Comprehensive Guide to Eczema: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Management Strategies
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a prevalent skin condition causing inflammation, dryness, and irritation. This comprehensive guide explores its causes, symptoms, triggers, and effective management strategies. From topical treatments and skincare routines to lifestyle adjustments and advanced therapies like phototherapy, learn how to control flare-ups and improve skin health. Understanding triggers and maintaining proper skin care are essential for living itch-free and reducing the impact of eczema on daily life. Empower yourself with knowledge and practical solutions for better skin health.
Comprehensive Guide to Eczema: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Management Strategies
Eczema, scientifically known as atopic dermatitis, is a pervasive and often challenging skin condition that affects millions worldwide. Characterized by inflammation, dryness, redness, and irritation of the skin’s outermost layer, eczema significantly impacts quality of life, especially when symptoms persist or worsen over time. This versatile skin disorder does not discriminate; it influences both children and adults across various age groups, with symptoms that can last from several months to many years depending on the severity and management strategies employed.
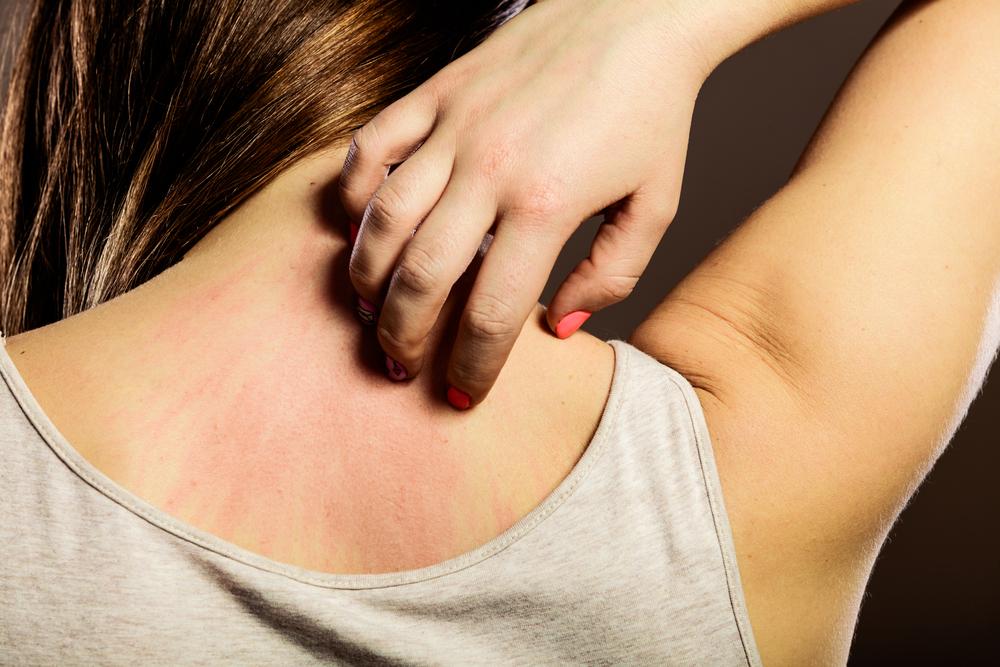
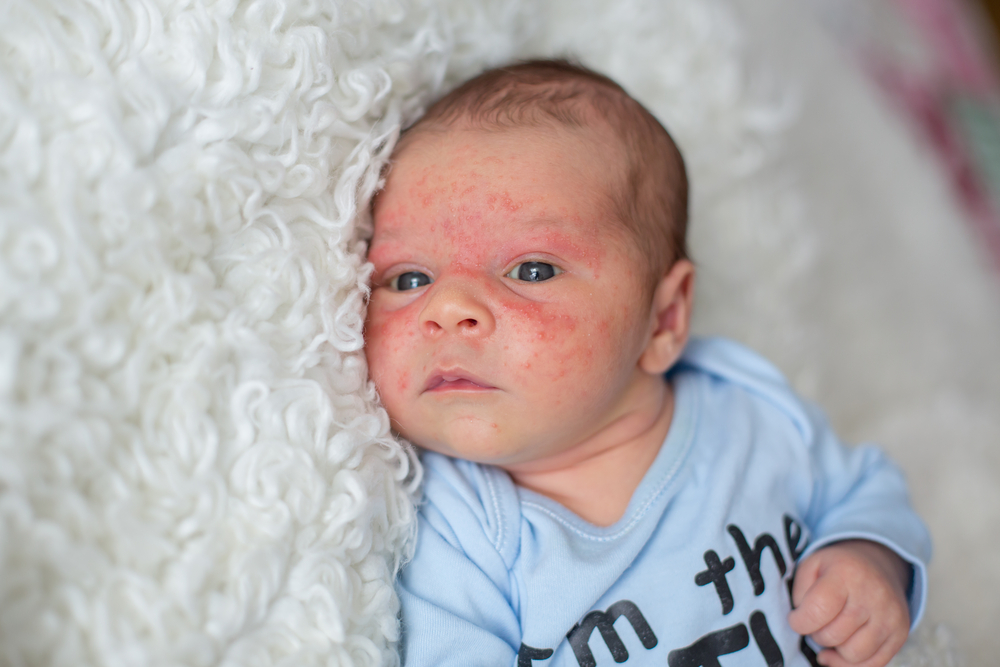
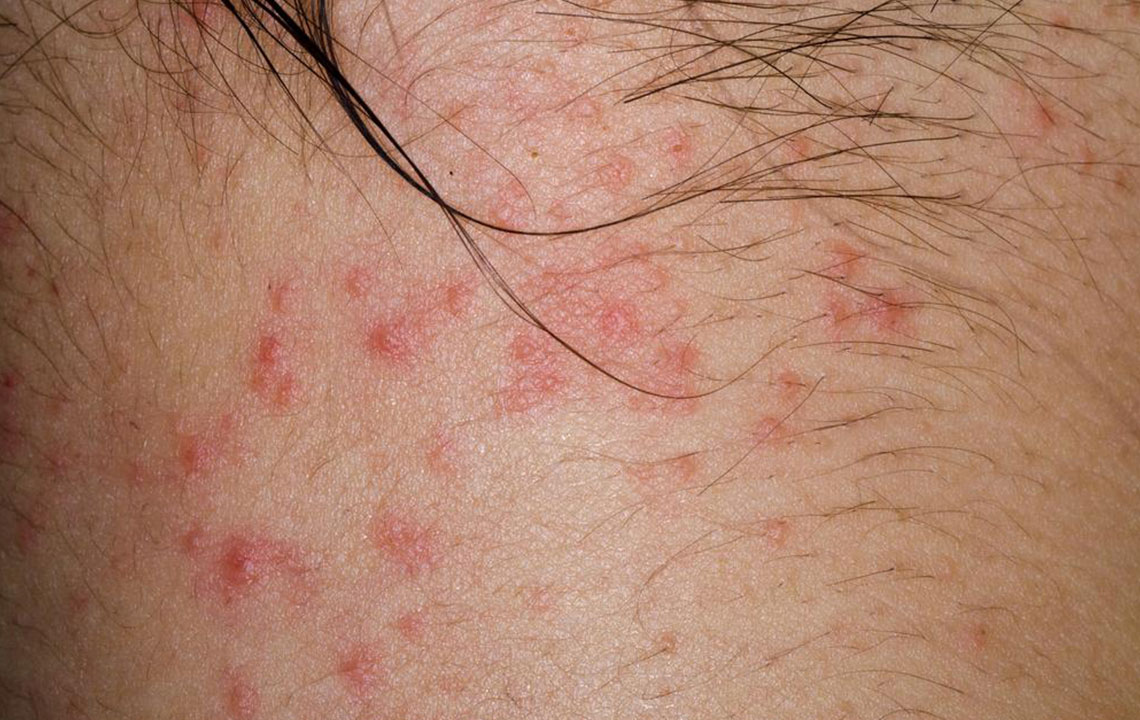
The hallmark signs of eczema include itchy, inflamed patches that often appear on common areas such as the face, wrists, elbows, behind the knees, and around the neck. In infants and young children, eczema may manifest with oozing, crusted lesions, particularly on the face and scalp, which can cause discomfort and concern for parents. As the condition progresses, skin thickening and discoloration may occur, especially in chronic cases. Despite its prevalence, the precise cause of eczema remains elusive; however, research indicates that it results from a complex interplay of genetic, environmental, and immune system factors.
