defense and can be used effectively for mild to moderate cases.
Moisturizers and Emollients
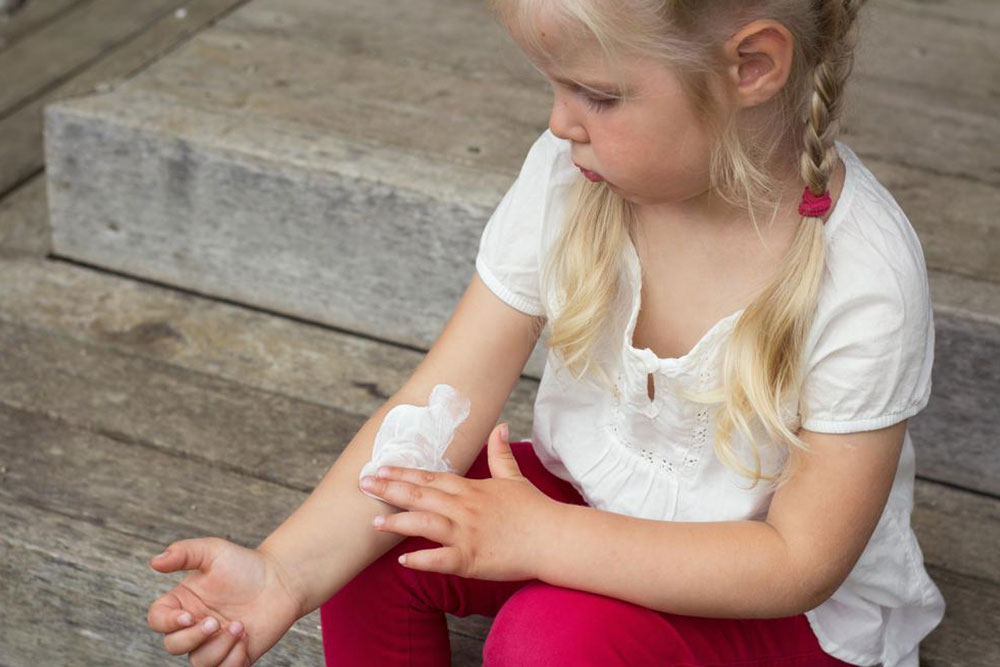
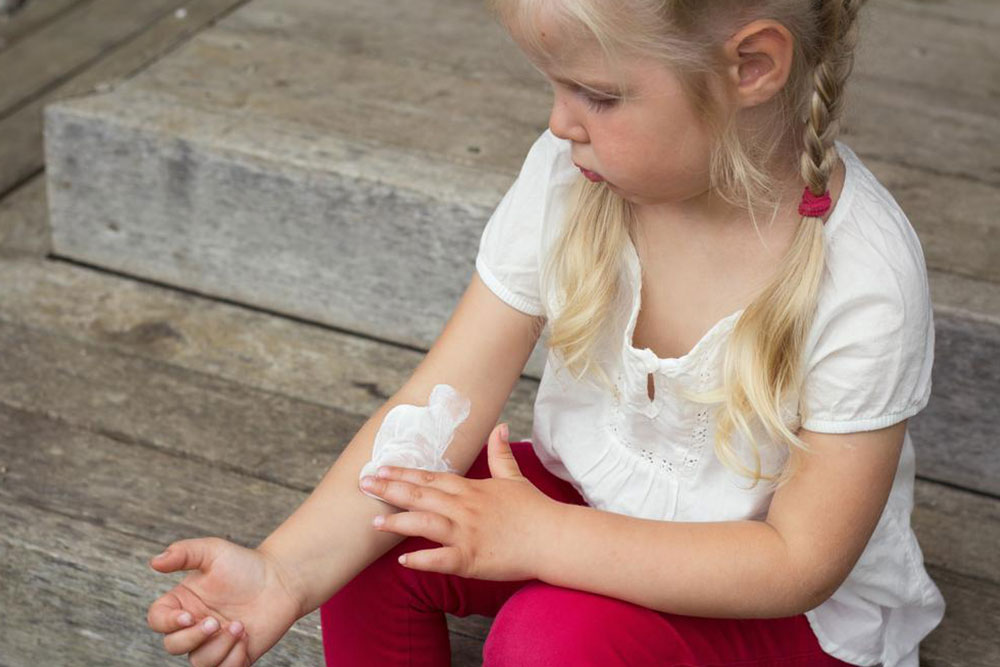
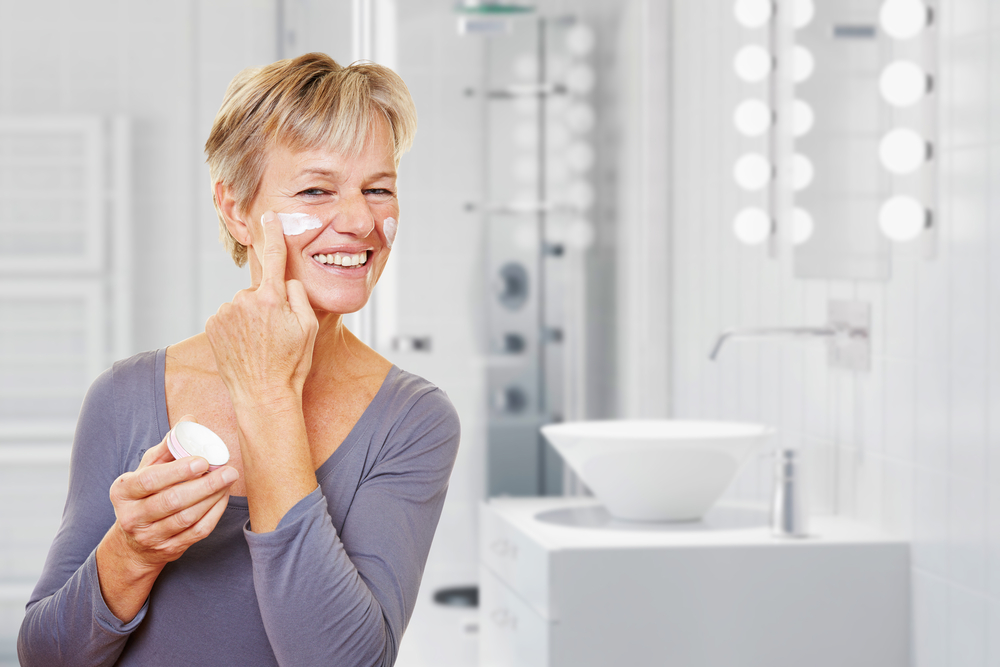
One of the foundational elements in managing atopic dermatitis is the consistent use of moisturizers. These products help restore and protect the skin’s natural barrier, which is often compromised in eczema patients. Moisturizers trap water within the skin, alleviating dryness and reducing itching. It is essential to apply moisturizer immediately after bathing, while the skin is still damp, to lock in moisture more effectively. Options include lotions, creams, and ointments, each tailored for different skin types and severity. For example, ointments like petroleum jelly provide a heavy barrier ideal for very dry skin, while lighter lotions are suitable for daytime use. Regular moisturizing helps prevent the skin from becoming excessively dry or cracked, minimizing the risk of flare-ups.
Topical Steroids
Low-potency corticosteroids such as over-the-counter hydrocortisone creams (brands like Nutracort, Cortaid) are effective for managing flare-ups and reducing inflammation. These creams are especially useful for short-term relief of redness, swelling, and itching. Application should be done after moisturizing for optimal results. It is important to follow usage instructions carefully to avoid potential side effects associated with prolonged or excessive use of steroids.
Antihistamines
Over-the-counter antihistamines, like diphenhydramine (Benadryl), are commonly used to help control severe itching and facilitate better sleep during flare-ups. Their sedative properties can be beneficial for night-time itching, enabling individuals to rest more peacefully. While antihistamines do not treat the skin condition directly, they can break the itch-scratch cycle, ultimately reducing further skin damage and inflammation.
