Comprehensive Guide to Effectively Managing Eczema Symptoms and Flare-Ups
This comprehensive guide explores effective eczema management strategies, including identifying triggers, skincare routines, natural remedies, and treatment options suitable for different age groups. Learn how to reduce flare-ups, soothe irritated skin, and improve overall quality of life through tailored care plans and lifestyle changes.

Essential Strategies for Controlling Eczema and Improving Skin Health
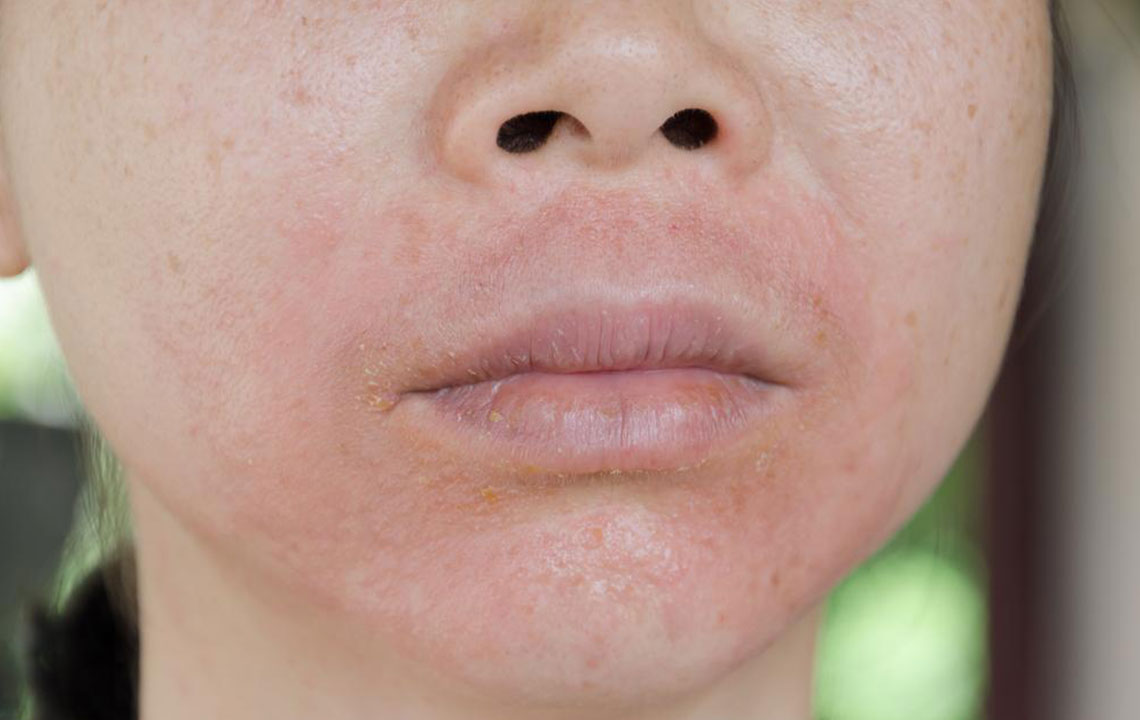
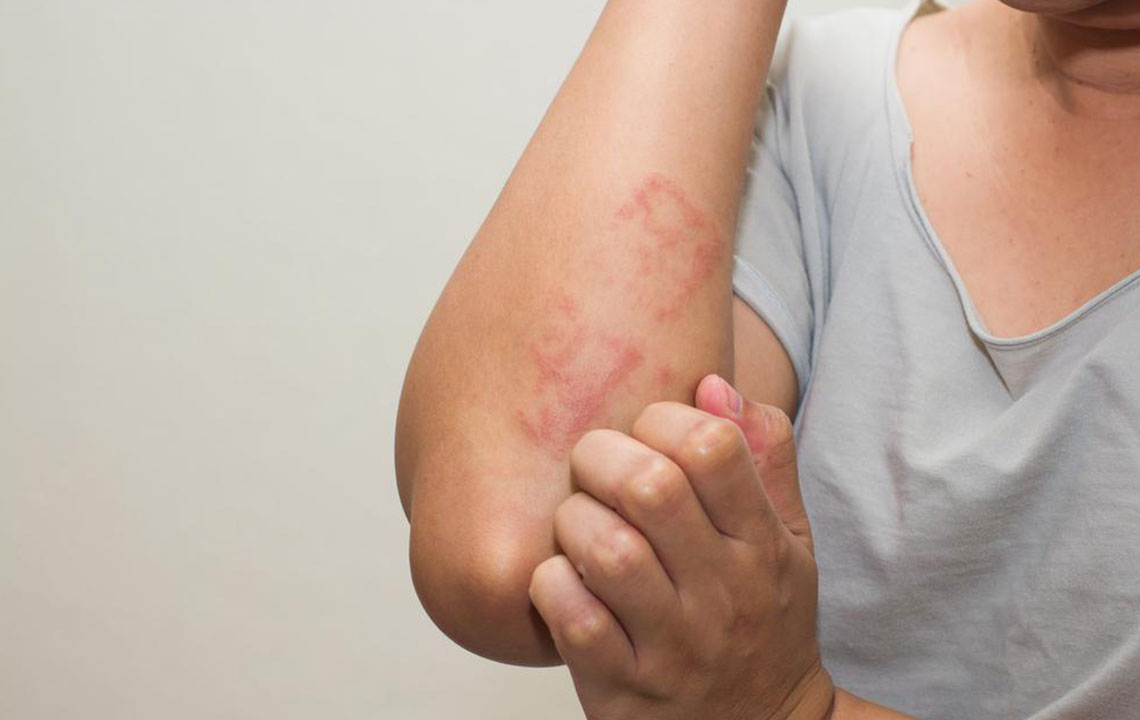
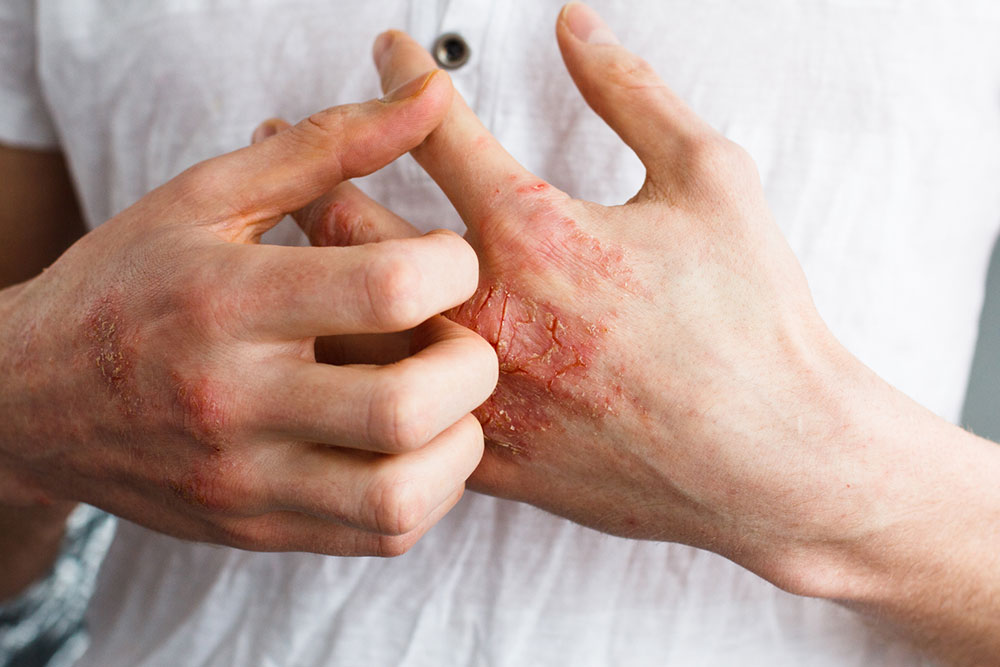
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a widespread chronic skin condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide, spanning all age groups from infants to adults. Characterized by episodes of inflamed, itchy, and dry skin, eczema can significantly diminish quality of life if not properly managed. The condition often manifests as red, rough patches on the skin, especially around the hands, feet, arms, legs, neck, and areas where skin folds, such as elbows and knees. Understanding how to manage eczema effectively involves recognizing its triggers, adopting appropriate skincare routines, and exploring various treatment options tailored to individual needs.
In-Depth Understanding of Eczema
Eczema, if left untreated or poorly managed, can lead to persistent skin issues such as bumps, cracks, and secondary infections due to skin barrier disruption. It often begins appearing on the face during infancy but can spread to other parts of the body over time. While eczema is not contagious, its symptoms can cause significant discomfort and may result in wounds prone to bacterial, fungal, or viral infections. The main categories include atopic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, seborrheic dermatitis, and others, each having unique triggers and clinical features.
