Comprehensive Guide to Managing Eczema: Effective Strategies and Treatments
This comprehensive guide explores effective strategies for managing eczema, including home remedies, skincare routines, lifestyle changes, and medical treatments. It provides detailed insights into symptoms, triggers, and personalized care plans to improve quality of life for eczema sufferers. Learn how to prevent flare-ups and promote skin health with expert advice tailored for both mild and severe cases, ensuring effective symptom control and pain relief.
Comprehensive Guide to Managing Eczema: Effective Strategies and Treatments
Eczema, scientifically known as atopic dermatitis, is a widespread and often persistent skin disorder that affects millions of individuals worldwide. Characterized by inflammation, itching, redness, cracking, and rough skin, eczema can significantly impact the quality of life of those affected. In some cases, the skin condition may lead to blisters and oozing, further complicating management efforts. Although eczema is not contagious, it can be triggered or exacerbated by various factors, including certain foods, environmental allergens such as pollen, smoke, and harsh weather conditions. Understanding how to effectively manage and treat eczema is crucial for minimizing flare-ups and maintaining healthy skin.
Understanding the Symptoms of Eczema
Infant Symptoms: Infants often develop characteristic rashes on the scalp, cheeks, and forehead. These rashes may appear red, inflamed, and sometimes blistered, leading to discomfort and fussiness.
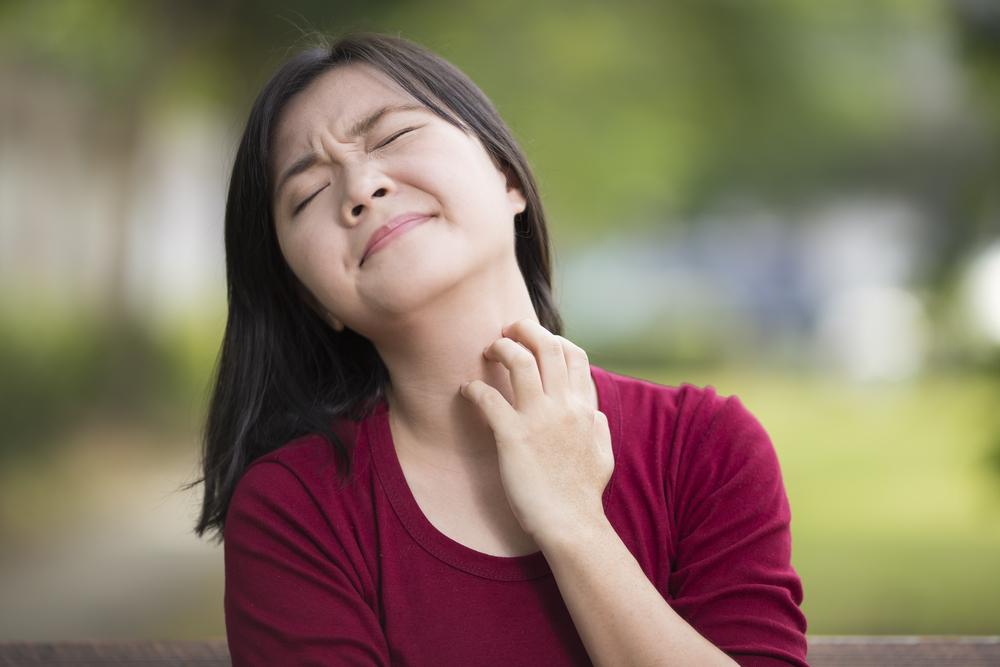
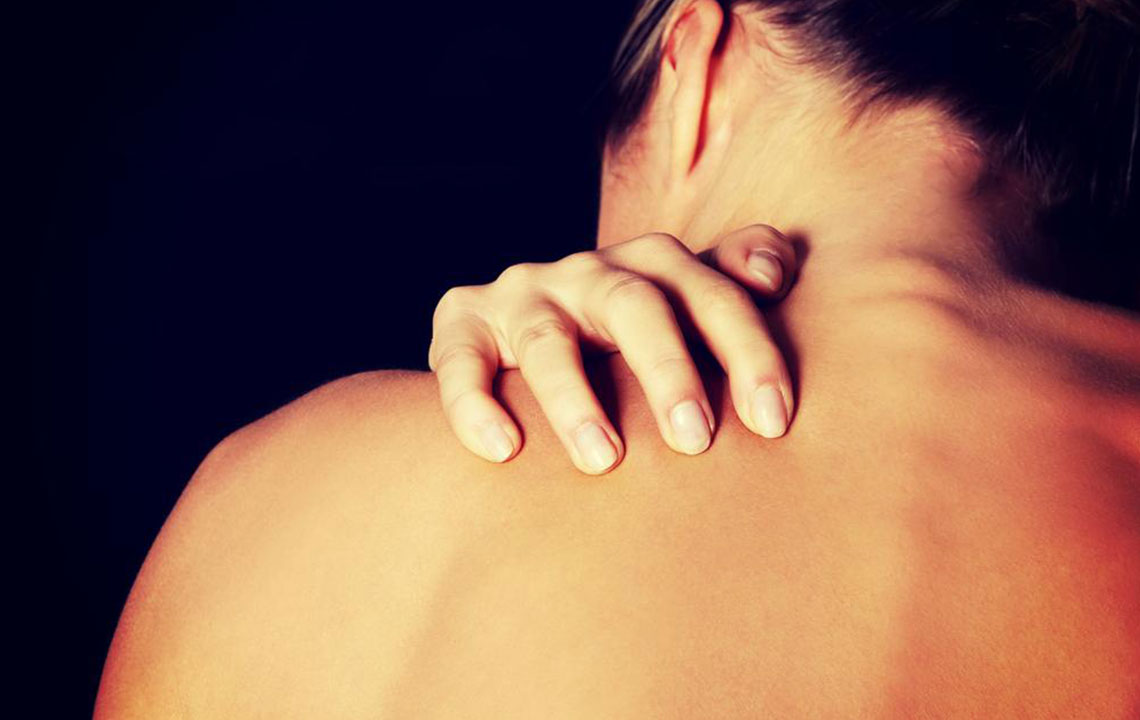
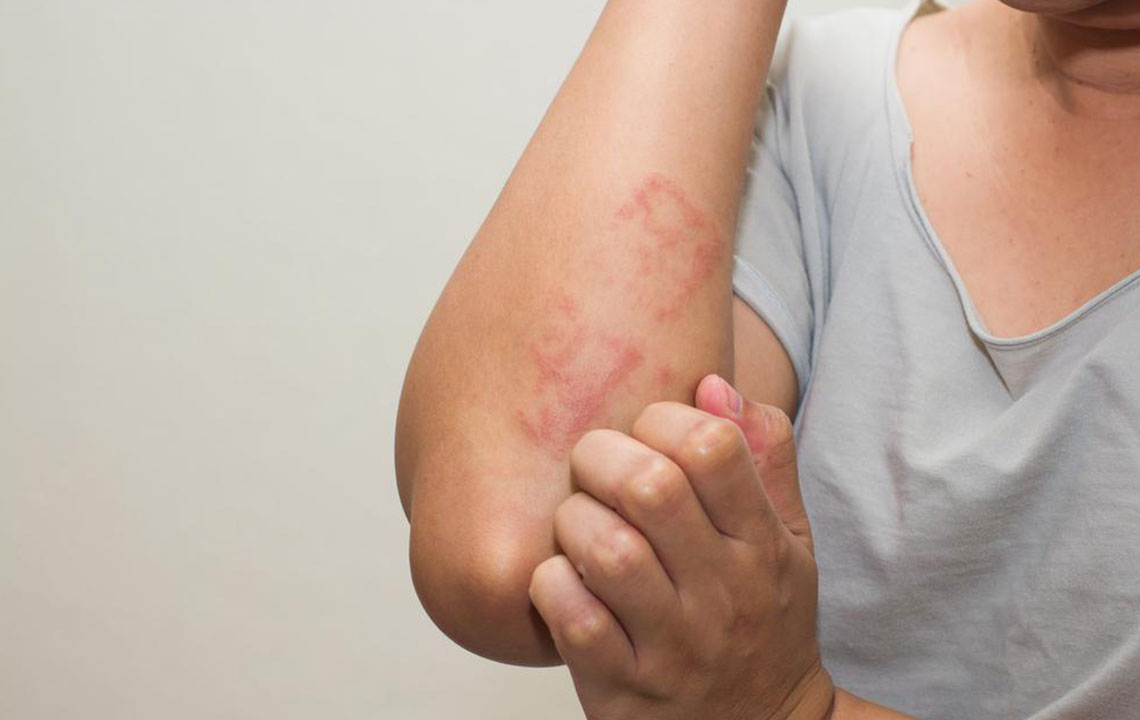
Visual Signs in Adults: In older children and adults, eczema tends to manifest behind the elbows, around the knees, and on the neck, face, and around the eyes. The skin may become thickened, dry, and prone to cracking.
Additional Indicators: Individuals with eczema are frequently accompanied by other allergic conditions such as asthma or hay fever, especially evident in children aged 10 to 15. The persistent itchiness often leads to scratching, which can worsen skin damage and increase the risk of secondary infections.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Adjustments for Eczema Relief
For those experiencing mild to moderate eczema symptoms, adopting specific home remedies and lifestyle modifications can significantly alleviate discomfort and reduce flare-ups. These practical approaches form the foundation of effective eczema management and include:
Lukewarm Baths: Taking baths in lukewarm water helps soothe irritated skin and diminishes persistent itching. Using gentle, fragrance-free bath additives can further prevent skin dryness.