One of the key contributors to eczema flare-ups is exposure to allergens and irritants. Harsh soaps, chemical cleaning agents, synthetic fabrics, and environmental factors such as pollen, pet dander, and smoke are common triggers that can exacerbate symptoms. Furthermore, psychological stress and climatic changes, especially cold and dry weather, can worsen the condition. It’s crucial for individuals with eczema to identify their specific triggers through observation and allergy testing, enabling them to adopt targeted avoidance strategies.
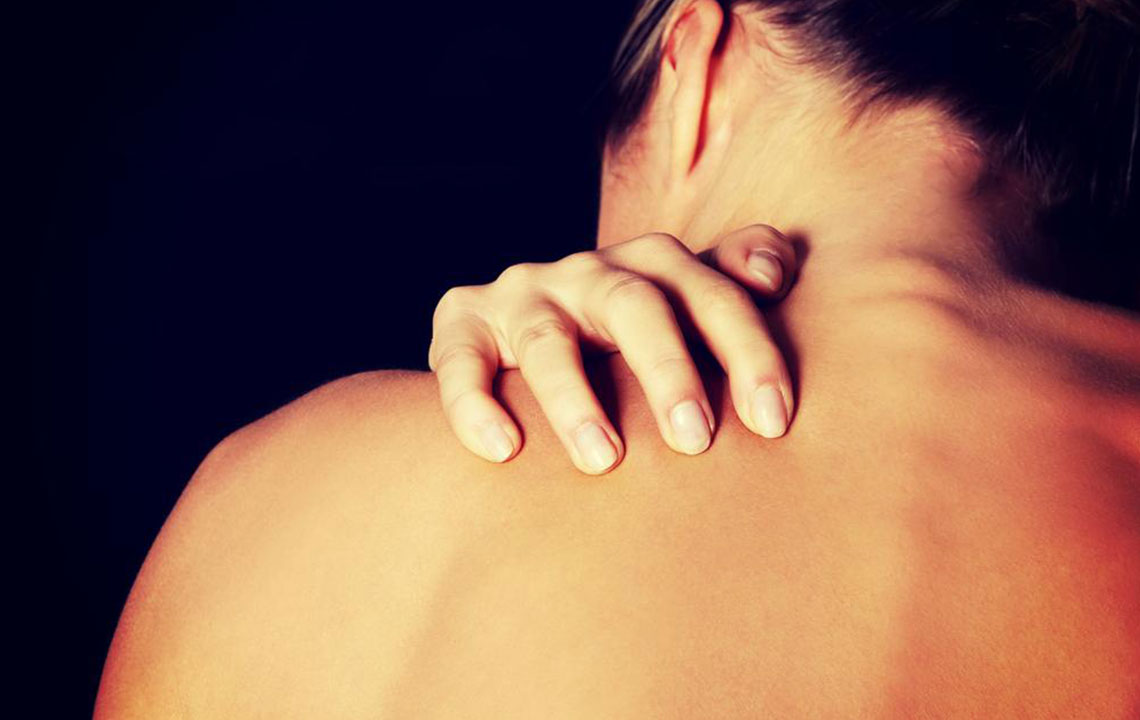
The primary symptoms experienced by those with eczema include inflamed, red patches that are intensely itchy. These areas tend to dry out, crack, and may leak fluids or ooze, especially during flare-ups. In severe cases, continuous scratching and persistent inflammation can lead to skin thickening, a condition known as lichenification, which causes the skin to become leathery and hyperpigmented. Eczema not only causes physical discomfort but can also have psychological effects, including anxiety, depression, and sleep disturbances, owing to constant itching and discomfort.
Beyond the discomfort, eczema is associated with other allergic conditions, such as asthma and hay fever, indicating an underlying atopic tendency. This interconnected allergic profile underscores the importance of a comprehensive approach to treatment and management. Approaches vary based on individual needs but often include topical medications, lifestyle modifications, and home remedies aimed at reducing inflammation, soothing the skin, and preventing future outbreaks.
Current treatment options for eczema encompass a wide spectrum. Topical corticosteroids remain the mainstay for controlling inflammation and reducing flare-ups. These are often prescribed for short-term use to minimize side effects while providing relief. Antihistamines can help alleviate itching and improve sleep quality. For more persistent or severe cases, systemic medications or phototherapy, which involves controlled exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light, may be recommended by dermatologists. These treatments aim to modulate immune responses and promote skin healing.