Signs of eczema vary, but common symptoms include intense itching, dry and sensitive skin, redness, swelling, crusting, and possible oozing. Recognizing these early signs helps in prompt management, reducing the risk of complications and improving comfort. The course of eczema varies among individuals, with fluctuating severity, sometimes triggered by environmental changes or internal factors. Consulting a healthcare professional is essential for proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plans.
Allergic reactions from pet dander, pollen, certain foods, and environmental allergens can provoke flare-ups.
Irritants, including soaps, detergents, fragrances, dyes, and rough fabrics, often exacerbate symptoms.
Environmental factors such as low humidity, excessive heat, sweating, or exposure to harsh weather conditions influence disease severity.
Stress, hormonal changes, and fatigue can heighten inflammation and worsen symptoms.
Effective eczema management focuses on avoiding known triggers, maintaining optimal skin hydration, and adhering to medical treatment regimens. Pharmacological options include topical corticosteroids, emollients, antihistamines, and sometimes light therapy. Tailoring care to age and severity ensures better outcomes.
Care Strategies for Children: Use gentle, fragrance-free cleansers and moisturizers regularly, consider bleach baths for preventing infections, and in severe cases, explore immunosuppressant therapies under medical supervision.
Approaches for Adults: Similar to pediatric care, but with adjustments in strength and formulation of medications, including corticosteroids and antihistamines to control inflammation and itchiness.
Natural remedies can offer additional relief—applications of aloe vera gel, diluted apple cider vinegar rinses, and colloidal oatmeal baths soothe irritated skin and reduce inflammation. Nutritional support plays a vital role; a balanced diet rich in vitamin D, omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants from fruits and vegetables, probiotics, and whole grains enhances skin health and immune function. Avoiding processed foods, allergens, and food triggers further helps in reducing flare-ups. Regular skin monitoring, managing stress levels, practicing good skincare routines, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle are crucial components for long-term eczema control and improved well-being.