Comprehensive Guide to Managing Eczema Symptoms Effectively
This comprehensive guide provides effective strategies for managing eczema symptoms, emphasizing lifestyle adjustments, topical treatments, and advanced medical options. It offers practical advice for controlling flare-ups, preventing triggers, and improving skin health through a holistic approach suitable for long-term relief.

Comprehensive Guide to Managing Eczema Symptoms Effectively
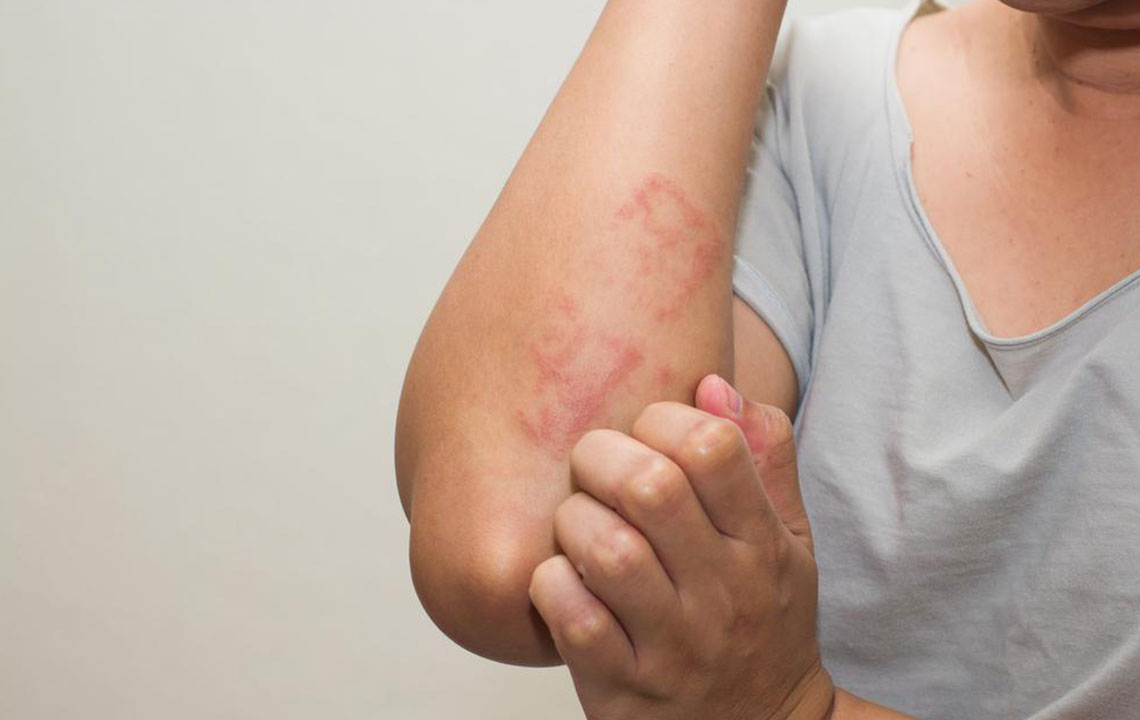
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition characterized by intense itching, inflammation, redness, and discomfort. It affects people of all ages but is particularly common among children. While the exact cause of eczema remains unknown, it is believed to be a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune system factors. Understanding these elements is crucial for effective management and improving quality of life for those affected.
In this extensive guide, we will explore various strategies to control and alleviate eczema symptoms. From lifestyle modifications and skincare routines to medical treatments and innovative therapies, this article provides a holistic approach for those seeking long-term relief. Managing eczema requires patience, consistency, and a personalized treatment plan tailored to individual needs.
Adopting Effective Behavioral Changes
The cornerstone of eczema management begins with lifestyle adjustments. Developing a diligent skincare routine is crucial. Use gentle, fragrance-free cleansers specifically formulated for sensitive skin to avoid irritation. After cleansing, always apply a high-quality moisturizer immediately to lock in moisture and prevent dryness, which can exacerbate eczema symptoms. During the day, protect your skin from ultraviolet (UV) rays by applying broad-spectrum sunscreen, even when indoors or cloudy for preventing UV-related skin damage.
Incorporate soothing remedies such as oatmeal baths or baking soda soaks during flare-ups. These natural remedies can help calm itching, reduce inflammation, and provide comfort. Additionally, wearing loose, breathable clothing made from natural fibers minimizes skin irritation and helps maintain skin health.
Preventing Exposure to Common Triggers and Irritants
Avoid contact with harsh soaps, heavy-duty detergents, and cleaning chemicals that strip natural oils from the skin. When handling cleaning agents, always wear protective gloves to prevent skin contact. Minimize exposure to environmental allergens such as pollen, pet dander, and dust mites. Stay vigilant about skincare products, opting for fragrance-free, hypoallergenic options.
Be cautious with dyes, fragrances, and raw foods that contain irritants. Removing jewelry that traps residues and dirt can prevent contact dermatitis. After washing, thoroughly dry and moisturize your hands to protect the skin barrier and prevent flare-ups.
Medical and Pharmacological Treatments for Eczema
Topical Therapeutic Interventions
Steroid Creams and Corticosteroids
These are primary treatments to control inflammation, redness, and itching during flare-ups. They come in various strengths, and a healthcare provider's guidance is essential to avoid side effects like skin thinning or pigmentation changes. Use them sparingly and only as prescribed.
Antihistamines
Oral antihistamines such as diphenhydramine or loratadine can help mitigate itching and promote restful sleep. However, they may cause drowsiness, so avoid operating machinery or driving after ingestion.
Additional Medical Options
Antibiotics
When secondary bacterial infections occur due to scratching or broken skin, physicians may prescribe topical or oral antibiotics to combat bacterial growth and promote healing.
Anti-inflammatory and Immunosuppressive Drugs
Medications like corticosteroid ointments and oral prednisone may temporarily reduce inflammation. In severe cases, immunomodulating drugs such as calcineurin inhibitors (tacrolimus and pimecrolimus) are used to regulate immune responses, especially in sensitive areas like the face or eyelids. These should be used under strict medical supervision.
Phototherapy (Light Therapy)
UVB and PUVA Treatments
Dermatologists utilize controlled ultraviolet light therapy, including narrowband UVB and psoralen plus UVA (PUVA), to improve symptoms. These treatments require multiple sessions in a clinical setting and have demonstrated efficacy in reducing eczema severity over time.
Systemic and Advanced Treatment Options
Biologic Therapies
For chronic, severe eczema resistant to traditional therapies, biologic medications such as dupilumab have revolutionized treatment options. These injectable drugs target specific immune pathways involved in eczema pathogenesis and significantly improve quality of life. However, they tend to be expensive and require ongoing medical supervision.
Complementary and Alternative Approaches
Acupuncture and Mind-Body Techniques
Some patients report symptom relief through acupuncture, which may help reduce inflammation and itching. Other complementary approaches include stress management, which plays a crucial role since stress is a known eczema trigger. Techniques such as meditation, yoga, and biofeedback can support overall skin health and emotional well-being.
Managing eczema effectively requires a multifaceted approach involving proper skincare, avoiding triggers, and utilizing medical treatments when necessary. Patients should work closely with healthcare providers to develop personalized management plans, monitor progress, and adjust treatments as needed. Long-term control of eczema is achievable with consistent effort and adherence to recommended therapies, ultimately leading to healthier skin and improved quality of life.