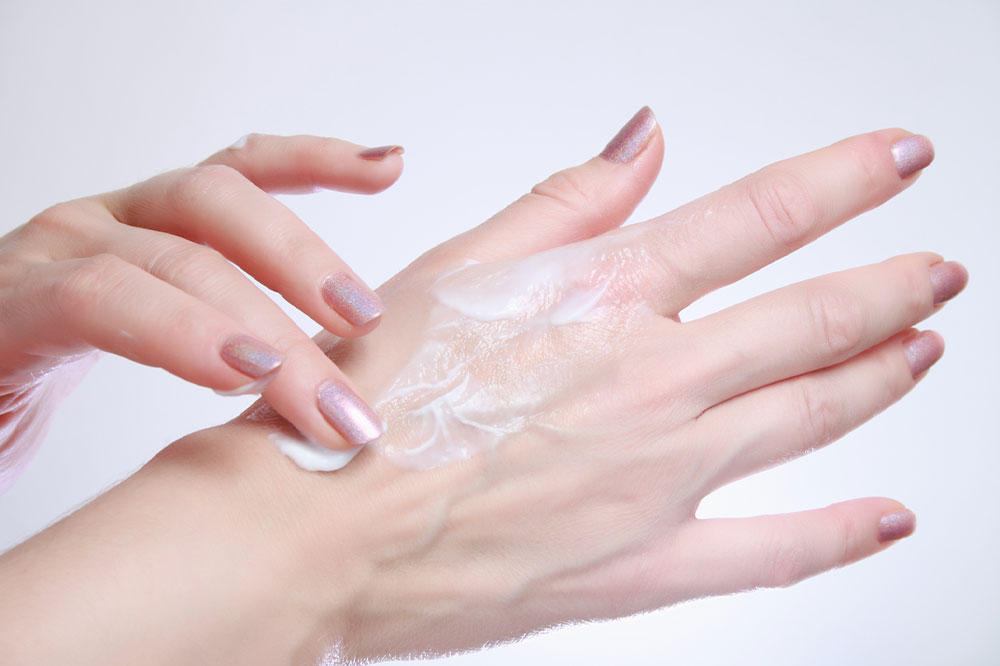
Aside from medical treatments, adopting effective skin care routines and lifestyle adjustments are fundamental for long-term management. Regularly moisturizing the skin with emollients helps maintain hydration barriers, preventing dryness and cracking. Rinsing with lukewarm water instead of hot water during baths and using gentle, fragrance-free cleansers reduces irritation. Wearing soft, breathable fabrics and avoiding synthetics can minimize skin irritation, while using humidifiers in dry indoor environments helps maintain optimal moisture levels in the air.
Living with eczema also involves identifying and avoiding personal triggers through careful observation. Managing stress through relaxation techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can significantly reduce flare-ups linked to psychological factors. Dietary modifications, such as eliminating allergenic foods or adding anti-inflammatory nutrients, might also play a role in controlling symptoms for some individuals. A balanced diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and vitamins supports overall skin health and immune function.
In cases where conventional treatments are insufficient, advanced therapies like phototherapy can be beneficial. This method involves exposing the affected skin to controlled UV light, which helps reduce inflammation and immune activity locally. Such treatments are usually administered in specialized clinics under medical supervision and are considered effective for stubborn or widespread eczema cases.
Beyond treatment, education about the condition is vital. Patients should be aware of the importance of consistent skincare routines, stress management, and allergen avoidance. Keeping detailed records of flare-ups and potential triggers can aid in developing personalized management plans. Additionally, support groups and counseling can provide emotional relief and practical advice for coping with the chronic nature of eczema.
In conclusion, eczema is a complex skin condition that requires an integrated approach involving medical intervention, lifestyle modifications, and ongoing self-care. Understanding its causes, recognizing symptoms early, and adopting effective management strategies can substantially improve quality of life. With proper treatment, lifestyle adjustments, and vigilant trigger management, individuals with eczema can reduce flare-ups, prevent complications, and enjoy healthier, more comfortable skin. Staying informed and proactive is the key to long-term control and well-being.