Effective Eczema Management: Comprehensive Strategies and Treatment Options
This comprehensive guide explores effective eczema management strategies, including medications, skin care routines, lifestyle adjustments, and emerging treatments. Collaborating with healthcare providers can significantly improve symptom control and skin health, ultimately enhancing quality of life. The article emphasizes personalized treatment plans, the importance of moisturizers, and advanced therapies for severe cases. Whether you're dealing with mild or severe eczema, adopting a holistic approach can lead to sustained relief and healthier skin, helping sufferers regain confidence and comfort.
Effective Eczema Management: Comprehensive Strategies and Treatment Options
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is one of the most common chronic skin conditions affecting millions worldwide. Characterized by itchy, inflamed, and dry skin, eczema can significantly impact a person's quality of life if not properly managed. Understanding the various treatment methods, skincare routines, and lifestyle adjustments is crucial to effectively control eczema symptoms and prevent flare-ups. This comprehensive guide explores the most effective eczema management strategies, including medications, skin care routines, lifestyle tips, and emerging therapies. Whether you're experiencing mild or severe eczema, adopting a tailored approach with medical guidance can lead to significant improvements and healthier skin.
Understanding Eczema and Its Impact
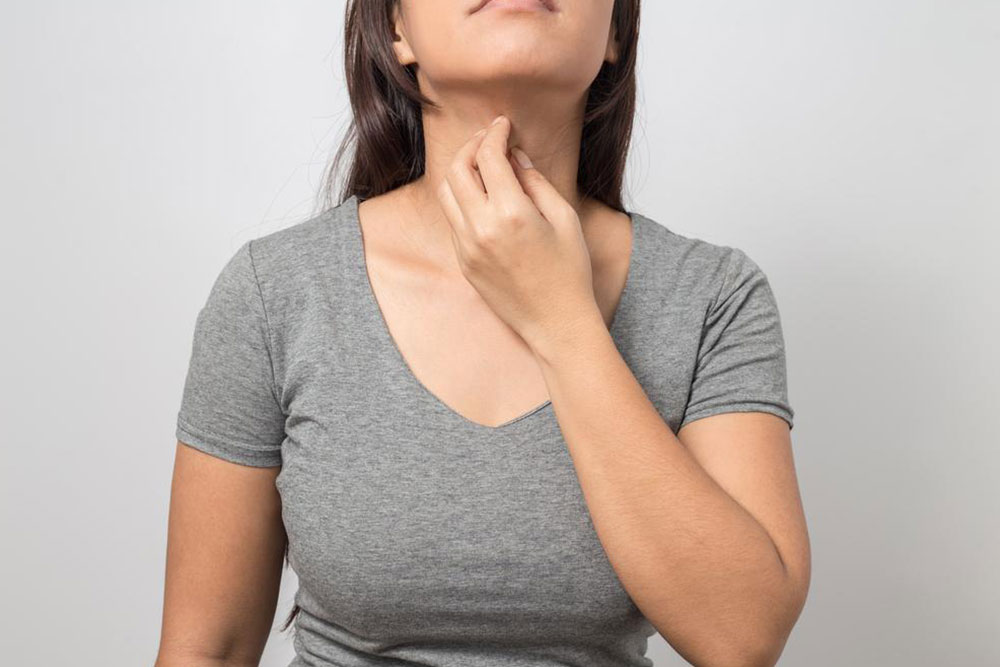
Eczema is a complex condition influenced by genetic, environmental, and immune factors. It often presents with symptoms like intense itching, redness, swelling, and dry patches. Scratching can lead to skin thickening and increase the risk of infections, creating a vicious cycle that complicates management. Eczema can affect individuals of all ages but is particularly prevalent among children and those with allergic tendencies.
Managing eczema requires a multifaceted approach that includes medications, skincare, lifestyle modifications, and sometimes advanced medical procedures. The goal is to reduce inflammation, repair the skin barrier, alleviate discomfort, and prevent future flare-ups.
Medications: Tailoring Treatment to Severity
Medications play a vital role in controlling eczema symptoms and are often customized based on the severity, location, and frequency of outbreaks. It’s essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to select appropriate treatments and avoid potential side effects.
