Complete Guide to Effectively Managing Eczema Symptoms and Improving Skin Health
This comprehensive guide provides in-depth insights into eczema, covering its causes, symptoms, and holistic management strategies. It emphasizes natural remedies, lifestyle changes, and medical treatments to help sufferers control flare-ups and improve skin health. Whether you're seeking home solutions or professional care, this article offers valuable advice to effectively manage eczema and enhance your quality of life.
Comprehensive Understanding of Eczema and Effective Management Strategies
Eczema, a persistent and often distressing skin condition, affects millions of individuals worldwide. Characterized by inflamed, itchy, and cracked skin patches, eczema encompasses a range of dermatological conditions such as atopic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, dyshidrotic eczema, neurodermatitis, and stasis dermatitis. Despite its widespread prevalence, the pathogenesis of eczema remains complex and multifaceted, involving genetic, environmental, and immune system factors. While a definitive cure has yet to be discovered, modern treatment approaches focus on alleviating symptoms, reducing flare-ups, and restoring skin barrier integrity. This comprehensive guide explores the causes, symptoms, management strategies—including natural remedies and medical treatments—and lifestyle modifications essential for living comfortably with eczema.
Understanding Eczema: What You Need to Know
Dietary factors such as dairy products, nuts, and certain preservatives can trigger flare-ups in susceptible individuals.
Age plays a significant role; for example, infants often exhibit different symptoms compared to adults, who may experience chronic patches on various parts of the body.
Environmental elements—pollen, dust mites, pet dander, smoke, and harsh weather conditions—can exacerbate eczema symptoms.
Although eczema is not contagious, its persistent nature can impact mental health and daily life.
Management essentially revolves around symptom relief, skin barrier repair, and avoidance of known triggers.
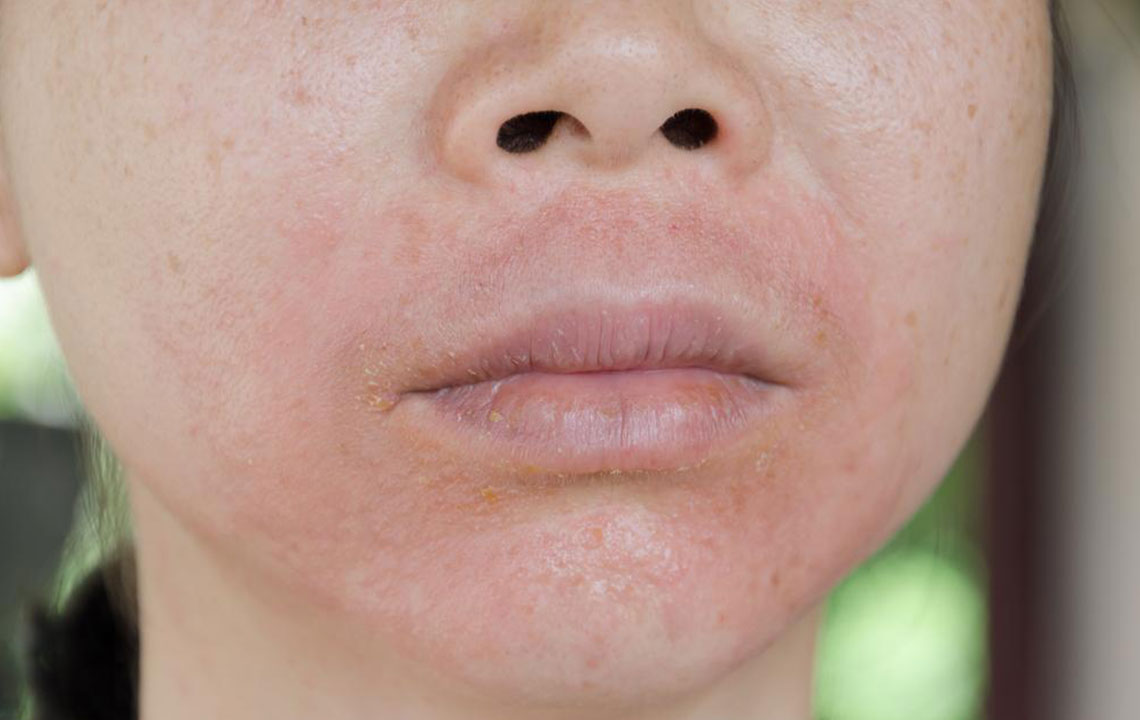
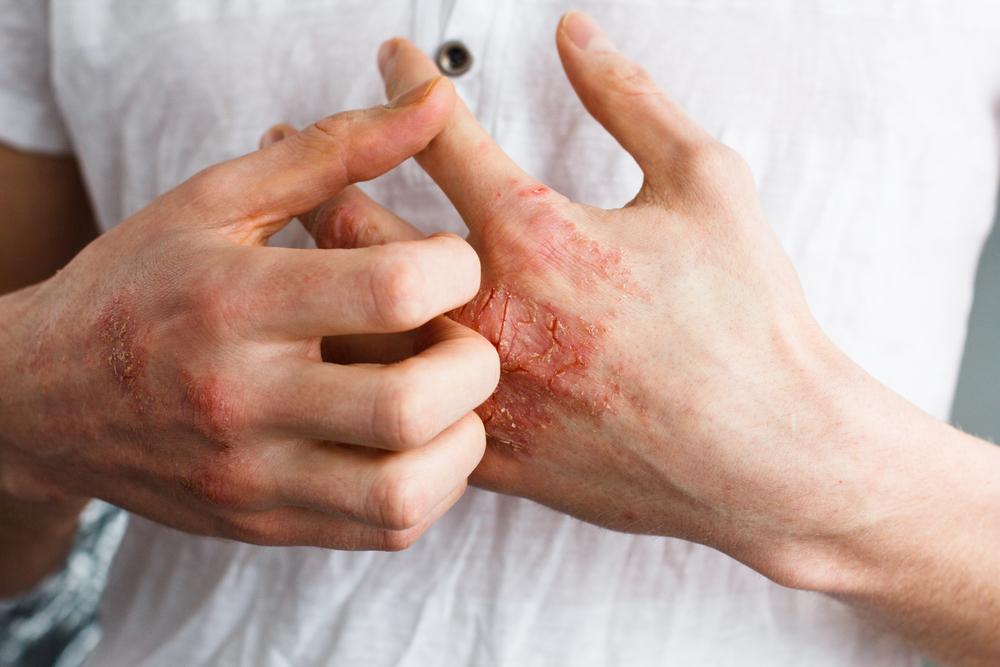
Recognizing the Key Symptoms of Eczema
Small, raised bumps that may ooze or crust during flare-ups.
Rough, dry, and cracked skin that often becomes inflamed and sensitive to touch.
Discolored patches typically appearing on the face, hands, feet, neck, elbows, or behind the knees.
Swelling, redness, and persistent itching causing discomfort and disrupting sleep.
Persistent rashes that may worsen with scratching or exposure to irritants.
Strategies for Managing Eczema Effectively