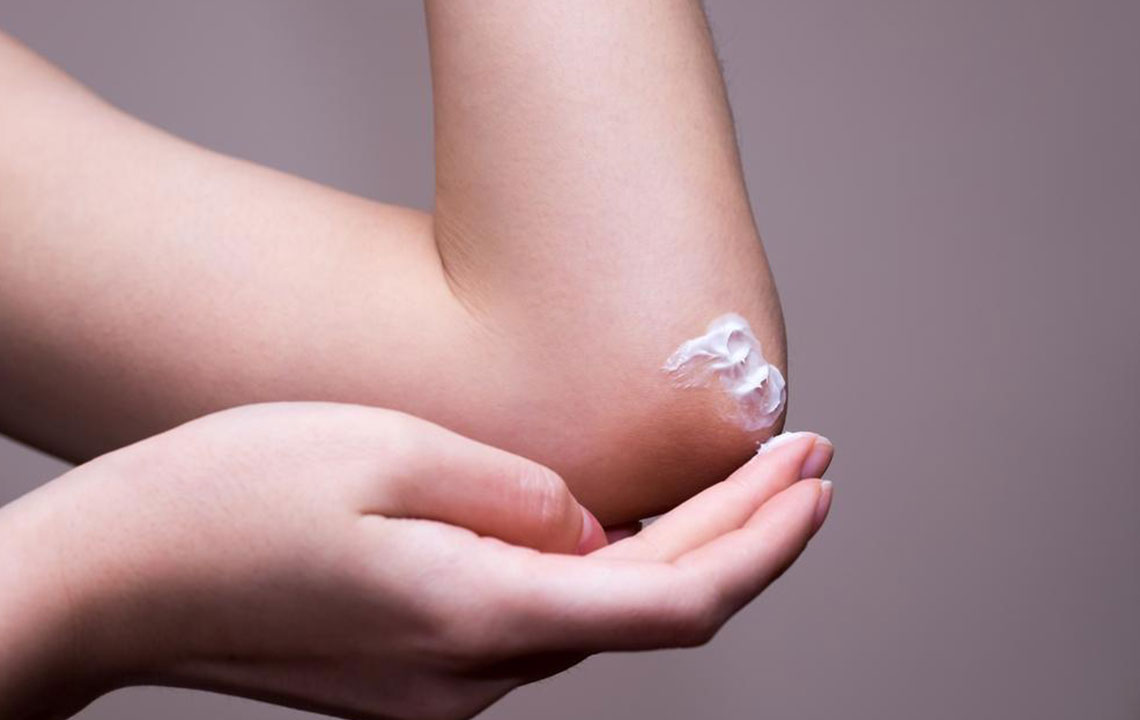
Moisturization: Applying a high-quality, fragrance-free moisturizer immediately after bathing helps trap moisture in the skin. Regular hydration supports the skin’s barrier function and prevents cracking.
Choosing Comfortable Clothing: Wearing loose, breathable fabrics such as cotton minimizes skin irritation and reduces friction, which can trigger flare-ups.
Gentle Cleansing: Opt for mild, fragrance-free cleansers that do not strip natural oils from the skin, thereby maintaining hydration and reducing dryness.
Managing Environmental Factors: Avoid activities that lead to excessive sweating or drastic temperature changes, which can exacerbate eczema symptoms. Use humidifiers during dry winter months to maintain optimal indoor humidity levels.
Hygiene and Skin Care: Maintain good personal hygiene without over-washing, and promptly treat skin cracks or minor infections to prevent complications.
Diet and Nutrition: Monitor dietary intake and identify potential food triggers that may exacerbate eczema. Consulting with a dietitian can help tailor an appropriate diet plan, especially for children or individuals with multiple allergies.
In cases where eczema symptoms are persistent or severe, medical intervention becomes necessary. Effective medications include:
Topical Corticosteroids: These anti-inflammatory creams or ointments are often the first line of treatment for reducing skin inflammation and controlling flare-ups.
Oral Medications and Injections: For more severe or widespread eczema, systemic drugs such as corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, or biologic therapies may be prescribed under dermatological supervision.
Antibiotics and Antifungals: Secondary bacterial or fungal infections require targeted treatments to resolve skin infections and promote healing.
Antihistamines: These medications can help mitigate itching, especially during nighttime, preventing scratching damage.
Calcineurin Inhibitors: Non-steroidal topical treatments that suppress the immune response and are useful for sensitive skin areas or long-term management.
Barrier Repair Moisturizers: Specialized emollients designed to reinforce the skin’s natural barrier, decreasing water loss and shielding against irritants.
Phototherapy: Controlled exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light under medical supervision can improve moderate to severe eczema cases that do not respond to topical treatments.
Cool Compresses and Wound Care: Applying cool compresses can soothe inflamed skin and aid in pain relief. Proper wound hygiene prevents infection and accelerates healing.
While eczema currently has no cure, effective management strategies focus on controlling symptoms, reducing flare-ups, and preventing skin damage. Treatment plans should always be tailored to individual needs, and consulting a qualified dermatologist is essential before initiating any medication or therapy. Regular follow-up with healthcare professionals ensures that treatment remains appropriate and effective, considering the evolving nature of eczema and patient responses. Maintaining good skin health through a combination of lifestyle adjustments, environmental controls, and medical interventions can significantly enhance the quality of life for those living with eczema.
It is important to seek personalized medical advice to avoid incorrect medication use, which may worsen symptoms. Implementing these carefully considered strategies, along with professional healthcare guidance, will enable sufferers to manage eczema more effectively and enjoy healthier, more comfortable skin.