Over-the-counter (OTC) Hydrocortisone Creams
Corticosteroid creams such as hydrocortisone are often the first line of defense against flare-ups. They are effective in reducing inflammation, redness, and itching quickly. Available in varying strengths, OTC hydrocortisone creams are suitable for mild eczema, applied typically 1-2 times daily as directed. For more severe inflammation, healthcare providers might prescribe stronger topical corticosteroids. It is important not to overuse these medications to prevent skin thinning or other side effects. Proper application following medical guidance ensures safe and effective relief.
NSAID Ointments and Topical Immunomodulators
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as Crisaborole ointment have become popular options for mild to moderate eczema. These ointments work by reducing inflammation without the side effects associated with corticosteroids. Applying twice daily helps maintain skin health and control flare-ups. Additionally, topical calcineurin inhibitors like Tacrolimus and Pimecrolimus are used for moderate to severe eczema cases, especially in sensitive areas like the face and neck. While they provide rapid relief from inflammation, patients must follow medical advice due to potential risks, including rare skin cancers with prolonged use.
Moisturizers: Strengthening the Skin Barrier
Regular use of moisturizers is essential in eczema management. Effective moisturizers restore the skin’s protective barrier, reduce dryness, and prevent irritants from penetrating the skin. Products should ideally be fragrance-free, hypoallergenic, and suited to sensitive skin. Both OTC and prescription options are available, and healthcare providers can recommend specific formulations based on individual needs. Applying moisturizers immediately after bathing enhances their effectiveness by locking in moisture and soothing irritated skin.
Immune System Modulators and Systemic Therapies
For severe or resistant eczema, systemic medications like Cyclosporine, Mycophenolate Mofetil, and Dupilumab (a biologic agent) may be prescribed. These drugs modulate or suppress the immune response to prevent flare-ups and inflammation. They require careful monitoring to mitigate side effects such as kidney impairment, hypertension, or infection risk. Such treatments are usually reserved for cases where topical therapies are insufficient, and they demand close medical supervision.
Phototherapy: Controlled Light Therapy
Ultraviolent (UV) light therapy is an effective treatment for persistent, severe eczema. By exposing affected skin to controlled UVB or UVA rays under medical supervision, phototherapy reduces immune activity and inflammation. PUVA therapy, which combines UVA light with a photosensitizing agent, is also used in certain cases. While generally safe when performed by experienced dermatologists, phototherapy carries potential risks such as skin aging and cancer, emphasizing the importance of proper dosing and follow-up.
Additional Treatments and Supportive Strategies
In some severe cases, corticosteroid injections or oral corticosteroids may be necessary to control acute flare-ups. Antibiotics are sometimes prescribed if bacterial infections occur due to scratching. Antihistamines can help reduce itching and promote sleep, especially during intense flare-ups. Lifestyle factors, such as avoiding known triggers like certain soaps, detergents, fragrances, and allergens, play a critical role in controlling eczema.
Holistic Approaches and Lifestyle Tips
Alongside medication, adopting healthy habits significantly impacts eczema management. Maintaining a regular skincare routine, avoiding harsh soaps, wearing breathable clothing, and managing stress can prevent flare-ups. Identifying and avoiding triggers such as certain foods, environmental allergens, or temperature changes reduces skin irritation. Dietary modifications, including increasing omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants, may support skin health. Staying well-hydrated and practicing good hygiene are also essential.
Emerging Therapies and Future Directions
The field of eczema treatment continues to evolve with the development of biologic drugs, gene therapy, and personalized medicine approaches. Researchers are exploring new medications that target specific immune pathways involved in eczema, promising more effective and safer treatments in the future. Patients should stay informed about emerging options and consult healthcare providers for tailored treatment plans.
In conclusion, managing eczema effectively requires a comprehensive, individualized approach that combines medications, skin care routines, lifestyle modifications, and emerging therapies. Collaborating closely with healthcare professionals ensures optimal control of symptoms, minimizes flare-ups, and improves overall skin health, ultimately enhancing the quality of life for those affected by this chronic condition.