Though curative options are unavailable, combining personalized treatment plans with lifestyle adjustments can significantly improve quality of life. Some patients find remission over time with consistent care. The goal is to control inflammation, hydrate the skin, and prevent recurrent flare-ups through a combination of natural and medical approaches.
Home-Based Strategies to Soothe and Prevent Eczema Flare-Ups
Use vegetable shortening: This natural moisturizer helps restore dryness and flakiness, creating a protective barrier on the skin.
Incorporate turmeric into your diet: Curcumin, the active compound in turmeric, possesses powerful anti-inflammatory properties that can speed healing and reduce flare severity.
Apply tea tree oil: Known for its antiseptic, antibacterial, and anti-inflammatory effects, tea tree oil can help soothe itching and prevent infections.
Eat flaxseeds: Rich in omega-3 fatty acids, flaxseeds combat inflammation internally and support healthy skin.
Consume fermented cod liver oil: This supplement provides vitamins A, D, and omega-3s, all of which play pivotal roles in skin health and reducing inflammation.
Take magnesium baths: Adding magnesium flakes, sea salt, and soothing essential oils like lavender can calm inflamed skin and promote relaxation.
Implement probiotic-rich foods: Kefir, miso, and yogurt can help balance gut health, which is increasingly linked to skin conditions including eczema.
Medical Interventions for Eczema Relief
Topical corticosteroids: Widely prescribed to reduce inflammation and relieve itching, these come in various potencies based on severity.
Systemic corticosteroids: Prescribed only for severe or widespread cases, but long-term use requires careful medical supervision due to potential side effects.
Antiviral and antifungal medications: Used when eczema becomes complicated by infections, common in compromised skin barriers.
Antibiotics: Necessary when bacterial superinfections develop on broken skin.
Antihistamines: Help alleviate itching, allowing for better sleep and overall comfort.
Barrier repair moisturizers: Specialized moisturizers that support skin barrier recovery and help lock in moisture.
Calcineurin inhibitors: Such as tacrolimus and pimecrolimus, these suppress immune responses to reduce skin inflammation without the side effects associated with steroids.
Phototherapy: Controlled exposure to ultraviolet light under medical supervision can reduce inflammation and improve chronic eczema management.
Effective eczema management requires an integrated approach—combining skincare routines, lifestyle modifications, and medical treatments as needed. Continual monitoring and personalized adjustments are crucial for maintaining skin health and minimizing flare-ups. While complete elimination of eczema remains challenging, adherence to these strategies can help sufferers regain control and enjoy healthier, more comfortable skin.