Comprehensive Guide to Managing Eczema: Effective Medications and Home Remedies
This comprehensive guide covers effective strategies for managing eczema, including medications, home remedies, and lifestyle tips. It emphasizes early recognition, trigger avoidance, and the importance of professional medical advice. By understanding symptoms and treatment options, individuals can control flare-ups and improve their skin health, leading to a better quality of life. The article also discusses innovative treatments like biologics for severe cases, offering hope for long-term management.

Comprehensive Guide to Managing Eczema: Effective Medications and Home Remedies
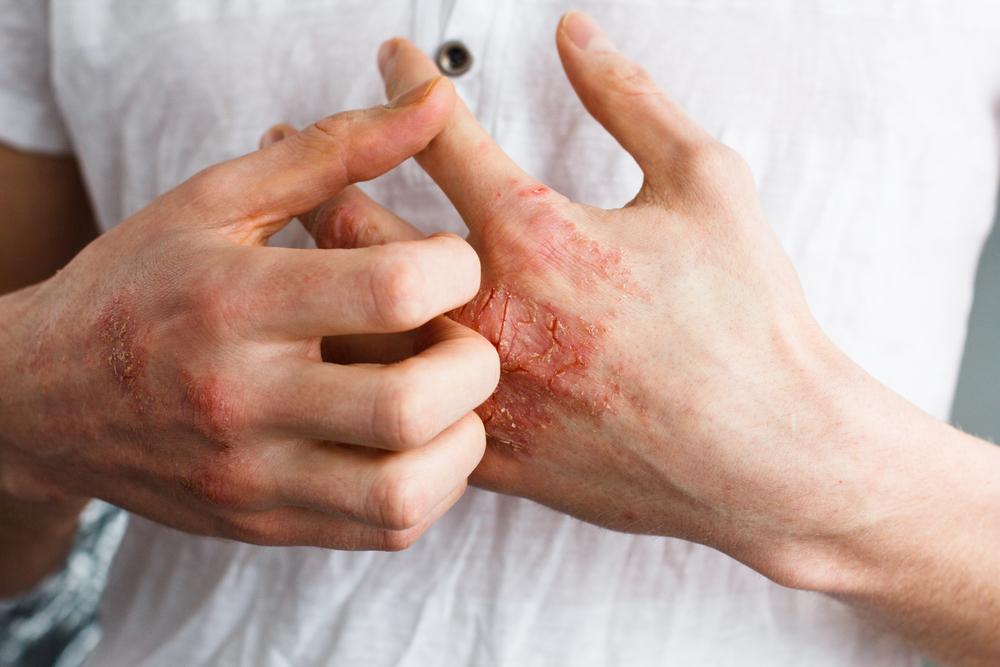
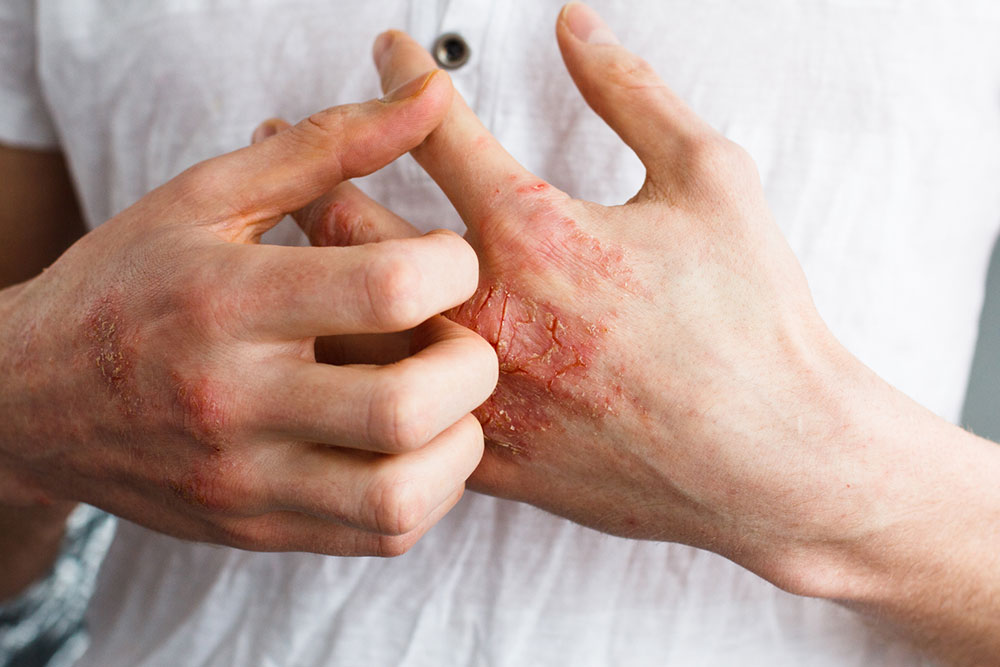
Eczema, also called atopic dermatitis, is a common chronic skin condition that affects millions worldwide. Characterized by inflamed, itchy, cracked, and reddened patches, eczema can significantly impact quality of life. While it cannot be entirely cured, proper management through medications and home remedies can effectively control symptoms and prevent flare-ups. Understanding the condition's symptoms, triggers, and treatment options is crucial for those affected, whether children or adults.