Prescription Medications for More Severe Cases
If OTC options do not sufficiently control atopic dermatitis symptoms, medical consultation is essential. Physicians may prescribe stronger topical treatments, such as higher-potency corticosteroids or topical calcineurin inhibitors like tacrolimus (Protopic) and pimecrolimus (Elidel), which modulate immune responses involved in eczema. For persistent or severe cases, injectable biologic therapies such as dupilumab (Dupixent) may be recommended. These medications target specific immune pathways responsible for inflammation. Additionally, oral medications, including antihistamines or corticosteroids, can be prescribed for managing widespread or acute flare-ups under medical supervision. Regular follow-ups and personalized treatment plans are critical to achieving the best outcomes.
Living with atopic dermatitis requires a comprehensive approach that combines skincare routines, lifestyle habits, and medical treatments. By understanding and employing a combination of OTC and prescription therapies, individuals can better manage their symptoms, minimize flare-ups, and enjoy an improved quality of life. In addition, maintaining skin hydration, avoiding known irritants and allergens, and keeping a consistent skincare regimen are vital components of long-term management. Consulting healthcare professionals for personalized advice is recommended to optimize treatment effectiveness and safety. Remember, proactive care and medicinal support are key to turning the challenges of atopic dermatitis into manageable conditions, ultimately allowing individuals to lead healthier and more comfortable lives.