In this comprehensive guide, we explore how eczema manifests across different age groups, the importance of early recognition, and practical strategies for managing this persistent skin condition. From identifying key symptoms to embracing effective medications and lifestyle modifications, this article aims to equip you with the knowledge necessary to handle eczema confidently.
Understanding Eczema: Symptoms and Signs
Recognizing the symptoms of eczema is vital for early intervention. The manifestation of eczema varies with age, and awareness can prevent complications and improve management outcomes.
Symptoms in Adults
Rashes commonly appearing on elbows, knees, neck, or wrists
Extremely dry, rough patches of skin
Persistent, intense itching that worsens at night
Scaly skin textures, often with peeling or flaking
Secondary infections such as bacterial or fungal infections from scratching
Symptoms in Infants and Children
Commonly affected areas include the scalp, cheeks, and torso
The appearance of blisters that may leak fluid
Severe discomfort leading to disturbed sleep patterns
Older Children and Teenagers
Development of bumpy rashes or nodules
Color changes from light to dark patches
Chronic itching leading to skin thickening (lichenification)
Key Factors and Triggers in Eczema Development
Understanding personal triggers is essential for controlling eczema. Common triggers include environmental allergens, irritants like soaps and detergents, stress, climate changes (especially dry weather), and certain foods.
Managing Eczema: The Role of Home Care and Medical Treatment
While eczema currently has no definitive cure, a combination of diligent home care and targeted medication can significantly reduce symptoms and prevent exacerbations. Establishing a consistent skin care routine and avoiding known triggers are foundational steps.
Home Care Strategies
Daily lukewarm baths or showers to hydrate skin, immediately followed by applying emollients or moisturizers to lock in moisture
Choosing gentle, fragrance-free skincare products to minimize irritation
Wearing soft, breathable fabrics like cotton to reduce skin friction and irritation
Utilizing humidifiers in dry environments to maintain ambient moisture
Keeping nails trimmed to prevent skin damage from scratching
Managing stress through relaxation techniques as stress can trigger flare-ups
Medical Treatments and Medications
Medications are vital in controlling eczema's inflammation, preventing infections, and reducing symptoms. Always consult a healthcare professional before starting any medication to ensure safety and appropriateness.
Bensal HP: Combines benzoic acid, salicylic acid, and red oak bark extract. It helps defend against bacterial infections and promotes removal of dead skin cells, reducing scaling and inflammation.
Alcortin A: Contains aloe polysaccharides, hydrocortisone, and iodoquinol, functioning as an anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and antifungal agent. It alleviates itching and promotes healing.
Aloquin: Formulated with aloe and iodoquinol, this medication is used to treat infected skin lesions and reduce inflammation caused by eczema.
Dupixent (dupilumab): A breakthrough biologic agent, it’s a monoclonal antibody that targets specific proteins involved in the inflammatory process. It is used in moderate-to-severe eczema cases that do not respond well to topical treatments.
Rayos (prednisone): A corticosteroid that reduces inflammation and immune responses, often used in short-term flare management under medical supervision.
Halog (halcinonide): An ultra-potent steroid cream used to decrease redness, swelling, and itching in stubborn cases.
Additional Considerations for Effective Eczema Management
Besides medications, lifestyle adjustments play a crucial role. Regular skin assessment, adhering to prescribed regimens, and lifestyle modifications can enhance outcomes.
When to Seek Medical Advice
If symptoms worsen, fail to respond to treatment, or if signs of infection (such as significant redness, swelling, or pus) appear, consult a healthcare provider promptly. In some cases, allergy testing or specialized treatments may be recommended.
Final Thoughts: A Proactive Approach to Eczema
Managing eczema is a continuous process that involves understanding your skin, avoiding triggers, and sticking to an effective treatment plan. Education about the condition empowers affected individuals to take control and improve their quality of life. Advanced medications like biologics have revolutionized treatment options, offering hope for those with severe cases. Remember always to work closely with healthcare professionals for personalized care advice.
In conclusion, while eczema can be a persistent condition, consistent care, proper medication use, and lifestyle changes can lead to significant symptom relief and enhanced skin health. Staying vigilant and proactive is the key to managing this troublesome skin disorder effectively.